最大期望算法(Expectation-maximization algorithm,又译期望最大化算法)在统计中被用于寻找,依赖于不可观察的隐性变量的概率模型中,参数的最大似然估计。
在统计计算中,最大期望(EM)算法是在概率(probabilistic)模型中寻找参数最大似然估计或者最大后验估计的算法,其中概率模型依赖于无法观测的隐藏变量(Latent Variable)。最大期望经常用在机器学习和计算机视觉的数据聚类(Data Clustering)领域。最大期望算法经过两个步骤交替进行计算,第一步是计算期望(E),利用对隐藏变量的现有估计值,计算其最大似然估计值;第二步是最大化(M),最大化在 E 步上求得的最大似然值来计算参数的值。M 步上找到的参数估计值被用于下一个 E 步计算中,这个过程不断交替进行。
历史
最大期望值算法由 Arthur Dempster,Nan Laird和Donald Rubin在他们1977年发表的经典论文中提出。他们指出此方法之前其实已经被很多作者"在他们特定的研究领域中多次提出过"。
[编辑]EM简单教程
EM是一个在已知部分相关变量的情况下,估计未知变量的迭代技术。EM的算法流程如下:
- 初始化分布参数
- 重复直到收敛:
- E步骤:估计未知参数的期望值,给出当前的参数估计。
- M步骤:重新估计分布参数,以使得数据的似然性最大,给出未知变量的期望估计。
应用于缺失值。
最大期望过程说明
我们用  表示能够观察到的不完整的变量值,用
表示能够观察到的不完整的变量值,用 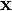 表示无法观察到的变量值,这样
表示无法观察到的变量值,这样 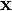 和
和  一起组成了完整的数据。
一起组成了完整的数据。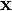 可能是实际测量丢失的数据,也可能是能够简化问题的隐藏变量,如果它的值能够知道的话。例如,在混合模型(Mixture Model)中,如果“产生”样本的混合元素成分已知的话最大似然公式将变得更加便利(参见下面的例子)。
可能是实际测量丢失的数据,也可能是能够简化问题的隐藏变量,如果它的值能够知道的话。例如,在混合模型(Mixture Model)中,如果“产生”样本的混合元素成分已知的话最大似然公式将变得更加便利(参见下面的例子)。
估计无法观测的数据
让 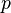 代表矢量
代表矢量  :
:  定义的参数的全部数据的概率分布(连续情况下)或者概率聚类函数(离散情况下),那么从这个函数就可以得到全部数据的最大似然值,另外,在给定的观察到的数据条件下未知数据的条件分布可以表示为:
定义的参数的全部数据的概率分布(连续情况下)或者概率聚类函数(离散情况下),那么从这个函数就可以得到全部数据的最大似然值,另外,在给定的观察到的数据条件下未知数据的条件分布可以表示为:
参考文献
§ Arthur Dempster, Nan Laird, and Donald Rubin. "Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm". Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 39(1):1–38, 1977 [1].
§ Robert Hogg, Joseph McKean and Allen Craig. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics. pp. 359-364. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005.
§ Radford Neal, Geoffrey Hinton. "A view of the EM algorithm that justifies incremental, sparse, and other variants". In Michael I. Jordan (editor),Learning in Graphical Models pp 355-368. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1999.
§ The on-line textbook: Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms,by David J.C. MacKay includes simple examples of the E-M algorithm such as clustering using the soft K-means algorithm, and emphasizes the variational view of the E-M algorithm.
§ A Gentle Tutorial of the EM Algorithm and its Application to Parameter Estimation for Gaussian Mixture and Hidden Markov Models,by J. Bilmesincludes a simplified derivation of the EM equations for Gaussian Mixtures and Gaussian Mixture Hidden Markov Models.
Information Geometry of the EM and em Algorithms for Neural Networks,by Shun-Ichi Amari give a view of EM algorithm from geometry view point
另外一篇博文,有关于EM算法详细推导:http://www.cnblogs.com/jerrylead/archive/2011/04/06/2006936.html
