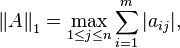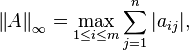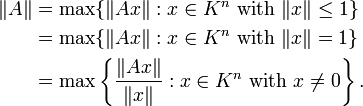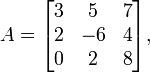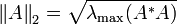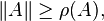Induced
norm
If vector norms on Km and Kn are
given (K is field of real or complex
numbers), then one defines the corresponding induced norm or operator norm on the space
of m-by-n matrices as the following maxima:
-
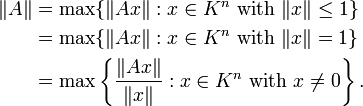
These are different from the entrywise p-norms and the Schatten p-norms for matrices treated below, which are also usually denoted by 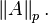
If m = n and one uses the same norm on the domain and the range, then the induced operator norm is a sub-multiplicative matrix norm.
The operator norm corresponding to the p-norm for vectors is:
-

In the case of p = 1 and 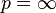 ,
,
the norms can be computed as:
-
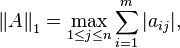 which
which
is simply the maximum absolute column sum of the matrix
-
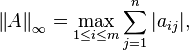 which
which
is simply the maximum absolute row sum of the matrix
For example, if the matrix A is defined by
-
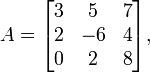
then we have ||A||1 = 7+4+8 = 19. and ||A||∞ =
3+5+7 = 15
In the special case of p = 2 (the Euclidean norm)
and m = n (square matrices), the induced matrix norm is the spectral norm. The spectral norm of a matrix A is the largest singular
value of A or the square root of the largest eigenvalue of the positive-semidefinite
matrix A*A:
-
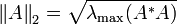
where A* denotes the conjugate
transpose of A.
Any induced norm satisfies the inequality
-
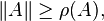
where ρ(A) is the spectral radius of A.
In fact, it turns out that ρ(A) is the infimum of all induced norms of A.
Furthermore, we have the spectral radius formula:
-

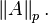
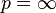 ,
,