android SDK提供了Service,用于类似*nix守护进程或者windows的服务。
Service有两种类型:
- 本地服务(Local Service):用于应用程序内部
- 远程服务(Remote Sercie):用于android系统内部的应用程序之间
前者用于实现应用程序自己的一些耗时任务,比如查询升级信息,并不占用应用程序比如Activity所属线程,而是单开线程后台执行,这样用户体验比较好。
后者可被其他应用程序复用,比如天气预报服务,其他应用程序不需要再写这样的服务,调用已有的即可。
编写不需和Activity交互的本地服务示例
本地服务编写比较简单。首先,要创建一个Service类,该类继承android的Service类。这里写了一个计数服务的类,每秒钟为计数器加一。在服务类的内部,还创建了一个线程,用于实现后台执行上述业务逻辑。
Service类:
package com.test;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class CountService extends Service {
public static final String TAG = "CountService";
private boolean threadDisable;
private int count ;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!threadDisable){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
Log.v(TAG , "Count="+count);
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
threadDisable = true;
Log.v(TAG , "onDestroy");
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
}
需要将该服务注册到配置文件AndroidManifest.xml中,否则无法找到:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.test"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="15" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".LocalServiceDemoActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name="CountService"/>
</application>
</manifest>
在Activity中启动和关闭本地服务:
package com.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class LocalServiceDemoActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
startService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
stopService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
}
}
可通过日志查看到后台线程打印的计数内容。
==================================================
编写本地服务和Activity交互的示例
上面的示例是通过startService和stopService启动关闭服务的。适用于服务和activity之间没有交互调用的情况。如果之间需要传递参数或者方法调用。需要使用bind和unbind方法。
具体做法是,服务类需要增加接口,比如ICountService,另外,服务类需要有一个内部类,这样可以方便访问外部类的封装数据,这个内部类需要继承Binder类并实现ICountService接口。还有,就是要实现Service的onBind方法,不能只传回一个null了。
这是新建立的接口代码:
package com.test;
public interface ICountService {
public abstract int getCount();
}
修改后的CountService代码:
package com.test;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class CountService extends Service {
public static final String TAG = "CountService";
private boolean threadDisable;
private int count ;
private ServiceBinder serviceBinder = new ServiceBinder();
public class ServiceBinder extends Binder implements ICountService{
@Override
public int getCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return count;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return serviceBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!threadDisable){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
Log.v(TAG , "Count="+count);
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
threadDisable = true;
Log.v(TAG , "onDestroy");
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
}
服务的注册也要做改动,AndroidManifest.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.test"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="15" />
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".LocalServiceDemoActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!-- <service android:name="CountService"/> -->
<service android:name="CountService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.test.CountService" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
Acitity代码不再通过startSerivce和stopService启动关闭服务,另外,需要通过ServiceConnection的内部类实现来连接Service和Activity。
package com.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class LocalServiceDemoActivity extends Activity {
private ICountService countService;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection(){
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
countService = (ICountService)service;
Log.v(CountService.TAG , "on service connected,count is:"+
countService.getCount());
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
countService = null ;
}
};
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//startService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
this.bindService(new Intent("com.test.CountService"),
this.serviceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Log.v(CountService.TAG , "last onDestroy,count is:"+
countService.getCount());
//stopService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
this.unbindService(serviceConnection);
}
}
编写传递基本型数据的远程服务
上面的示例,可以扩展为,让其他应用程序复用该服务。这样的服务叫远程(remote)服务,实际上是进程间通信(RPC)。
这时需要使用android接口描述语言(AIDL)来定义远程服务的接口,而不是上述那样简单的java接口。扩展名为aidl而不是java。可用上面的ICountService改动而成ICountSerivde.aidl,eclipse会自动生成相关的java文件。
package com.test;
interface ICountService {
int getCount();
}
编写服务(Service)类,稍有差别,主要在binder是通过远程获得的,需要通过桩(Stub)来获取。桩对象是远程对象的本地代理
package com.test;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
public class CountService extends Service {
public static final String TAG = "CountService";
private boolean threadDisable;
private int count ;
private ICountService.Stub serviceBinder = new ICountService.Stub(){
@Override
public int getCount() throws RemoteException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return count;
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return serviceBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!threadDisable){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
Log.v(TAG , "Count="+count);
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
threadDisable = true;
Log.v(TAG , "onDestroy");
}
}
配置文件AndroidManifest.xml和上面的类似,没有区别。
在Activity中使用服务的差别不大,只需要对ServiceConnection中的调用远程服务的方法时,要捕获异常。
package com.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
public class LocalServiceDemoActivity extends Activity {
private ICountService countService;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection(){
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
countService = (ICountService)service;
try {
Log.v(CountService.TAG , "on service connected,count is:"+
countService.getCount());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
countService = null ;
}
};
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//startService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
this.bindService(new Intent("com.test.CountService"),
this.serviceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
try {
Log.v(CountService.TAG , "last onDestroy,count is:"+
countService.getCount());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//stopService(new Intent(this , CountService.class));
this.unbindService(serviceConnection);
}
}
这样就可以在同一个应用程序中使用远程服务的方式和自己定义的服务交互了。
如果是另外的应用程序使用远程服务,需要做的是复制上面的aidl文件和相应的包构到应用程序中,其他调用等都一样。
编写传递复杂数据类型的远程服务
服务的生命周期
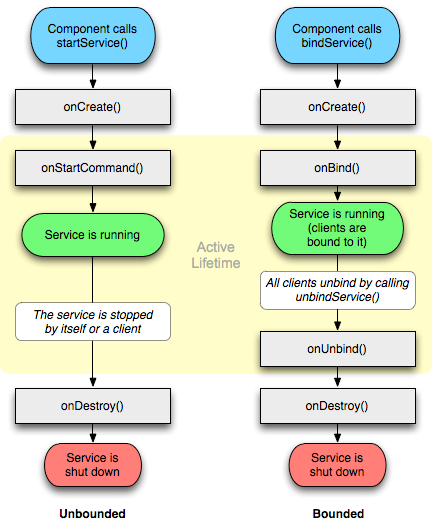
http://marshal.easymorse.com/archives/1564