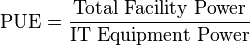Data center
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes redundant or backup
power supplies, redundant data communications connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression) and security devices. Large data centers are industrial scale operations using as much electricity as a small town[1] and
sometimes are a significant source of air pollution in the form of diesel exhaust.[2]
History[edit]
Data centers have their roots in the huge computer rooms of the early ages of the computing industry. Early computer systems were complex to operate and maintain, and required a special environment
in which to operate. Many cables were necessary to connect all the components, and methods to accommodate and organize these were devised, such as standard racks to
mount equipment, raised floors, and cable
trays (installed overhead or under the elevated floor). Also, a single mainframe required a great deal of power, and had to be cooled to avoid overheating. Security was important – computers were expensive, and were often used for military purposes. Basic
design guidelines for controlling access to the computer room were therefore devised.
During the boom of the microcomputer industry, and especially during the 1980s, computers started to be deployed everywhere, in many cases with little or no care about operating requirements.
However, as information technology (IT) operations started to grow in complexity, companies grew
aware of the need to control IT resources. With the advent of Linux and the subsequent proliferation of freely available Unix compatible
PC operating systems during the 1990s, as well as MS-DOS finally giving way to a multi-tasking capable Windows
OS, PCs started to find their places in the old computer rooms. These were called "servers"
as timesharing operating systems like Unix rely heavily on the client-server
model to facilitate sharing unique resources between multiple users. The availability of inexpensive networking equipment,
coupled with new standards for network structured cabling, made it possible to use a hierarchical design
that put the servers in a specific room inside the company. The use of the term "data center," as applied to specially designed computer rooms, started to gain popular recognition about this time.
The boom of data centers came during the dot-com
bubble. Companies needed fast Internet connectivity and nonstop operation to deploy systems and establish a presence on the Internet. Installing such equipment was not viable for many smaller companies. Many companies started building very large facilities,
called Internet data centers (IDCs), which provide businesses with a range of solutions for systems deployment and operation. New technologies and practices were designed to handle the scale and the operational requirements of such large-scale operations.
These practices eventually migrated toward the private data centers, and were adopted largely because of their practical results. Data centers for cloud computing are called cloud data centers (CDCs). But nowadays, the division of these terms has almost disappeared
and they are being integrated into a term "data center."
With an increase in the uptake of cloud computing,
business and government organizations are scrutinizing data centers to a higher degree in areas such as security, availability, environmental impact and adherence to standards. Standard Documents from accredited professional groups, such as the Telecommunications
Industry Association, specify the requirements for data center design. Well-known operational metrics for data center availability can be used to evaluate the business impact of a disruption. There is still a lot of development being done in operation
practice, and also in environmentally friendly data center design. Data centers are typically very expensive to build and maintain.
Requirements for modern data centers[edit]
IT operations are a crucial aspect of most organizational operations around the world. One of the main concerns is business continuity; companies rely on their information
systems to run their operations. If a system becomes unavailable, company operations may be impaired or stopped completely. It is necessary to provide a reliable infrastructure for IT operations, in order to minimize any chance of disruption. Information security
is also a concern, and for this reason a data center has to offer a secure environment which minimizes the chances of a security breach. A data center must therefore keep high standards for assuring the integrity and functionality of its hosted computer environment.
This is accomplished through redundancy of both fiber optic cables and power, which includes emergency backup power generation.
The Telecommunications
Industry Association's TIA-942
Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers, specifies the minimum requirements for telecommunications infrastructure of data centers and computer rooms including single tenant enterprise data centers and multi-tenant Internet hosting data
centers. The topology proposed in this document is intended to be applicable to any size data center.[3]
Telcordia GR-3160, NEBS
Requirements for Telecommunications Data Center Equipment and Spaces, provides guidelines for data center spaces within telecommunications networks, and environmental requirements for the equipment intended for installation in those spaces. These
criteria were developed jointly by Telcordia and industry representatives. They may be applied to data center spaces housing data processing or Information Technology (IT) equipment. The equipment may be used to:
- Operate and manage a carrier’s telecommunication network
- Provide data center based applications directly to the carrier’s customers
- Provide hosted applications for a third party to provide services to their customers
- Provide a combination of these and similar data center applications
Effective data center operation requires a balanced investment in both the facility and the housed equipment. The first step is to establish a baseline facility environment suitable for equipment
installation. Standardization and modularity can yield savings and efficiencies in the design and construction of telecommunications data centers.
Standardization means integrated building and equipment engineering. Modularity has the benefits of scalability and easier growth, even when planning forecasts are less than optimal. For these
reasons, telecommunications data centers should be planned in repetitive building blocks of equipment, and associated power and support (conditioning) equipment when practical. The use of dedicated centralized systems requires more accurate forecasts of future
needs to prevent expensive over construction, or perhaps worse — under construction that fails to meet future needs.
The "lights-out" data center, also known as a darkened or a dark data center, is a data center that, ideally, has all but eliminated the need for direct access by personnel, except under extraordinary
circumstances. Because of the lack of need for staff to enter the data center, it can be operated without lighting. All of the devices are accessed and managed by remote systems, with automation programs used to perform unattended operations. In addition to
the energy savings, reduction in staffing costs and the ability to locate the site further from population centers, implementing a lights-out data center reduces the threat of malicious attacks upon the infrastructure.[4][5]
There is a trend to modernize data centers in order to take advantage of the performance and energy efficiency increases of newer IT equipment and capabilities, such as cloud
computing. This process is also known as data center transformation.[6]
Organizations are experiencing rapid IT growth but their data centers are aging. Industry research companyInternational
Data Corporation (IDC) puts the average age of a data center at nine years old.[6] Gartner,
another research company says data centers older than seven years are obsolete.[7]
In May 2011, data center research organization Uptime
Institute, reported that 36 percent of the large companies it surveyed expect to exhaust IT capacity within the next 18 months.[8]
Data center transformation takes a step-by-step approach through integrated projects carried out over time. This differs from a traditional method of data center upgrades that takes a serial
and siloed approach.[9] The typical
projects within a data center transformation initiative include standardization/consolidation, virtualization,automation and
security.
- Standardization/consolidation: The purpose of this project is to reduce the number of data centers a large organization may have. This project also helps to reduce the number of hardware, software platforms, tools and processes
within a data center. Organizations replace aging data center equipment with newer ones that provide increased capacity and performance. Computing, networking and management platforms are standardized so they are easier to manage.[10]
- Virtualize: There is a trend to use IT virtualization technologies to replace or consolidate multiple data center equipment, such as servers. Virtualization helps to lower capital and operational expenses,[11] and
reduce energy consumption.[12] Virtualization
technologies are also used to create virtual desktops, which can then be hosted in data centers and rented out on a subscription basis.[13] Data
released by investment bank Lazard Capital Markets reports that 48 percent of enterprise operations will be virtualized by 2012. Gartner views virtualization as a catalyst for modernization.[14]
- Automating: Data center automation involves automating tasks such as provisioning,
configuration, patching, release management and compliance. As enterprises suffer from few skilled IT workers,[10] automating
tasks make data centers run more efficiently.
- Securing: In modern data centers, the security of data on virtual systems is integrated with existing security of physical infrastructures.[15] The
security of a modern data center must take into account physical security, network security, and data and user security.
Carrier neutrality[edit]
Today many data centers are run by Internet
service providers solely for the purpose of hosting their own and third party servers.
However traditionally data centers were either built for the sole use of one large company, or as carrier
hotels orNetwork-neutral data centers.
These facilities enable interconnection of carriers and act as regional fiber hubs serving local business in addition to hosting content servers.
Data center tiers[edit]
The Telecommunications
Industry Association is a trade association accredited by ANSI (American National Standards Institute). In 2005 it published ANSI/TIA-942,
Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers, which defined four levels (called tiers) of data centers in a thorough, quantifiable manner. TIA-942 was amended in 2008 and again in 2010. TIA-942:Data Center Standards Overview describes
the requirements for the data center infrastructure. The simplest is a Tier 1 data center, which is basically a server
room, following basic guidelines for the installation of computer systems. The most stringent level is a Tier 4 data center, which is designed to host mission critical computer systems, with fully redundant subsystems and compartmentalized security zones
controlled bybiometric access controls methods. Another consideration is the placement of the data
center in a subterranean context, for data security as well as environmental considerations such as cooling requirements.[16]
The German Datacenter star audit program uses an auditing process to certify 5 levels of "gratification" that affect Data Center criticality.
Independent from the ANSI/TIA-942 standard, the Uptime
Institute, a think tank and professional-services organization based in Santa Fe, New
Mexico, has defined its own four levels. The levels describe the availability of data from the hardware at a location. The higher the tier, the greater the availability. The levels are: [17] [18]
| Tier Level | Requirements |
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
| 4 |
|
The difference between 99.671%, 99.741%, 99.982%, and 99.995%, while seemingly nominal, could be significant depending on the application.
Whilst no down-time is ideal, the tier system allows the below durations for services to be unavailable within one year (525,600 minutes):
- Tier 1 (99.671%) status would allow 1729.224 minutes
- Tier 2 (99.741%) status would allow 1361.304 minutes
- Tier 3 (99.982%) status would allow 94.608 minutes
- Tier 4 (99.995%) status would allow 26.28 minutes
Design considerations[edit]
A data center can occupy one room of a building, one or more floors, or an entire building. Most of the equipment is often in the form of servers mounted in 19
inch rack cabinets, which are usually placed in single rows forming corridors (so-called aisles) between them. This allows people access to the front and rear of each cabinet. Servers differ greatly in size from 1U
serversto large freestanding storage silos which occupy many square feet of floor space. Some equipment such as mainframe
computers and storage devices are often as big as the racks themselves, and are placed
alongside them. Very large data centers may use shipping containers packed with 1,000 or more servers
each;[19] when repairs or upgrades
are needed, whole containers are replaced (rather than repairing individual servers).[20]
Local building codes may govern the minimum ceiling heights.
Design programming[edit]
Design programming, also known as architectural programming, is the process of researching and making decisions to identify the scope of a design project.[21]Other
than the architecture of the building itself there are three elements to design programming for data centers: facility topology design (space planning), engineering infrastructure design (mechanical systems such as cooling and electrical systems including
power) and technology infrastructure design (cable plant). Each will be influenced by performance assessments and modelling to identify gaps pertaining to the owner’s performance wishes of the facility over time.
Various vendors who provide data center design services define the steps of data center design slightly differently, but all address the same basic aspects as given below.
Modeling criteria[edit]
Modeling criteria are used to develop future-state scenarios for space, power, cooling, and costs.[22] The
aim is to create a master plan with parameters such as number, size, location, topology, IT floor system layouts, and power and cooling technology and configurations.
Design recommendations[edit]
Design recommendations/plans generally follow the modelling criteria phase. The optimal technology infrastructure is identified and planning criteria is developed, such as critical power capacities,
overall data center power requirements using an agreed upon PUE (power utilization efficiency), mechanical cooling capacities, kilowatts per cabinet, raised floor space, and the resiliency level for the facility.
Conceptual design[edit]
Conceptual designs embody the design recommendations or plans and should take into account “what-if” scenarios to ensure all operational outcomes are met in order to future-proof the facility.
Conceptual floor layouts should be driven by IT performance requirements as well as lifecycle costs associated with IT demand, energy efficiency, cost efficiency and availability. Future-proofing will also include expansion capabilities, often provided in
modern data centers through modularity.
Detail design[edit]
Detail design is undertaken once the appropriate conceptual design is determined, typically including a proof of concept. The detail design phase should include the development of facility
schematics and construction documents as well as schematic of technology infrastructure, detailed IT infrastructure design and IT infrastructure documentation.
Mechanical engineering infrastructure design[edit]
Mechanical engineering infrastructure design addresses mechanical systems involved in maintaining the interior environment of a data center, such as heating, ventilation and air conditioning
(HVAC); humidification and dehumidification equipment; pressurization; and so on.[23] This
stage of the design process should be aimed at saving space and costs, while ensuring business and reliability objectives are met as well as achieving PUE and green requirements.[24] Modern
designs include modularizing and scaling IT loads, and making sure capital spending on the building construction is optimized.
Electrical engineering infrastructure design[edit]
Electrical Engineering infrastructure design is focused on designing electrical configurations that accommodate various reliability requirements and data center sizes. Aspects may include utility
service planning; distribution, switching and bypass from power sources; uninterruptable power source (UPS) systems; and more.[23]
These designs should dovetail to energy standards and best practices while also meeting business objectives. Electrical configurations should be optimized and operationally compatible with
the data center user’s capabilities. Modern electrical design is modular and scalable,[25] and
is available for low and medium voltage requirements as well as DC (direct current).
Technology infrastructure design[edit]
Technology infrastructure design addresses the telecommunications cabling systems that run throughout data centers. There are cabling systems for all data center environments, including horizontal
cabling, voice, modem, and facsimile telecommunications services, premises switching equipment, computer and telecommunications management connections, keyboard/video/mouse connections and data communications.[26] Wide
area, local area, and storage area networks should link with other building signaling systems (e.g. fire, security, power, HVAC, EMS).
Availability expectations[edit]
The higher the availability needs of a data center, the higher the capital and operational costs of building and managing it. Business needs should dictate the level of availability required
and should be evaluated based on characterization of the criticality of IT systems estimated cost analyses from modeled scenarios. In other words, how can an appropriate level of availability best be met by design criteria to avoid financial and operational
risks as a result of downtime? If the estimated cost of downtime within a specified time unit exceeds the amortized capital costs and operational expenses, a higher level of availability should be factored into the data center design. If the cost of avoiding
downtime greatly exceeds the cost of downtime itself, a lower level of availability should be factored into the design.[27]
Site selection[edit]
Aspects such as proximity to available power grids, telecommunications infrastructure, networking services, transportation lines and emergency services can affect costs, risk, security and
other factors to be taken into consideration for data center design. Location affects data center design also because the climatic conditions dictate what cooling technologies should be deployed. In turn this impacts uptime and the costs associated with cooling.[28] For
example, the topology and the cost of managing a data center in a warm, humid climate will vary greatly from managing one in a cool, dry climate.
Modularity and flexibility[edit]
Modularity and flexibility are key elements in allowing for a data center to grow and change over time. Data center modules are pre-engineered, standardized building blocks that can be easily
configured and moved as needed.[29]
A modular data center may consist of data center equipment contained within shipping containers or similar portable containers.[30] But
it can also be described as a design style in which components of the data center are prefabricated and standardized so that they can be constructed, moved or added to quickly as needs change.[31]
Environmental control[edit]
The physical environment of a data center is rigorously controlled. Air
conditioning is used to control the temperature and humidity in the data center. ASHRAE's "Thermal Guidelines for Data Processing
Environments"[32]recommends a temperature
range of 18–27 °C (64–81 °F), a dew point range of 5–15 °C (41–59 °F), and a maximum relative humidity of 60% for data center environments.[33] The
temperature in a data center will naturally rise because the electrical power used heats the air. Unless the heat is removed, the ambient temperature will rise, resulting in electronic equipment malfunction. By controlling the air temperature, the server components
at the board level are kept within the manufacturer's specified temperature/humidity range. Air conditioning systems help control humidity by
cooling the return space air below the dew point. Too much humidity, and water may begin to condense on
internal components. In case of a dry atmosphere, ancillary humidification systems may add water vapor if the humidity is too low, which can result in static
electricity discharge problems which may damage components. Subterranean data centers may keep computer equipment cool while expending less energy than conventional designs.
Modern data centers try to use economizer cooling, where they use outside air to keep the data center cool. At least one data center (located in Upstate
New York) will cool servers using outside air during the winter. They do not use chillers/air conditioners, which creates potential energy savings in the millions.[34]
Telcordia GR-2930, NEBS:
Raised Floor Generic Requirements for Network and Data Centers, presents generic engineering requirements for raised floors that fall within the strict NEBS guidelines.
There are many types of commercially available floors that offer a wide range of structural strength and loading capabilities, depending on component construction and the materials used. The
general types of raised floors include stringerless, stringered, and structural platforms, all of which are discussed in detail in GR-2930 and summarized below.
- Stringerless raised floors - One non-earthquake type of raised floor generally consists of an array of pedestals that provide the necessary height for routing cables and also serve to support each corner
of the floor panels. With this type of floor, there may or may not be provisioning to mechanically fasten the floor panels to the pedestals. This stringerless type of system (having no mechanical attachments between the pedestal heads) provides maximum accessibility
to the space under the floor. However, stringerless floors are significantly weaker than stringered raised floors in supporting lateral loads and are not recommended.
- Stringered raised floors - This type of raised floor generally consists of a vertical array of steel pedestal assemblies (each assembly is made up of a steel base plate, tubular upright, and a head)
uniformly spaced on two-foot centers and mechanically fastened to the concrete floor. The steel pedestal head has a stud that is inserted into the pedestal upright and the overall height is adjustable with a leveling nut on the welded stud of the pedestal
head.
- Structural platforms - One type of structural platform consists of members constructed of steel angles or channels that are welded or bolted together to form an integrated platform for supporting equipment.
This design permits equipment to be fastened directly to the platform without the need for toggle bars or supplemental bracing. Structural platforms may or may not contain panels or stringers.
Data centers typically have raised flooring made
up of 60 cm (2 ft) removable square tiles. The trend is towards 80–100 cm (31–39 in) void to cater for better and uniform air distribution. These provide a plenum for
air to circulate below the floor, as part of the air conditioning system, as well as providing space for power cabling.
Metal whiskers[edit]
Raised floors and other metal structures such as cable trays and ventilation ducts have caused many problems withzinc
whiskers in the past, and likely are still present in many data centers. This happens when microscopic metallic filaments form on metals such as zinc or tin that protect many metal structures and electronic components from corrosion. Maintenance on a raised
floor or installing of cable etc. can dislodge the whiskers, which enter the airflow and may short circuit server components or power supplies, sometimes through a high current metal vaporplasma
arc. This phenomenon is not unique to data centers, and has also caused catastrophic failures of satellites and military hardware.[35]
Electrical power[edit]
Backup power consists of one or more uninterruptible
power supplies, battery banks, and/or diesel / gas
turbine generators.[36]
To prevent single points of
failure, all elements of the electrical systems, including backup systems, are typically fully duplicated, and critical servers are connected to both the "A-side" and "B-side" power feeds. This arrangement is often made to achieve N+1
redundancy in the systems. Static transfer switches are sometimes used to ensure
instantaneous switchover from one supply to the other in the event of a power failure.
Low-voltage cable routing[edit]
Data cabling is typically routed through overhead cable
trays in modern data centers. But some[who?] are
still recommending under raised floor cabling for security reasons and to consider the addition of cooling systems above the racks in case this enhancement is necessary. Smaller/less expensive data centers without raised flooring may use anti-static tiles
for a flooring surface. Computer cabinets are often organized into a hot
aisle arrangement to maximize airflow efficiency.
Fire protection[edit]
Data centers feature fire protection systems,
including passive and activedesign
elements, as well as implementation of fire prevention programs in operations. Smoke
detectors are usually installed to provide early warning of a fire at its incipient stage. This allows investigation, interruption of power, and manual fire suppression using hand held fire extinguishers before the fire grows to a large size. An active
fire protection system, such as afire sprinkler system or a clean
agent fire suppression gaseous system, is often provided to control a full scale fire if it develops. High sensitivity smoke detectors, such as Aspirating
smoke detectors, activating clean agentfire suppression gaseous systems activate earlier than
fire sprinklers. However, as gaseous systems have a limited fire suppression agent storage quantity, the provision of a clean agent system and a sprinkler system protects the building should the fire reignite after the gaseous agent has dispersed. Passive
fire protection elements include the installation of fire walls around the data center, so
a fire can be restricted to a portion of the facility for a limited time in the event of the failure of the active fire protection systems. Fire wall penetrations into the server room, such as cable penetrations, coolant line penetrations and air ducts, must
be provided with fire rated penetration assemblies, such as fire stoping.
Security[edit]
Physical security also plays a large role with data centers. Physical access to the site is usually restricted to selected personnel, with controls including bollards and mantraps.[37] Video
camera surveillance and permanentsecurity guards are almost always present if the data center is large or
contains sensitive information on any of the systems within. The use of finger print recognition mantraps is starting to be
commonplace.
Energy use[edit]
Energy use is a central issue for data centers. Power draw for data centers ranges from a few kW for a rack of servers in a closet to several tens of MW for large facilities. Some facilities
have power densities more than 100 times that of a typical office building.[38] For
higher power density facilities, electricity costs are a dominant operating expense and account for over
10% of the total cost of ownership (TCO) of a data center.[39] By
2012 the cost of power for the data center is expected to exceed the cost of the original capital investment.[40]
Greenhouse gas emissions[edit]
In 2007 the entire information
and communication technologies or ICT sector was estimated to be responsible for roughly 2% of global carbon
emissions with data centers accounting for 14% of the ICT footprint.[41] The
US EPA estimates that servers and data centers are responsible for up to 1.5% of the total US electricity consumption,[42] or
roughly .5% of US GHG emissions,[43] for
2007. Given a business as usual scenario greenhouse gas emissions from data centers is projected to more than double from 2007 levels by 2020.[41]
Siting is one of the factors that affect the energy consumption and environmental effects of a datacenter. In areas where climate favors cooling and lots of renewable electricity is available
the environmental effects will be more moderate. Thus countries with favorable conditions, such as: Canada,[44] Finland,[45] Sweden[46] and
Switzerland,[47]are trying to attract
cloud computing data centers.
In an 18-month investigation by scholars at Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy in Houston and the Institute for Sustainable and Applied Infodynamics in Singapore, data center-related
emissions will more than triple by 2020. [48]
Energy efficiency[edit]
The most commonly used metric to determine the energy efficiency of a data center is power
usage effectiveness, or PUE. This simple ratio is the total power entering the data center divided by the power used by the IT equipment.
Power used by support equipment, often referred to as overhead load, mainly consists of cooling systems, power delivery, and other facility infrastructure like lighting. The average data center
in the US has a PUE of 2.0,[42]meaning
that the facility uses one watt of overhead power for every watt delivered to IT equipment. State-of-the-art data center energy efficiency is estimated to be roughly 1.2.[49] Some
large data center operators like Microsoft andYahoo! have
published projections of PUE for facilities in development; Google publishes quarterly actual efficiency performance from data
centers in operation.[50]
The U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency has an Energy Star rating for standalone or large data centers. To qualify for
the ecolabel, a data center must be within the top quartile of energy efficiency of all reported facilities.[51]
European Union also has a similar initiative: EU Code of Conduct for Data Centres[52]
Energy use analysis[edit]
Often, the first step toward curbing energy use in a data center is to understand how energy is being used in the data center. Multiple types of analysis exist to measure data center energy
use. Aspects measured include not just energy used by IT equipment itself, but also by the data center facility equipment, such as chillers and fans.[53]
Power and cooling analysis[edit]
Power is the largest recurring cost to the user of a data center.[54] A
power and cooling analysis, also referred to as a thermal assessment, measures the relative temperatures in specific areas of your data center, as well as the ability of your data center to tolerate specific temperatures.[55] Among
other things, a power and cooling analysis can help to identify hot spots, over-cooled areas that can handle greater power use density, the breakpoint of equipment loading, the effectiveness of a raised-floor strategy, and optimal equipment positioning (such
as AC units) to balance temperatures across the data center. Power cooling density is a measure of how much square footage the center can cool at maximum capacity.[56]
Energy efficiency analysis[edit]
An energy efficiency analysis measures the energy use of data center IT and facilities equipment. A typical energy efficiency analysis measures factors such as a data center’s power use effectiveness
(PUE) against industry standards, identifies mechanical and electrical sources of inefficiency, and identifies air-management metrics.[57]
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis[edit]
This type of analysis uses sophisticated tools and techniques to understand the unique thermal conditions present in each data center—predicting the temperature, airflow, and pressure behavior
of a data center to assess performance and energy consumption, using numerical modeling.[58] By
predicting the effects of these environmental conditions, CFD analysis in the data center can be used to predict the impact of high-density racks mixed with low-density racks[59]and
the onward impact on cooling resources, poor infrastructure management practices and AC failure of AC shutdown for scheduled maintenance.
Thermal zone mapping[edit]
Thermal zone mapping uses sensors and computer modeling to create a three-dimensional image of the hot and cool zones in a data center.[60]
This information can help to identify optimal positioning of data center equipment. For example, critical servers might be placed in a cool zone that is serviced by redundant AC units.
Green datacenters[edit]
Datacenters use a lot of power, consumed by two main usages: the power required to run the actual equipment and then the power required to cool the equipment. The first category is addressed
by designing computers and storage systems that are more and more power-efficient. And to bring down the cooling costs datacenter designers try to use natural ways to cool the equipment. Many datacenters have to be located near people-concentrations to manage
the equipment, but there are also many circumstances where the datacenter can be miles away from the users and don't need a lot of local management. Examples of this are the 'mass' datacenters like Google or Facebook: these DC's are built around many standarised
servers and storage-arrays and the actual users of the systems are located all around the world. After the initial build of a datacenter there is not much staff required to keep it running: especially datacenters that provide mass-storage or computing power
don't need to be near population centers. Datacenters in arctic locations where outside air provides all cooling are getting more popular as cooling and electricity are the two main variable cost components.[61]
Network infrastructure[edit]
Communications in data centers today are most often based on networks running
the IP protocol suite.
Data centers contain a set of routers and switches that
transport traffic between the servers and to the outside world. Redundancy of the Internet
connection is often provided by using two or more upstream service providers (see Multihoming).
Some of the servers at the data center are used for running the basic Internetand intranet services
needed by internal users in the organization, e.g., e-mail servers, proxy
servers, and DNS servers.
Network security elements are also usually deployed: firewalls, VPN gateways,intrusion
detection systems, etc. Also common are monitoring systems for the network and some of the applications. Additional off site monitoring systems are also typical, in case of a failure of communications inside the data center.
Data center infrastructure management[edit]
Data
center infrastructure management (DCIM) is the integration of information technology (IT)
and facility management disciplines to centralize monitoring, management and intelligent capacity planning of a data center's critical systems. Achieved through the implementation of specialized software, hardware and sensors, DCIM enables common, real-time
monitoring and management platform for all interdependent systems across IT and facility infrastructures.
Depending on the type of implementation, DCIM products can help data center managers identify and eliminate sources of risk to increase availability of critical IT systems. DCIM products also
can be used to identify interdependencies between facility and IT infrastructures to alert the facility manager to gaps in system redundancy, and provide dynamic, holistic benchmarks on power consumption and efficiency to measure the effectiveness of “green
IT” initiatives.
Measuring and understanding important data center efficiency metrics. A lot of the discussion in this area has focused on energy issues, but other metrics beyond the PUE can give a more detailed
picture of the data center operations. Server, storage, and staff utilization metrics can contribute to a more complete view of an enterprise data center. In many cases, disc capacity goes unused and in many instances the organizations run their servers at
20% utilization or less.[62] More
effective automation tools can also improve the number of servers or virtual machines that a single admin can handle.
Applications[edit]
The main purpose of a data center is running the applications that handle the core business and operational data of the organization. Such systems may be proprietary and developed internally
by the organization, or bought fromenterprise software vendors. Such common applications are ERP and CRM systems.
A data center may be concerned with just operations
architecture or it may provide other services as well.
Often these applications will be composed of multiple hosts, each running a single component. Common components of such applications are databases, file
servers, application servers, middleware,
and various others.
Data centers are also used for off site backups. Companies may subscribe to backup services provided by a data center. This is often used in conjunction with backup
tapes. Backups can be taken of servers locally on to tapes. However, tapes stored on site pose a security threat and are also susceptible to fire and flooding. Larger companies may also send their backups off site for added security. This can be done by
backing up to a data center. Encrypted backups can be sent over the Internet to another data center where they can be stored securely.
For quick deployment or disaster recovery,
several large hardware vendors have developed mobile solutions that can be installed and made operational in very short time. Companies such as Cisco
Systems,[63] Sun
Microsystems (Sun Modular Datacenter),[64][65] Bull,[66] IBM (Portable
Modular Data Center), HP (Performance
Optimized Datacenter),[67] andGoogle (Google
Modular Data Center) have developed systems that could be used for this purpose.[68][69]