Train Problem I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 20678 Accepted Submission(s): 7779
Problem Description
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes
a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves,
train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your
task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
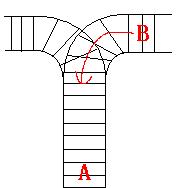
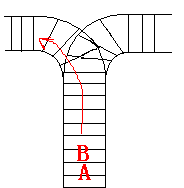
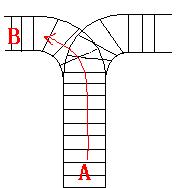
a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves,
train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your
task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.



Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file.
More details in the Sample Input.
More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out"
for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321 3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes. in in in out out out FINISH No. FINISH/*题解: 和括号配对问题有点像,运用栈的思想。注意几种测试数据:1 2 3 3 2 1 1 3 2 1 2 3(这也是对的),如下图*/
1 3 2 1 2 3(这也是对的),如下图*/#include<cstdio> int main() { char in[12],out[12],stack[20]; int n,i,j,k,top,flag[20]; while(scanf("%d %s %s",&n,in,out)!=EOF) { top=1; i=j=k=0; while(i<n&&j<n+1) //进栈时j++,出栈时i++,先进栈后出栈,进栈完毕后任不能结束,故j<n+1 { if(out[i]==stack[top-1]&&top!=1) { i++,top--; //出栈 flag[k++]=0; } else { stack[top]=in[j]; //进栈 j++,top++; flag[k++]=1; } } if(k==2*n) { printf("Yes.\n"); for(i=0; i<k; i++) { if(flag[i]) printf("in\n"); else printf("out\n"); } } else { printf("No.\n"); } printf("FINISH\n"); } return 0; }
