Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) 旨在帮助开发人员解决线程的难题。这样,大多数 WPF 开发人员都不必编写使用多个线程的接口。由于多线程程序很复杂,且难以调试,因此只要存在单线程解决方案,就应避免使用多个线程。
但是,无论体系结构多么完善,没有任何 UI 框架能够为每一类问题提供单线程解决方案。WPF 接近这一理想,但是在某些情况下,仍然可通过采用多个线程来提高用户界面 (UI) 响应速度或应用程序性能。在讨论一些背景材料后,本文将探讨其中一些情况,最后从较低层次进行一些详细讨论。
本主题包括下列各节:
- 概述和调度程序
- 操作中的线程:示例
- 技术细节和难点
- 相关主题
概述和调度程序
通常,WPF 应用程序从两个线程开始:一个用于处理呈现,一个用于管理 UI。呈现线程有效地隐藏在后台运行,而 UI 线程则接收输入、处理事件、绘制屏幕以及运行应用程序代码。大多数应用程序都使用一个 UI 线程,但在某些情况下,最好使用多个线程。我们将在后面举例说明这一点。
UI 线程在一个名为 的对象内部对工作项进行排队。 基于优先级选择工作项,并运行每一个工作项直到完成。 每个 UI 线程都必须至少有一个 ,并且每个 都只能在一个线程中执行工作项。
要构建响应速度快、且用户友好的应用程序,诀窍是减小工作项,以最大限度地提高 吞吐量。这样,工作项将永远不会因为在 队列中等待处理而失效。输入与响应之间的任何可察觉的延迟都会使用户不快。
那么,WPF 应用程序应如何处理大型操作? 如果您的代码涉及大型计算,或者需要查询某台远程服务器上的数据库,应怎么办? 通常的办法是在单独的线程中处理大型操作,而专门让 UI 线程来处理 队列中的工作项。当大型操作完成时,可以将结果报告给 UI 线程来显示。
一直以来,Windows 只允许创建 UI 元素的线程访问这些元素。这意味着负责一些长时间运行任务的后台线程无法更新已完成的文本框。Windows 这样做是为了确保 UI 组件的完整性。如果列表框的内容在绘制过程中被后台线程更新,那么该列表框看上去将会很奇怪。
WPF 使用一种内置互斥机制来强制执行这种协调。WPF 中的大多数类都派生自 。 在构造时存储一个对链接到当前运行线程的 的引用。实际上, 与创建它的线程关联。在程序执行过程中, 可以调用它的公共 方法。 检查与当前线程关联的 ,并将它与构造过程中存储的 引用进行比较。如果两者不匹配, 将引发异常。 用于在每个属于 的方法的开头调用。
如果只有一个线程可以修改 UI,那么后台线程如何与用户交互? 后台线程可以请求 UI 线程代表它执行操作,这是通过向 UI 线程的 注册工作项来完成的。 类提供两个注册工作项的方法: 和 。两个方法均调度一个委托来执行。 是同步调用,也就是说,直到 UI 线程实际执行完该委托后才返回。 是异步的,将立即返回。
按优先级对其队列中的元素进行排序。向 队列中添加元素时可指定 10 个级别。这些优先级在 枚举中维护。有关 级别的详细信息可以在 Windows SDK 文档中找到。
操作中的线程:示例
具有长时间运行计算的单线程应用程序
大多数图形用户界面 (GUI) 的大部分空闲时间都是因为等待响应用户交互而生成的事件而造成的。
. 通过仔细地编程,可以建设性地使用这一空闲时间,同时不影响 UI 的响应。WPF 线程模型不允许输入中断在 UI 线程中发生的操作。这意味着您必须定期返回到 来处理挂起的输入事件,以防止它们失效。
请看下面的示例:
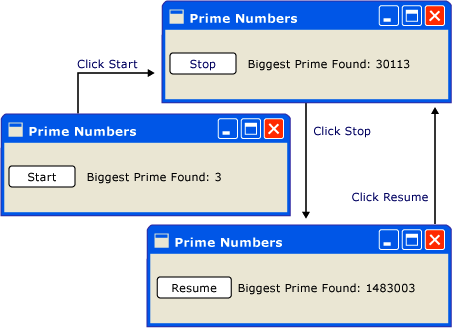
这是一个简单的应用程序,从 3 开始往上数,搜索质数。当用户单击“Start”(开始)按钮时,搜索开始。当程序找到一个质数时,则会用它的搜索结果更新用户界面。用户可以随时停止搜索。
尽管此应用程序非常简单,但质数搜索可以无限地继续下去,这带来了一定的困难。 如果在按钮的 click 事件处理程序中处理整个搜索,UI 线程将永远没有机会处理其他事件。UI 将无法响应输入或处理消息。它永远不会重新绘制,也永远不会响应按钮单击。
我们可以在一个单独的线程中执行质数搜索,但之后需要处理同步问题。使用单线程方法,可以直接更新列出找到的最大质数的标签。
如果将计算任务分成多个易管理的块,就可以定期返回到 来处理事件。可以给 WPF 提供一个机会来重新绘制和处理输入。
在计算与事件处理之间划分处理时间的最佳方法是从 中管理计算。使用 方法,可以在从中提取 UI 事件的同一队列中调度质数检查。在本示例中,一次仅调度一个质数检查。在该质数检查完成后,将立即调度下一次检查。此检查仅在挂起的 UI 事件已处理后才会继续。

Microsoft Word 就是使用这一机制来实现拼写检查。拼写检查是利用 UI 线程的空闲时间在后台执行的。我们来看一看代码。
下面的示例演示创建用户界面的 XAML。
| WPF | |
|---|---|
<Window x:Class="SDKSamples.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Prime Numbers" Width="260" Height="75"
>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" VerticalAlignment="Center" >
<Button Content="Start"
Click="StartOrStop"
Name="startStopButton"
Margin="5,0,5,0"
/>
<TextBlock Margin="10,5,0,0">Biggest Prime Found:</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Name="bigPrime" Margin="4,5,0,0">3</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
|
|
下面的示例演示代码隐藏。
| C# | |
|---|---|
using System; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Threading; using System.Threading; namespace SDKSamples { public partial class Window1 : Window { public delegate void NextPrimeDelegate(); //Current number to check private long num = 3; private bool continueCalculating = false; public Window1() : base() { InitializeComponent(); } public void StartOrStop(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (continueCalculating) { continueCalculating = false; startStopButton.Content = "Resume"; } else { continueCalculating = true; startStopButton.Content = "Stop"; startStopButton.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( DispatcherPriority.Normal, new NextPrimeDelegate(CheckNextNumber)); } } public void CheckNextNumber() { // Reset flag. NotAPrime = false; for (long i = 3; i <= Math.Sqrt(num); i++) { if (num % i == 0) { // Set not a prime flag to ture. NotAPrime = true; break; } } // If a prime number. if (!NotAPrime) { bigPrime.Text = num.ToString(); } num += 2; if (continueCalculating) { startStopButton.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.SystemIdle, new NextPrimeDelegate(this.CheckNextNumber)); } } private bool NotAPrime = false; } } |
|
下面的示例演示 的事件处理程序。
| C# | |
|---|---|
public void StartOrStop(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (continueCalculating) { continueCalculating = false; startStopButton.Content = "Resume"; } else { continueCalculating = true; startStopButton.Content = "Stop"; startStopButton.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( DispatcherPriority.Normal, new NextPrimeDelegate(CheckNextNumber)); } } |
|
除了更新 上的文本外,此处理程序还负责通过向 队列添加委托来调度第一次质数检查。在此事件处理程序完成其工作后的一段时间内, 会选择此委派来执行。
前面已提到, 是用于调度委托来执行的 成员。在这种情况下,选择 优先级。只有当没有重要的事件要处理时, 才执行此委托。UI 响应比数字检查更重要。我们还传递一个表示数字检查例程的新委托。
| C# | |
|---|---|
public void CheckNextNumber() { // Reset flag. NotAPrime = false; for (long i = 3; i <= Math.Sqrt(num); i++) { if (num % i == 0) { // Set not a prime flag to ture. NotAPrime = true; break; } } // If a prime number. if (!NotAPrime) { bigPrime.Text = num.ToString(); } num += 2; if (continueCalculating) { startStopButton.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.SystemIdle, new NextPrimeDelegate(this.CheckNextNumber)); } } private bool NotAPrime = false; |
|
此方法检查下一个奇数是否是质数。如果是质数,此方法将直接更新 bigPrime 来反映搜索结果。由于计算发生在用于创建组件的同一线程中,因此可以执行此操作。如果选择对计算使用单独的线程,则必须使用一种更复杂的同步机制,并在 UI 线程中执行更新。我们将在下面演示这一情况。
有关此示例的完整源代码,请参见 。
用后台线程处理阻止操作
在图形应用程序中处理阻止操作很困难。我们不希望从事件处理程序中调用阻止方法,因为这样应用程序看上去好像已冻结。可以使用一个单独的线程来处理这些操作,但是完成后必须与 UI 线程同步,因为不能从辅助线程直接修改 GUI。可以使用 或 向 UI 线程的 中插入委托。最终,这些委托将以修改 UI 元素的权限来执行。
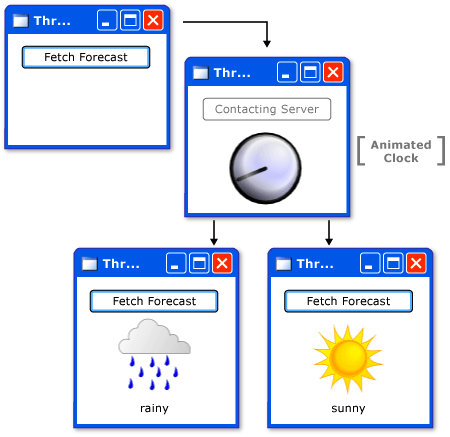
在本示例中,模拟检索天气预报的远程过程调用。使用一个单独的辅助线程来执行此调用,并在完成后在 UI 线程的 中调度一个更新方法。
| C# | |
|---|---|
using System; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Media; using System.Windows.Media.Animation; using System.Windows.Media.Imaging; using System.Windows.Shapes; using System.Windows.Threading; using System.Threading; namespace SDKSamples { public partial class Window1 : Window { // Delegates to be used in placking jobs onto the Dispatcher. private delegate void NoArgDelegate(); private delegate void OneArgDelegate(String arg); // Storyboards for the animations. private Storyboard showClockFaceStoryboard; private Storyboard hideClockFaceStoryboard; private Storyboard showWeatherImageStoryboard; private Storyboard hideWeatherImageStoryboard; public Window1(): base() { InitializeComponent(); } private void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // Load the storyboard resources. showClockFaceStoryboard = (Storyboard)this.Resources["ShowClockFaceStoryboard"]; hideClockFaceStoryboard = (Storyboard)this.Resources["HideClockFaceStoryboard"]; showWeatherImageStoryboard = (Storyboard)this.Resources["ShowWeatherImageStoryboard"]; hideWeatherImageStoryboard = (Storyboard)this.Resources["HideWeatherImageStoryboard"]; } private void ForecastButtonHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // Change the status image and start the rotation animation. fetchButton.IsEnabled = false; fetchButton.Content = "Contacting Server"; weatherText.Text = ""; hideWeatherImageStoryboard.Begin(this); // Start fetching the weather forecast asynchronously. NoArgDelegate fetcher = new NoArgDelegate( this.FetchWeatherFromServer); fetcher.BeginInvoke(null, null); } private void FetchWeatherFromServer() { // Simulate the delay from network access. Thread.Sleep(4000); // Tried and true method for weather forecasting - random numbers. Random rand = new Random(); String weather; if (rand.Next(2) == 0) { weather = "rainy"; } else { weather = "sunny"; } // Schedule the update function in the UI thread. tomorrowsWeather.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Normal, new OneArgDelegate(UpdateUserInterface), weather); } private void UpdateUserInterface(String weather) { //Set the weather image if (weather == "sunny") { weatherIndicatorImage.Source = (ImageSource)this.Resources[ "SunnyImageSource"]; } else if (weather == "rainy") { weatherIndicatorImage.Source = (ImageSource)this.Resources[ "RainingImageSource"]; } //Stop clock animation showClockFaceStoryboard.Stop(this); hideClockFaceStoryboard.Begin(this); //Update UI text fetchButton.IsEnabled = true; fetchButton.Content = "Fetch Forecast"; weatherText.Text = weather; } private void HideClockFaceStoryboard_Completed(object sender, EventArgs args) { showWeatherImageStoryboard.Begin(this); } private void HideWeatherImageStoryboard_Completed(object sender, EventArgs args) { showClockFaceStoryboard.Begin(this, true); } } } |
|
下面给出了一些值得注意的细节。
-
创建按钮处理程序
C# private void ForecastButtonHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // Change the status image and start the rotation animation. fetchButton.IsEnabled = false; fetchButton.Content = "Contacting Server"; weatherText.Text = ""; hideWeatherImageStoryboard.Begin(this); // Start fetching the weather forecast asynchronously. NoArgDelegate fetcher = new NoArgDelegate( this.FetchWeatherFromServer); fetcher.BeginInvoke(null, null); }
当单击按钮时,显示时钟图并开始显示它的动画效果。禁用该按钮,在一个新线程中调用 FetchWeatherFromServer 方法,然后返回,这样 就可以在我们等待收集天气预报时处理事件。
-
获取天气预报
C# private void FetchWeatherFromServer() { // Simulate the delay from network access. Thread.Sleep(4000); // Tried and true method for weather forecasting - random numbers. Random rand = new Random(); String weather; if (rand.Next(2) == 0) { weather = "rainy"; } else { weather = "sunny"; } // Schedule the update function in the UI thread. tomorrowsWeather.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke( System.Windows.Threading.DispatcherPriority.Normal, new OneArgDelegate(UpdateUserInterface), weather); }
为简单起见,此示例中实际没有任何网络代码。通过使新线程休眠四秒钟来模拟网络访问的延迟。此时,原始 UI 线程仍然正在运行并响应事件。为了对此进行演示,我们使一个动画保持运行,并使最小化和最大化按钮也继续工作。
-
更新 UI
C# private void UpdateUserInterface(String weather) { //Set the weather image if (weather == "sunny") { weatherIndicatorImage.Source = (ImageSource)this.Resources[ "SunnyImageSource"]; } else if (weather == "rainy") { weatherIndicatorImage.Source = (ImageSource)this.Resources[ "RainingImageSource"]; } //Stop clock animation showClockFaceStoryboard.Stop(this); hideClockFaceStoryboard.Begin(this); //Update UI text fetchButton.IsEnabled = true; fetchButton.Content = "Fetch Forecast"; weatherText.Text = weather; }
当 UI 线程中的 有时间时,会对 UpdateUserInterface 执行预定调用。此方法停止时钟动画并选择一个图像来描绘天气。它显示此图像并还原“fetch forecast”(获取预报)按钮。
有关此示例的完整源代码,请参见 。
多个窗口,多个线程
一些 WPF 应用程序需要多个高级别窗口。一个线程/ 组合管理多个窗口是完全可接受的,但有时使用多个线程可更出色地完成工作。如果其中一个窗口有可能独占该线程,那么采用多个线程就更有必要。
Windows 资源管理器就是以这种方式工作的。每个新的资源管理器窗口都属于原始进程,但是在独立线程的控制下创建的。
使用 WPF 控件可以显示网页。我们可以轻松地创建一个简单的 Internet Explorer 替代控件。从一个重要的功能开始,即打开新的资源管理器窗口。当用户单击“new window”(新建窗口)按钮时,便在一个单独的线程中启动了窗口的一个副本。这样,一个窗口中的长时间运行或阻止操作就不会锁定其他所有窗口。
事实上,Web 浏览器模型有它自己的复杂线程模型。我们选择它是因为大多数读者对它都很熟悉。
下面的示例演示代码。
| XAML | |
|---|---|
<Window x:Class="SDKSamples.Window1"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MultiBrowse"
Height="600"
Width="800"
Loaded="OnLoaded"
>
<StackPanel Name="Stack" Orientation="Vertical">
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<Button Content="New Window"
Click="NewWindowHandler" />
<TextBox Name="newLocation"
Width="500" />
<Button Content="GO!"
Click="Browse" />
</StackPanel>
<Frame Name="placeHolder"
Width="800"
Height="550"></Frame>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
|
|
| C# | |
|---|---|
using System; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Data; using System.Windows.Threading; using System.Threading; namespace SDKSamples { public partial class Window1 : Window { public Window1() : base() { InitializeComponent(); } private void OnLoaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { placeHolder.Source = new Uri("http://www.msn.com"); } private void Browse(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { placeHolder.Source = new Uri(newLocation.Text); } private void NewWindowHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { Thread newWindowThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadStartingPoint)); newWindowThread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA); newWindowThread.IsBackground = true; newWindowThread.Start(); } private void ThreadStartingPoint() { Window1 tempWindow = new Window1(); tempWindow.Show(); System.Windows.Threading.Dispatcher.Run(); } } } |
|
在本语境中,这些代码中的以下线程片段最有意义:
| C# | |
|---|---|
private void NewWindowHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { Thread newWindowThread = new Thread(new ThreadStart(ThreadStartingPoint)); newWindowThread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA); newWindowThread.IsBackground = true; newWindowThread.Start(); } |
|
当单击“new window”(新建窗口)按钮时,调用此方法。它创建一个新线程并以异步方式启动它。
| C# | |
|---|---|
private void ThreadStartingPoint() { Window1 tempWindow = new Window1(); tempWindow.Show(); System.Windows.Threading.Dispatcher.Run(); } |
|
此方法是新线程的起点。我们在此线程的控制下创建一个新窗口。WPF 自动创建一个新的 来管理新线程。要使此窗口工作,只需启动 。
有关此示例的完整源代码,请参见 。
技术细节和难点
使用线程编写组件
Microsoft .NET Framework Developer's Guide(《Microsoft .NET Framework 开发人员指南》)介绍了组件向客户端公开异步行为的一种模式(请参见 )。例如,假定我们希望将 FetchWeatherFromServer 方法打包到一个可重用的非图形组件中。如果采用标准的 Microsoft .NET Framework 模式,那么代码应与下面类似。
| C# | |
|---|---|
public class WeatherComponent : Component { //gets weather: Synchronous public string GetWeather() { string weather = ""; //predict the weather return weather; } //get weather: Asynchronous public void GetWeatherAsync() { //get the weather } public event GetWeatherCompletedEventHandler GetWeatherCompleted; } public class GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs : AsyncCompletedEventArgs { public GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs(Exception error, bool canceled, object userState, string weather) : base(error, canceled, userState) { _weather = weather; } public string Weather { get { return _weather; } } private string _weather; } public delegate void GetWeatherCompletedEventHandler(object sender, GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs e); |
|
GetWeatherAsync 将使用前面介绍的一种技术(如创建后台线程)来异步执行工作,同时不阻止调用线程。
此模式的最重要部分之一是最初在调用方法名称 Async 方法的线程上调用方法名称 Completed 方法。通过存储 ,您可以使用 WPF 轻松地实现这一点。但是,之后只能在 WPF 应用程序中使用该非图形组件,而不能在 Windows 窗体或 ASP.NET 程序中使用该组件。
类可满足这一需求。可以将该类视为还使用其他 UI 框架的 的简化版本。
| C# | |
|---|---|
public class WeatherComponent2 : Component { public string GetWeather() { return fetchWeatherFromServer(); } private DispatcherSynchronizationContext requestingContext = null; public void GetWeatherAsync() { if (requestingContext != null) throw new InvalidOperationException("This component can only handle 1 async request at a time"); requestingContext = (DispatcherSynchronizationContext)DispatcherSynchronizationContext.Current; NoArgDelegate fetcher = new NoArgDelegate(this.fetchWeatherFromServer); // Launch thread fetcher.BeginInvoke(null, null); } private void RaiseEvent(GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs e) { if (GetWeatherCompleted != null) GetWeatherCompleted(this, e); } private string fetchWeatherFromServer() { // do stuff string weather = ""; GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs e = new GetWeatherCompletedEventArgs(null, false, null, weather); SendOrPostCallback callback = new SendOrPostCallback(DoEvent); requestingContext.Post(callback, e); requestingContext = null; return e.Weather; } private void DoEvent(object e) { //do stuff } public event GetWeatherCompletedEventHandler GetWeatherCompleted; public delegate string NoArgDelegate(); } |
|
嵌套泵
有时完全锁定 UI 线程是不可行的。我们可以考虑 类的 方法。