HTTP是个大协议,完整功能的HTTP服务器必须响应资源请求,将URL转换为本地系统的资源名。响应各种形式的HTTP请求(GET、POST等)。处理不存在的文件请求,返回各种形式的状态码,解析MIME类型等。但许多特定功能的HTTP服务器并不需要所有这些功能。例如,很多网站只是想显示“建设中“的消息。很显然,Apache对于这样的网站是大材小用了。这样的网站完全可以使用只做一件事情的定制服务器。Java网络类库使得编写这样的单任务服务器轻而易举。
定制服务器不只是用于小网站。大流量的网站如Yahoo,也使用定制服务器,因为与一般用途的服务器相比,只做一件事情的服务器通常要快得多。针对某项任务来优化特殊用途的服务器很容易;其结果往往比需要响应很多种请求的一般用途服务器高效得多。例如,对于重复用于多页面或大流量页面中的图标和图片,用一个单独的服务器处理会更好(并且还可以避免在请求时携带不必要的Cookie,因而可以减少请求/响应数据,从而减少下载带宽,提升速度);这个服务器在启动时把所有图片文件读入内存,从RAM中直接提供这些文件,而不是每次请求都从磁盘上读取。此外,如果你不想在包含这些图片的页面请求之外单独记录这些图片,这个单独服务器则会避免在日志记录上浪费时间。
本篇为大家简要演示三种HTTP服务器:
(1) 简单的单文件服务器
(2) 重定向服务器
(3) 完整功能的HTTP服务器
简单的单文件服务器
该服务器的功能:无论接受到何种请求,都始终发送同一个文件。这个服务器命名为SingleFileHTTPServer,文件名、本地端口和内容编码方式从命令行读取。如果缺省端口,则假定端口号为80。如果缺省编码方式,则假定为ASCII。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SingleFileHTTPServer extends Thread {
private byte[] content;
private byte[] header;
private int port=80;
private SingleFileHTTPServer(String data, String encoding,
String MIMEType, int port) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this(data.getBytes(encoding), encoding, MIMEType, port);
}
public SingleFileHTTPServer(byte[] data, String encoding, String MIMEType, int port)throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
this.content=data;
this.port=port;
String header="HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n"+
"Server: OneFile 1.0\r\n"+
"Content-length: "+this.content.length+"\r\n"+
"Content-type: "+MIMEType+"\r\n\r\n";
this.header=header.getBytes("ASCII");
}
public void run() {
try {
ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(this.port);
System.out.println("Accepting connections on port "+server.getLocalPort());
System.out.println("Data to be sent:");
System.out.write(this.content);
while (true) {
Socket connection=null;
try {
connection=server.accept();
OutputStream out=new BufferedOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
InputStream in=new BufferedInputStream(connection.getInputStream());
StringBuffer request=new StringBuffer();
while (true) {
int c=in.read();
if (c=='\r'||c=='\n'||c==-1) {
break;
}
request.append((char)c);
}
//如果检测到是HTTP/1.0及以后的协议,按照规范,需要发送一个MIME首部
if (request.toString().indexOf("HTTP/")!=-1) {
out.write(this.header);
}
out.write(this.content);
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}finally{
if (connection!=null) {
connection.close();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Could not start server. Port Occupied");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String contentType="text/plain";
if (args[0].endsWith(".html")||args[0].endsWith(".htm")) {
contentType="text/html";
}
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(args[0]);
ByteArrayOutputStream out=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int b;
while ((b=in.read())!=-1) {
out.write(b);
}
byte[] data=out.toByteArray();
//设置监听端口
int port;
try {
port=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if (port<1||port>65535) {
port=80;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
port=80;
}
String encoding="ASCII";
if (args.length>2) {
encoding=args[2];
}
Thread t=new SingleFileHTTPServer(data, encoding, contentType, port);
t.start();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Usage:java SingleFileHTTPServer filename port encoding");
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e);// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
SingleFileHTTPServer类本身是Thread的子类。它的run()方法处理入站连接。此服务器可能只是提供小文件,而且只支持低吞吐量的web网站。由于服务器对每个连接所需完成的所有工作就是检查客户端是否支持HTTP/1.0,并为连接生成一两个较小的字节数组,因此这可能已经足够了。另一方面,如果你发现客户端被拒绝,则可以使用多线程。许多事情取决于所提供文件的大小,每分钟所期望连接的峰值数和主机上Java的线程模型。对弈这个程序复杂写的服务器,使用多线程将会有明显的收益。
Run()方法在指定端口创建一个ServerSocket。然后它进入无限循环,不断地接受连接并处理连接。当接受一个socket时,就会由一个InputStream从客户端读取请求。它查看第一行是否包含字符串HTTP。如果包含此字符串,服务器就假定客户端理解HTTP/1.0或以后的版本,因此为该文件发送一个MIME首部;然后发送数据。如果客户端请求不包含字符串HTTP,服务器就忽略首部,直接发送数据。最后服务器关闭连接,尝试接受下一个连接。
而main()方法只是从命令行读取参数。从第一个命令行参数读取要提供的文件名。如果没有指定文件或者文件无法打开,就显示一条错误信息,程序退出。如果文件能够读取,其内容就读入byte数组data.关于文件的内容类型,将进行合理的猜测,结果存储在contentType变量中。接下来,从第二个命令行参数读取端口号。如果没有指定端口或第二个参数不是0到65535之间的整数,就使用端口80。从第三个命令行参数读取编码方式(前提是提供了)。否则,编码方式就假定为ASCII。然后使用这些值构造一个SingleFileHTTPServer对象,开始运行。这是唯一可能的接口。
下面是测试的结果:
命令行编译代码并设置参数:
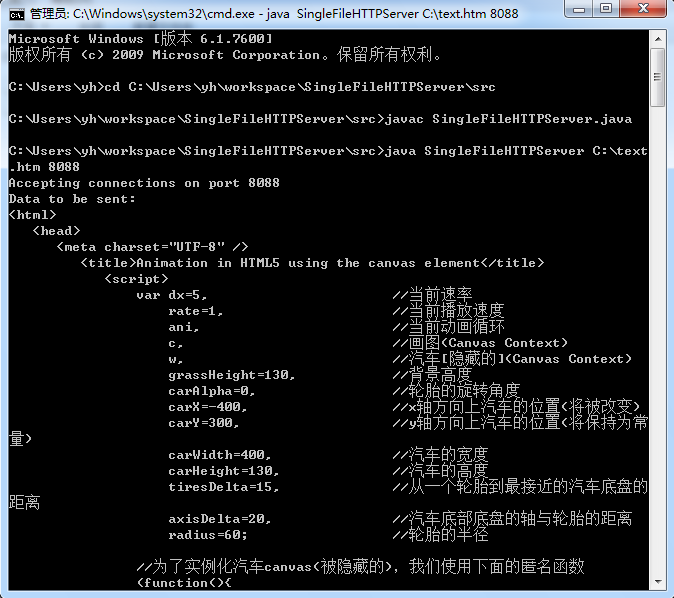
telnet::
首先,启用telnet服务(如果不会,自行google之),接着测试该主机的端口:

结果(可以看到请求的输出内容):
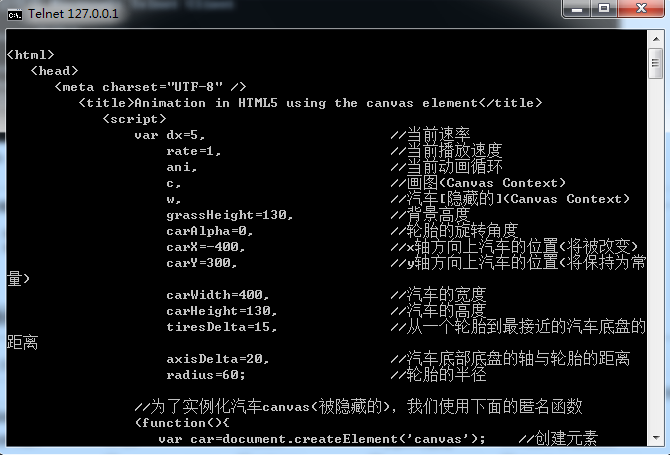
HTTP协议测试:

文档(这是之前一篇文章--小车动画的文档):
重定向服务器
实现的功能——将用户从一个Web网站重定向到另一个站点。下例从命令行读取URL和端口号,打开此端口号的服务器可能速度会很快,因此不需要多线程。尽管日次,使用多线程可能还是会带来一些好处,尤其是对于网络带宽很低、吞吐量很小的网站。在此主要是为了演示,所以,已经将该服务器做成多线程的了。这里为了简单起见,为每个连接都启用了一个线程,而不是采用线程池。或许更便于理解,但这真的有些浪费系统资源并且显得低效。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.net.BindException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Date;
public class Redirector implements Runnable {
private int port;
private String newSite;
public Redirector(String site, int port){
this.port=port;
this.newSite=site;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("Redirecting connection on port"
+server.getLocalPort()+" to "+newSite);
while (true) {
try {
Socket socket=server.accept();
Thread thread=new RedirectThread(socket);
thread.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
} catch (BindException e) {
System.err.println("Could not start server. Port Occupied");
}catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println(e);
}
}
class RedirectThread extends Thread {
private Socket connection;
RedirectThread(Socket s) {
this.connection=s;
}
public void run() {
try {
Writer out=new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(connection.getOutputStream(),"ASCII"));
Reader in=new InputStreamReader(
new BufferedInputStream(connection.getInputStream()));
StringBuffer request=new StringBuffer(80);
while (true) {
int c=in.read();
if (c=='\t'||c=='\n'||c==-1) {
break;
}
request.append((char)c);
}
String get=request.toString();
int firstSpace=get.indexOf(' ');
int secondSpace=get.indexOf(' ', firstSpace+1);
String theFile=get.substring(firstSpace+1, secondSpace);
if (get.indexOf("HTTP")!=-1) {
out.write("HTTP/1.0 302 FOUND\r\n");
Date now=new Date();
out.write("Date: "+now+"\r\n");
out.write("Server: Redirector 1.0\r\n");
out.write("Location: "+newSite+theFile+"\r\n");
out.write("Content-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n");
out.flush();
}
//并非所有的浏览器都支持重定向,
//所以我们需要生成一个适用于所有浏览器的HTML文件,来描述这一行为
out.write("<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Document moved</TITLE></HEAD>\r\n");
out.write("<BODY><H1>Document moved</H1></BODY>\r\n");
out.write("The document "+theFile
+" has moved to \r\n<A HREF=\""+newSite+theFile+"\">"
+newSite+theFile
+"</A>.\r\n Please update your bookmarks");
out.write("</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
}finally{
try {
if (connection!=null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (IOException e2) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int thePort;
String theSite;
try {
theSite=args[0];
//如果结尾有'/',则去除
if (theSite.endsWith("/")) {
theSite=theSite.substring(0,theSite.length()-1);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Usage: java Redirector http://www.newsite.com/ port");
return;
}
try {
thePort=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
} catch (Exception e) {
thePort=80;
}
Thread t=new Thread(new Redirector(theSite, thePort));
t.start();
}
}
HTTP测试:
侦听8010端口,此处重定向到百度:
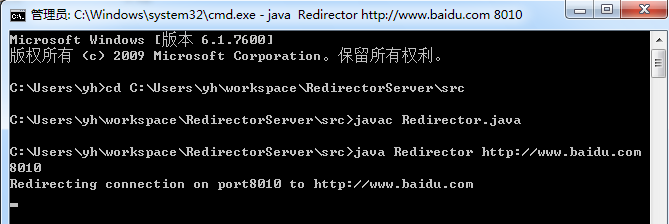

main()方法提供一个非常简单的界面,读取新网站的URL(为了把链接重定向到该URL)和监听本地端口。它使用这些信息构造了一个Rredirector对象。然后它使用所生成的Runnable对象(Redirector实现了Runnable)来生成一个新线程并启动。如果没有指定端口,Rredirector则会监听80端口。
Redirectro的run()方法将服务器socket绑定与此端口,显示一个简短的状态消息,然后进入无限循环,监听连接。每次接受连接,返回的Socket对象会用来构造一个RedirectThread。然后这个RedirectThread被启动。所有与客户端进一步的交互由此新线程完成。Redirector的run()方法只是等待下一个入站连接。
RedirectThread的run()方法完成了很多工作。它先把一个Writer链接到Socket的输出流,把一个Reader链接到Socket的输入流。输入流和输出流都有缓冲。然后run()方法读取客户端发送的第一行。虽然客户端可能会发送整个Mime首部,但我们会忽略这些。第一行包含所有所需的信息。这一行内容可能会是这样:
GET /directory/filename.html HTTP/1.0
可能第一个词是POST或PUT,也可能没有HTTP版本。
返回的输出,第一行显示为:
HTTP/1.0 302 FOUND
这是一个HTTP/1.0响应吗,告知客户端要被重定向。第二行是“Date:”首部,给出服务器的当前时间。这一行是可选的。第三行是服务器的名和版本;这一行也是可选的,但蜘蛛程序可用它来统计记录最流行的web服务器。下一行是“Location:”首部,对于此服务器这是必须的。它告知客户端要重定向的位置。最后是标准的“Content-type:”首部。这里发送内容类型text/html,只是客户端将会看到的HTML。最后,发送一个空行来标识首部数据的结束。
如果浏览器不支持重定向,那么那段HTML标签就会被发送。
功能完整的HTTP服务器
这里,我们来开发一个具有完整功能的HTTP服务器,成为JHTTP,它可以提供一个完整的文档树,包括图片、applet、HTML文件、文本文件等等。它与SingleFileHTTPServer非常相似,只不过它所关注的是GET请求。此服务器仍然是相当轻量级的;看过这个代码后,我们将讨论可能希望添加的其他特性。
由于这个服务器必须为可能很慢的网络连接提供文件系统的大文件,因此要改变其方式。这里不再在执行主线程中处理到达的每个请求,而是将入站连接放入池中。由一个RequestProcessor类实例从池中移走连接并进行处理。
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import org.omg.CORBA.Request;
public class JHTTP extends Thread {
private File documentRootDirectory;
private String indexFileName="index.html";
private ServerSocket server;
private int numThreads=50;
public JHTTP(File documentRootDirectory,int port , String indexFileName)throws IOException {
if (!documentRootDirectory.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException(documentRootDirectory+" does not exist as a directory ");
}
this.documentRootDirectory=documentRootDirectory;
this.indexFileName=indexFileName;
this.server=new ServerSocket(port);
}
private JHTTP(File documentRootDirectory, int port)throws IOException {
this(documentRootDirectory, port, "index.html");
}
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++) {
Thread t=new Thread(new RequestProcessor(documentRootDirectory, indexFileName));
t.start();
}
System.out.println("Accepting connection on port "
+server.getLocalPort());
System.out.println("Document Root: "+documentRootDirectory);
while (true) {
try {
Socket request=server.accept();
RequestProcessor.processRequest(request);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
File docroot;
try {
docroot=new File(args[0]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Usage: java JHTTP docroot port indexfile");
return;
}
int port;
try {
port=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if (port<0||port>65535) {
port=80;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
port=80;
}
try {
JHTTP webserver=new JHTTP(docroot, port);
webserver.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Server could not start because of an "+e.getClass());
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
JHTTP类的main()方法根据args[0]设置文档的根目录。端口从args[1]读取,或者使用默认的80.然后构造一个新的JHTTP线程并启动。此JHTTP线程生成50个RequestProcessor线程处理请求,每个线程在可用时从RequestProcessor池获取入站连接请求。JHTTP线程反复地接受入站连接,并将其放在RequestProcessor池中。每个连接由下例所示的RequestProcessor类的run()方法处理。此方法将一直等待,直到从池中得到一个Socket。一旦得到Socket,就获取输入和输出流,并链接到阅读器和书写器。接着的处理,除了多出文档目录、路径的处理,其他的同单文件服务器。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class RequestProcessor implements Runnable {
private static List pool=new LinkedList();
private File documentRootDirectory;
private String indexFileName="index.html";
public RequestProcessor(File documentRootDirectory,String indexFileName) {
if (documentRootDirectory.isFile()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.documentRootDirectory=documentRootDirectory;
try {
this.documentRootDirectory=documentRootDirectory.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
if (indexFileName!=null) {
this.indexFileName=indexFileName;
}
}
public static void processRequest(Socket request) {
synchronized (pool) {
pool.add(pool.size(),request);
pool.notifyAll();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
//安全性检测
String root=documentRootDirectory.getPath();
while (true) {
Socket connection;
synchronized (pool) {
while (pool.isEmpty()) {
try {
pool.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
connection=(Socket)pool.remove(0);
}
try {
String fileName;
String contentType;
OutputStream raw=new BufferedOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
Writer out=new OutputStreamWriter(raw);
Reader in=new InputStreamReader(new BufferedInputStream(connection.getInputStream()), "ASCII");
StringBuffer request=new StringBuffer(80);
while (true) {
int c=in.read();
if (c=='\t'||c=='\n'||c==-1) {
break;
}
request.append((char)c);
}
String get=request.toString();
//记录日志
System.out.println(get);
StringTokenizer st=new StringTokenizer(get);
String method=st.nextToken();
String version="";
if (method=="GET") {
fileName=st.nextToken();
if (fileName.endsWith("/")) {
fileName+=indexFileName;
}
contentType=guessContentTypeFromName(fileName);
if (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
version=st.nextToken();
}
File theFile=new File(documentRootDirectory,fileName.substring(1,fileName.length()));
if (theFile.canRead()&&theFile.getCanonicalPath().startsWith(root)) {
DataInputStream fis=new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(theFile)));
byte[] theData=new byte[(int)theFile.length()];
fis.readFully(theData);
fis.close();
if (version.startsWith("HTTP ")) {
out.write("HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
Date now=new Date();
out.write("Date: "+now+"\r\n");
out.write("Server: JHTTP 1.0\r\n");
out.write("Content-length: "+theData.length+"\r\n");
out.write("Content-Type: "+contentType+"\r\n\r\n");
out.flush();
}
raw.write(theData);
raw.flush();
}else {
if (version.startsWith("HTTP ")) {
out.write("HTTP/1.0 404 File Not Found\r\n");
Date now=new Date();
out.write("Date: "+now+"\r\n");
out.write("Server: JHTTP 1.0\r\n");
out.write("Content-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n");
out.flush();
}
out.write("<HTML>\r\n");
out.write("<HEAD><TITLE>File Not Found</TITLE></HRAD>\r\n");
out.write("<BODY>\r\n");
out.write("<H1>HTTP Error 404: File Not Found</H1>");
out.write("</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
}
}else {//方法不等于"GET"
if (version.startsWith("HTTP ")) {
out.write("HTTP/1.0 501 Not Implemented\r\n");
Date now=new Date();
out.write("Date: "+now+"\r\n");
out.write("Server: JHTTP 1.0\r\n");
out.write("Content-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n");
out.flush();
}
out.write("<HTML>\r\n");
out.write("<HEAD><TITLE>Not Implemented</TITLE></HRAD>\r\n");
out.write("<BODY>\r\n");
out.write("<H1>HTTP Error 501: Not Implemented</H1>");
out.write("</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}finally{
try {
connection.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {
}
}
}
}
public static String guessContentTypeFromName(String name) {
if (name.endsWith(".html")||name.endsWith(".htm")) {
return "text/html";
}else if (name.endsWith(".txt")||name.endsWith(".java")) {
return "text/plain";
}else if (name.endsWith(".gif")) {
return "image/gif";
}else if (name.endsWith(".class")) {
return "application/octet-stream";
}else if (name.endsWith(".jpg")||name.endsWith(".jpeg")) {
return "image/jpeg";
}else {
return "text/plain";
}
}
}
不足与改善:
这个服务器可以提供一定的功能,但仍然十分简单,还可以添加以下的一些特性:
(1) 服务器管理界面
(2) 支持CGI程序和Java Servlet API
(3) 支持其他请求方法
(4) 常见Web日志文件格式的日志文件
(5) 支持多文档根目录,这样各用户可以有自己的网站
最后,花点时间考虑一下可以采用什么方法来优化此服务器。如果真的希望使用JHTTP运行高流量的网站,还可以做一些事情来加速此服务器。第一点也是最重要的一点就是使用即时编译器(JIT),如HotSpot。JIT可以将程序的性能提升大约一个数量级。第二件事就是实现智能缓存。记住接受的请求,将最频繁的请求文件的数据存储在Hashtable中,使之保存在内存中。使用低优先级的线程更新此缓存。
——参考自网络编程