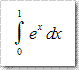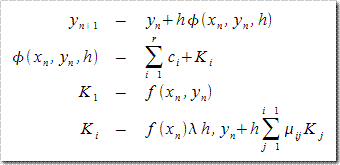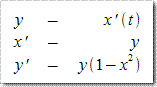GNU Scientific Library(以下简称GSL)是来自开源社区的重磅礼物,历史悠久功能强大,集成了最基础的同时也是最重要的科学计算算法如BLAS、Monte Carlo积分等。本文讲解了其基本使用方法,结合笔者的经验点明其应用,并提供代码进行参考。这里是PDF文档下载。
一、基础
如果你是Windows用户,请访问GNUWin32下载最新的预编译库或者源代码包手动编译,为了程序运行稳定起见推荐使用后者。编译时可以选择生成静态链接库还是动态链接库。如果我们在程序中要使用动态连接库那么需要预定义GSL_DLL,否则链接器会找不到符号。经过笔者测试使用Debug模式生成的库存在Bug,具体表现为在使用Nonlinear Least-Squares Fitting(非线性最小二次方拟合)实现Moving Least Square(MLS,点云模型重组的流行算法)算法时会陷入死循环,所以推荐使用Release模式生成库附带生成调试符号。使用GSL编程的形式大同小异,首先初始化核心结构,使用这个结构进行操作,最后释放。GSL的接口被统一设计成C的风格而不是C++的风格,清晰而优雅。对比其他的数值分析工具如Matlab、Octave、SciLab、LAPACK,GSL具有小巧、全面、经典、易用的优点。
笔者推荐在阅读本教程前最少需要掌握基本的线性代数、信号处理、数值分析、数学分析等知识,并且在实际生产中对其内容能够有所联系,达到举一反三快速进步之目的。虽然大部分人很有可能一辈子都不需要使用那些让人抓破头皮的数学知识,笔者还是在后面列出了推荐书目,有兴趣的朋友可以看一下。由于笔者学习的是图形学,所以文中大部分引用都和图形学相关,如果读者觉得别扭请多多包涵。这个不长的教程特别适合具有优秀动手能力同时有强烈的愿望在计算机科学上有所造诣的学生学习。笔者就是走了许多弯路浪费了许多不必要的时间,回首以往的学习过程,就此特此将学习经验总结一番,以供有希望的青年朋友学习与参考。
详细内容请参阅《GSL Reference Manual》,本教程正如标题“Non-Complete”,绝对并不是大全宝典。
二、实战
Basic Function基本数学函数
不知道自己所使用的CRT是如何实现sin、cos等基本函数的?没关系,看一下GSL的代码就可以。GSL使用Chebyshev(中文数学教科书译作“切比雪夫”)展开计算sin、cos等三角函数。正如其注释中所说,“library sin() is just a black box.So we have to roll our own.”。CRT提供的函数固然可以,但是那是个黑盒,所以我们最好还是明白其实现。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_sf_trig.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
double piDIVfour = 3.1415926 / 4.0;
printf("sin(pi) = %f\n",sin(piDIVfour));
printf("gsl_sf_sin(pi) = %f\b",gsl_sf_sin(piDIVfour));
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Complex复数
C++标准库中实现了complex类,GSL也有复数的实现,不过复数只是个结构体,以及一堆操作函数。下面的代码展示了基本的操作。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_complex.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_complex_math.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
gsl_complex a,b;
GSL_SET_COMPLEX(&a,3,4);//a=3+4i
GSL_SET_COMPLEX(&b,6,8);//b=6+8i
gsl_complex c = gsl_complex_add(a,b);
printf("a+b\treal : %f image : %f\n",c.dat[0],c.dat[1]);
c = gsl_complex_sub(a,b);
printf("a-b\treal : %f image : %f\n",c.dat[0],c.dat[1]);
c = gsl_complex_mul(a,b);
printf("a*b\treal : %f image : %f\n",c.dat[0],c.dat[1]);
c = gsl_complex_div(a,b);
printf("a/b\treal : %f image : %f\n",c.dat[0],c.dat[1]);
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Vector And Matrix基本向量与矩阵的操作
GSL的矩阵以及向量操作是经典的get/set模式。特别需要提到的是get/set在C++类设计中也有着重要地位。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_vector.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
gsl_vector* x = gsl_vector_calloc(3);
gsl_vector* y = gsl_vector_calloc(3);
for(size_t i=0; i<3; i++)
{
double n = rand() / (double)RAND_MAX * 2.0 - 1.0;
gsl_vector_set( x,i,n );
n = rand() / (double)RAND_MAX * 2.0 - 1.0;
gsl_vector_set( y,i,n );
}
gsl_vector_free(x);
gsl_vector_free(y);
//释放内存
x = NULL;
y = NULL;
gsl_matrix* m = gsl_matrix_calloc(4,4);
gsl_matrix_set_identity(m);
for(size_t i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(size_t j=0; j<4; j++)
{
double n = rand() / (double)RAND_MAX;
gsl_matrix_set(m,i,j,n);
}
}
gsl_vector_view c = gsl_matrix_column(m,0);
gsl_matrix_set_col(m,0,x);
gsl_matrix_free(m);
m = NULL;
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Random Number Generator随机数生成器
随机数的生成总是计算机科学中津津乐道的问题。一般情况下CRT附带的rand()函数就可以满足需求,但是在许多特殊的场合需要使用其他的生成器,比如在《Realistics Image Synthesis Using Photon Mapping》中使用的就是rand48这个UNIX上的古老的随机数生成器。GSL中实现了包括UNIX上的许多随机数生成器,打开gsl_rng.h我们就可以看到那些RNG的类型。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_rng.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
gsl_rng* rng = gsl_rng_alloc(gsl_rng_rand48);
for( int i=0; i<10; i++ )
{
printf("%u\t%f\n",gsl_rng_get(rng),gsl_rng_uniform(rng));
}
gsl_rng_free(rng);
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
Quasi Random Sequence伪随机序列
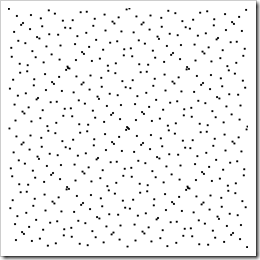
Quasi Monte Carlo(QMC)的精髓是使用Low Discrepancy(LD)数字序列代替随机数列。但是LD的基本思路却是,使用现有的样本决定下一个样本。比较有名的伪随机序列有Van der Corput、Niederreiter 、Sobol、Hammersley、Halton等(详情请参阅《Monte Carlo and Beyond Course Notes》Alexander Keller),由于年代原因GSL只实现了Niederreiter 与sobel算法。LD序列的直观特性是很分散,而使用rand()这些依赖线性同余算法的实现生成的点许多会聚集在一起,这样使得方差变大,影响MC积分速度和精度。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_qrng.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
#include <gl/glut.h>
#include <gl/gl.h>
void Display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT|GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
const int n = 100;
gsl_qrng* qrng = gsl_qrng_alloc(gsl_qrng_sobol,2);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glColor3f(0,0,0);
for( int i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
double s[2];
gsl_qrng_get(qrng,s);
glVertex3f(s[0],s[1],0.0);
}
glEnd();
gsl_qrng_free(qrng);
glutSwapBuffers();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc,argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_RGBA|GLUT_DOUBLE);
glutInitWindowSize(512,512);
glutCreateWindow("GSL Quasi Random Number Generator");
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glClearColor(1,1,1,1);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glTranslatef(-1,-1,0);
glScalef(2,2,1);
glViewport(0,0,512,512);
glPointSize(4.0);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
生成结果如下
当n=500时情况如下,
此即为Low Discrepancy序列。应用于物理模拟的序列多达上G,需要在大型机上跑几个月进行MC模拟。关于Hammersley与Halton点集的生成请参阅《Sampling with Hammersley and Halton Points》。
Linear Algebra线性代数
线性代数的基本算法如LU、QR、SVD等在GSL中都有实现,在大规模科学计算海量数据分析中有着重要地位。一些直观的计算比如矩阵求逆使用LU分解要比使用传统的高斯消元法稳定效率高。关于这些算法的分析请参阅数学数值相关书籍。下面以简单矩阵进行演示。已知矩阵
求其LU、SVD的结果及其逆阵。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_linalg.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
double n[9] = {3,-1,-1,4,-2,-1,-3,2,1};
int k=0;
gsl_matrix* m = gsl_matrix_alloc(3,3);
gsl_matrix* mi = gsl_matrix_alloc(3,3);
for(size_t i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(size_t j=0; j<3; j++)
{
gsl_matrix_set(m,i,j,n[k]);
k++;
}
}
//LU
int sig = 0;
gsl_permutation* perm = gsl_permutation_alloc(3);
gsl_linalg_LU_decomp(m,perm,&sig);
printf("%s\n","LU\n[");
for(size_t i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(size_t j=0; j<3; j++)
{
printf("\t%f",gsl_matrix_get(m,i,j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("]\n%s\n","Inverse\n[");
gsl_linalg_LU_invert(m,perm,mi);
for(size_t i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(size_t j=0; j<3; j++)
{
printf("\t%f",gsl_matrix_get(mi,i,j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("]\n");
//SVD
gsl_matrix* v = gsl_matrix_alloc(3,3);
gsl_vector* s = gsl_vector_alloc(3),*work = gsl_vector_alloc(3);
gsl_linalg_SV_decomp(m,v,s,work);
printf("SVD - V\n[\n");
for(size_t i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(size_t j=0; j<3; j++)
{
printf("\t%f",gsl_matrix_get(v,i,j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("]\n");
printf("SVD - S [\t%f\t%f\t%f\t]\n",gsl_vector_get(s,0),gsl_vector_get(s,1),gsl_vector_get(s,2));
printf("SVD - Work [\t%f\t%f\t%f\t]\n",gsl_vector_get(work,0),gsl_vector_get(work,1),gsl_vector_get(work,2));
gsl_matrix_free(m);
gsl_matrix_free(mi);
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
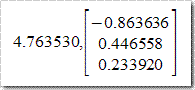
计算得到其逆矩阵为
LU分解结果为
特征值及其对应特征向量为
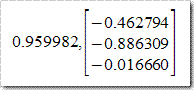

Fourier Transform And Wavelet Transform傅利叶变换与小波变换
Fourier Transform(FT)与Wavelet Transform(WT)是信号处理中的最基本的算法。对于FT来说解决方案有流行的基于CPU的fftw与利用GPU的CUDA。FFT广泛应用于数据压缩(比如JPEG)、信号处理(音频FFT过滤器)、光线传输的频率分析中(见《A Frequency Analysis of Light Transport》SIGGRAPH 2005)。而WT中的DWT的应用与FFT类似,比如JP2K的压缩、场景间接光照计算(见《Direct-to-Indirect Transfer for Cinematic Relighting》Cornell University CG Department)。注意,如果是图片的FFT或者DWT处理我们可以直接使用图形库比如CxImage、CImg等,不需要使用GSL的这部分功能,省得多此一举。
Monte Carlo Integration蒙特卡罗积分
Monte Carlo与Las Vegas是世界上两个著名的赌城,前者在摩洛哥后者在美国。同时MC中也有个著名算法名称叫做VEGAS,基于Importance Sampling,直接采样Probability Distribution Function(PDF,中文教科书一般翻译为“概率分布函数”),这样采样点都落在积分函数的区域内,使得贡献比较大,同时速度也更快。MISER法采用的是Recursive Stratified Sampling,目的是将积分点放在方差最大的区域尽量获的准确的数值,目前已经应用在CG技术中(见《Rendering With Adaptive Integration》)。下面的代码表现了如何使用GSL中的VEGAS算法计算
这个简单的定积分。首先我们需要手动计算一下:

#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_monte_vegas.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_rng.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
double function(double* x, size_t dim, void * params)
{
return exp(x[0]);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
size_t dim = 1;
double xl[1] = {0};
double xu[1] = {1};
gsl_monte_function func;
func.dim = 1;
func.params = NULL;
func.f = function;
gsl_rng* R = gsl_rng_alloc(gsl_rng_rand);
double result = 0.0;
double abserr = 0.0;
gsl_monte_vegas_state* S = gsl_monte_vegas_alloc(dim);
gsl_monte_vegas_init(S);
gsl_monte_vegas_integrate(&func,xl,xu,dim,1024,R,S,&result,&abserr);
gsl_monte_vegas_free(S);
gsl_rng_free(R);
printf("Result = %f\nVariance = %f\n",result,abserr);
system("PAUSE");
return 0;
}
计算的结果为1.718291,方差为0.000014,精度基本满足FP32的使用需要。
Ordinary Differential Equation 常微分方程
GSL提供了经典的Runge-Kutta(中文数学书一般译作“龙格·库塔”)和Bulirsch-Stoer(笔者学识有限,目前没见过翻译,姑且将其德语语音翻译为中文“布利厄施·施多厄)方法计算常微分方程的数值解。我们都知道ODE数值解法最经典的方法有欧拉法、后退欧拉法、改进欧拉法,不过它们都是RK法的子集,其形式如下,
这里![]() 均为常数。当
均为常数。当![]() 时,就是欧拉法,此时阶p=1。当r=2时则为改进欧拉法。详情请参阅数值分析相关书籍。譬如我们想解如下偏微分方程(摘自《GSL Reference》),
时,就是欧拉法,此时阶p=1。当r=2时则为改进欧拉法。详情请参阅数值分析相关书籍。譬如我们想解如下偏微分方程(摘自《GSL Reference》),
此为Van der Pol(中文物理书籍译作“范德波尔”)方程。为了使用GSL解这个方程首先需要做变量替换,
计算代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_errno.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_odeiv.h>
int func (double t, const double y[], double f[], void *params)
{
double mu = *(double *)params;
f[0] = y[1];
f[1] = -y[0] - mu*y[1]*(y[0]*y[0] – 1);
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
int jac (double t, const double y[], double *dfdy, double dfdt[], void *params)
{
double mu = *(double *)params;
gsl_matrix_view dfdy_mat = gsl_matrix_view_array (dfdy, 2, 2);
gsl_matrix * m = &dfdy_mat.matrix;
gsl_matrix_set (m, 0, 0, 0.0);
gsl_matrix_set (m, 0, 1, 1.0);
gsl_matrix_set (m, 1, 0, -2.0*mu*y[0]*y[1] – 1.0);
gsl_matrix_set (m, 1, 1, -mu*(y[0]*y[0] – 1.0));
dfdt[0] = 0.0; dfdt[1] = 0.0;
return GSL_SUCCESS;
}
int main (void)
{
const gsl_odeiv_step_type * T = gsl_odeiv_step_rk8pd;
gsl_odeiv_step * s = gsl_odeiv_step_alloc (T, 2);
gsl_odeiv_control * c = gsl_odeiv_control_y_new (1e-6, 0.0);
gsl_odeiv_evolve * e = gsl_odeiv_evolve_alloc (2);
double mu = 10;
gsl_odeiv_system sys = {func, jac, 2, &mu};
double t = 0.0, t1 = 100.0;
double h = 1e-6;
double y[2] = { 1.0, 0.0 };
while (t < t1)
{
int status = gsl_odeiv_evolve_apply (e, c, s,&sys, &t, t1,&h, y);
if (status != GSL_SUCCESS)
break;
printf ("%.5e %.5e %.5e\n", t, y[0], y[1]);
}
gsl_odeiv_evolve_free (e);
gsl_odeiv_control_free (c);
gsl_odeiv_step_free (s);
return 0;
}
Interpolation插值
插值是比较古老的数学方法,比较常用的有线性插值、样条插值(包括B-Spline、Bezier、Catmull-Rom等)等。譬如将实验测的数据拟合为连续函数就充分利用到了插值相关的知识。目前许多数学分析软件包(Matlab、GNU Octave等)中都集成了强大的插值功能,需要的时候我们也可以调用那些软件包提供的函数进行计算。下列代表演示了如何使用GSL的插值功能进行计算并使用OpenGL显示结果。
#define GSL_DLL
#include <gsl/gsl_spline.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#pragma comment(lib,"libgsl_dll.lib")
#include <gl/glut.h>
#include <gl/gl.h>
void Display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT|GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
const size_t n = 4;
double x[] = {0,0.333336,0.666666,1};
double y[] = {0,0.5,0.9,0};
gsl_interp* interps[3] = {NULL,NULL,NULL};
interps[0] = gsl_interp_alloc(gsl_interp_linear,n);
interps[1] = gsl_interp_alloc(gsl_interp_polynomial,n);
interps[2] = gsl_interp_alloc(gsl_interp_cspline,n);
gsl_interp_init(interps[0],x,y,n);
gsl_interp_init(interps[1],x,y,n);
gsl_interp_init(interps[2],x,y,n);
gsl_interp_accel* acc = gsl_interp_accel_alloc();
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for(double t=0.0; t<=1.025; t+=0.025)
{
glColor3f(1,0,0);
glVertex3f(t,gsl_interp_eval(interps[0],x,y,t,acc),0.0);
}
glEnd();
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for(double t=0.0; t<=1.025; t+=0.025)
{
glColor3f(0,1,0);
glVertex3f(t,gsl_interp_eval(interps[1],x,y,t,acc),0.0);
}
glEnd();
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
for(double t=0.0; t<=1.025; t+=0.025)
{
glColor3f(0,0,1);
glVertex3f(t,gsl_interp_eval(interps[2],x,y,t,acc),0.0);
}
glEnd();
gsl_interp_accel_free(acc);
gsl_interp_free(interps[0]);
gsl_interp_free(interps[1]);
gsl_interp_free(interps[2]);
glutSwapBuffers();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc,argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE|GLUT_RGBA);
glutInitWindowSize(512,512);
glutCreateWindow("GSL Interpolation");
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glClearColor(1,1,1,1);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glTranslatef(-1,-1,0);
glScalef(2,2,1);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glViewport(0,0,512,512);
glLineWidth(4.0);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
下面是显示结果,
三、附录
推荐书目如下
|
书籍名称 |
作者 |
出版社 |
备注 |
|
数值分析第4版 |
李庆扬 王能超 易大义 |
清华大学出版社 Springer |
经典入门教材,我学校(NJFU)应用数学专业的数值分析课本 |
|
应用数值分析第7版改编版 |
Curtis F. Gerald Patrick O. Wheatley 白峰杉 |
高等教育出版社 |
算是对上一本的补充,对英文水平要求不高 |
|
C数值算法第2版 |
Saul A.Teukolsky William T.Vetterling Brian P.Flannery |
电子工业出版社 |
NMC中的经典之作,大部头,比较难买,可以网上订 |
|
数学分析讲义第3版 |
Г.И.阿黑波夫 B.A.萨多夫尼奇 B.H.丘巴里阔夫 王昆扬 译 |
高等教育出版社 |
俄罗斯数学教材,绿皮。简明扼要的阐述,清晰翔实的论证 |
|
Matrix Theory And Applications |
Denis Serre |
Springer |
GTM系列数学丛书在“听雨尘心@含藏识”博客可以下载 |
|
The Fast Fourier Transform |
E. Oran Brigham |
Prentice-Hall |
经典之作 |
|
Monte Carlo Concept Algorithms and Applications |
George S. Fishman |
Springer |
|
|
Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods |
J.E.Gentle |
Springer |
|
|
Fundamental Numerical Methods and Data Analysis |
George W. Collins, II |
|
在这里可以下载的到 |
|
A Guide to Monte Carlo Simulations in Statistical Physics |
David P. Landau Kurt Binder |
Cambridge |
看不看随便,比较偏向物理 |
以及,如果可能,将所有曾经发表过在SIGGRAPH、EUROGRAPHICS的论文都实现一遍(有些不太可能☺,尽力而为)。
http://www.cnblogs.com/Jedimaster/archive/2008/06/22/1227656.html
"Vector And Matrix基本向量与矩阵的操作"的代码中有问题, 运
行会非法操作
gsl_matrix_set_col(m,0,x); //有问题, 此时x已经释放
改为:
//创建x
x = gsl_vector_calloc(4);
for (size_t i=0; i<4; i++)
{
gsl_vector_set(x,i,i);
}
gsl_matrix_set_col(m,0,x);
gsl_vector_free(x);
x = NULL;