图像处理之二值腐蚀
概述:
腐蚀是图像形态学的两个基本操作之一,另外一个是膨胀(Dilate)。二值图像上的腐蚀是腐蚀最典
型的运用,但是腐蚀操作同样可以运用于灰度图像。二值图像腐蚀操作最基本的效果是腐蚀图像
中前景色区域的边缘。使得前景图像区域变小,前景图像内部的背景区域被放大。
基本原理:
腐蚀操作要求有待处理的2D图像F(x,y)以及操作数矩阵(类似卷积操作中的Kernel矩阵),常见的
为3X3的操作数矩阵。二值图像腐蚀操作的数学定义如下:
1. 假设X是二值图像中所有像素欧几里德坐标的集合,K为3X3的操作数矩阵
2. Kx表示操作数处理X的结果,x表示起始像素点
3. 腐蚀操作K对X的所有像素点操作,Kx是X所有像素点的子集。
一个二值图像腐蚀的例子如下,操作数矩阵为3X3,起始点为中心像素点,前景像素表示为1,背
景像素表示为0.图示如下:
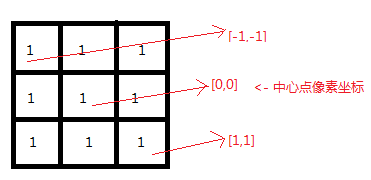
当操作数在像素矩阵上移动时,任何一个在操作数之下的输入像素为背景像素时,则设置中心像素
为背景像素0,否则中心像素[0,0]下的输入像素值不变。
三:程序效果

package com.gloomyfish.morphology;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class ErosionFilter extends BinaryFilter {
private Color backgroundColor;
public ErosionFilter() {
backgroundColor = Color.WHITE;
}
public Color getBackColor() {
return backgroundColor;
}
public void setBackColor(Color forgeColor) {
this.backgroundColor = forgeColor;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
if ( dest == null )
dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null );
int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width*height];
src = super.filter(src, null); // we need to create new one
getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );
int index = 0, index1 = 0, newRow = 0, newCol = 0;
int ta1 = 0, tr1 = 0, tg1 = 0, tb1 = 0;
for(int row=0; row<height; row++) {
int ta = 0, tr = 0, tg = 0, tb = 0;
for(int col=0; col<width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
ta = (inPixels[index] >> 24) & 0xff;
tr = (inPixels[index] >> 16) & 0xff;
tg = (inPixels[index] >> 8) & 0xff;
tb = inPixels[index] & 0xff;
boolean erosion = false;
for(int offsetY=-1; offsetY<=1; offsetY++) {
for(int offsetX=-1; offsetX<=1; offsetX++) {
if(offsetY==0 && offsetX==0) {
continue;
}
newRow = row + offsetY;
newCol = col + offsetX;
if(newRow <0 || newRow >=height) {
newRow = 0;
}
if(newCol < 0 || newCol >=width) {
newCol = 0;
}
index1 = newRow * width + newCol;
ta1 = (inPixels[index1] >> 24) & 0xff;
tr1 = (inPixels[index1] >> 16) & 0xff;
tg1= (inPixels[index1] >> 8) & 0xff;
tb1 = inPixels[index1] & 0xff;
if(tr1 == backgroundColor.getRed() && tg1 == tb1) {
erosion = true;
break;
}
}
if(erosion){
break;
}
}
if(erosion) {
tr = tg = tb = backgroundColor.getRed();
} else {
tr = tg = tb = 255 - backgroundColor.getRed();
}
outPixels[index] = (ta << 24) | (tr << 16) | (tg << 8) | tb;
}
}
setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels );
return dest;
}
}
转载请注明出处