1. C语言平面几何1-数据类型的定义
数学中的部分概念在C语言中的定义如下(注:为了与数学一致,有些参数使用了大写):
/* 点 */
typedef struct point
{
double x;
double y;
}Point;
/* 向量 */
typedef Point Vector;
/* 线段AB */
typedef struct segment
{
Point A;
Point B;
}Segment;
/* 直线 * 直线方程一般式:Ax+By+C=0 */
typedef struct line
{
double A;
double B;
double C;
}Line;
/* 三角形ABC */
typedef struct triangle
{
Point A;
Point B;
Point C;
}Triangle; /*
边平行于坐标轴的矩形 */
typedef struct rectangle
{
double xmin;
double ymin;
double xmax;
double ymax;
}Rectangle;
/* MBR:最小包容矩形 */
typedef Rectangle MBR;
/* 圆 */
typedef struct circle
{
Point centre;
double radius;
}Circle
2 C语言平面几何2-距离、长度、模的计算
(1)计算两点之间的距离,或线段的长度
/* 两点之间的距离,线段的长度 */
double DistanceOfPoints(Point A, Point B)
{
return (double)sqrt((A.x-B.x)*(A.x-B.x) + (A.y-B.y)*(A.y-B.y));
}
(2)计算点到直线的距离
/* 点到直线的距离 */
double DistanceOfPointToLine(Point P, Line l)
{
double m = (double)sqrt(l.A * l.A + l.B * l.B);
// 分母
double n = l.A * P.x + l.B * P.y + l.C;
// 分子
if (n < 0)
n = 0 - n;
return n / m;
}
(3)计算向量的模,即向量的长度
/* 向量的模,即向量的长度 */
double VectorLength(Vector v)
{
return (double)sqrt(v.x * v.x + v.y * v.y);
}
3 C语言平面几何3-点是否在线段上
判断点P是否在线段AB上方法很多,这里给出两种。
(1)通过距离判断,点P在线段AB上<=>|AP|+|PB|=|AB|
(2)通过向量叉积判断,点在线段上<=>向量AP×向量AB=0,并且点P坐标在AB坐标之间

C语言代码如下:
/* 点是否在线段上: 距离判断 */
int PointIsOnSegment(Point P, Point A, Point B)
{
double d1 = DistanceOfPoints(P, A);
double d2 = DistanceOfPoints(P, B);
double d3 = DistanceOfPoints(A, B);
if (d1 + d2 == d3)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* 点是否在线段上: 向量判断 */
int PointIsOnSegment(Point P, Point A, Point B)
{
Vector AP = VectorConstruct(P, P);
Vector AB = VectorConstruct(A, B);
// 两向量不平行
if (CrossProduct(AP, AB) == 0 && P.x >= Min(A.x, B.x) && P.x <= Max(A.x, B.x) && P.y >= Min(A.y, B.y) && P.y <= Max(A.y, B.y))
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
/* * 由两个点构造一个向量 */
Vector VectorConstruct(Point A, Point B)
{
Vector v; v.x = B.x - A.x; v.y = B.y - A.y;
return v;
}
// 向量的叉积
double CrossProduct(Vector a, Vector b)
{
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
4 C语言平面几何4-两线段是否相交
判断两线段是否相交:
方法(1):快速排斥(两个MBR是否有交集)+跨立(一个线段的两个端点在另一线段的两端)。
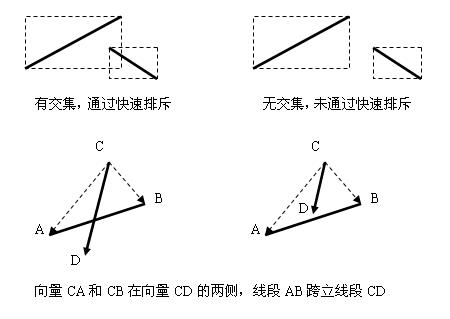
给出C语言代码如下:
/* * 由两个点构造一个向量 */
Vector VectorConstruct(Point A, Point B)
{
Vector v; v.x = B.x - A.x; v.y = B.y - A.y;
return v;
}
// 向量的叉积
double CrossProduct(Vector a, Vector b)
{
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
/* * 由两个点构造一个MBR */
MBR MbrConstruct(Point A, Point B)
{
MBR m;
if (A.x > B.x)
{
m.xmax = A.x;
m.xmin = B.x;
}
else
{
m.xmax = B.x;
m.xmin = A.x;
}
if (A.y > B.y)
{
m.ymax = A.y;
m.ymin = B.y;
}
else
{
m.ymax = B.y;
m.ymin = A.y;
}
return m;
}
/* * 判断两个MBR是否有交集,有返回1,否0 */
int MbrOverlap(MBR m1, MBR m2)
{
double xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax;
xmin = Max(m1.xmin, m2.xmin);
xmax = Min(m1.xmax, m2.xmax);
ymin = Max(m1.ymin, m2.ymin);
ymax = Min(m1.ymax, m2.ymax);
return (xmax >= xmin && ymax >= ymin) ? 1 : 0;
}
/* * 判断两线段(线段AB和CD)是否相交,是返回1,否0 * 快速排斥+跨立 */
int SegmentIntersection(Point A, Point B, Point C, Point D)
{
// (1)判断AB和CD所在的MBR是否相交
MBR m1 = MbrConstruct(A, B);
MBR m2 = MbrConstruct(C, D);
if (MbrOverlap(m1, m2) == 0)
return 0;
// (2)跨立判断
Vector CA = VectorConstruct(C, A);
Vector CB = VectorConstruct(C, B);
Vector CD = VectorConstruct(C, D);
Vector AC = VectorConstruct(A, C);
Vector AD = VectorConstruct(A, D);
Vector AB = VectorConstruct(A, B);
// AB跨立CD,并且,CD跨立AB
if (CrossProduct(CD, CA) * CrossProduct(CD, CB) <= 0 && CrossProduct(AC, AB) * CrossProduct(AD, AB) <= 0)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
方法(2):判断是否为凸多边形。凸多边形的判断是,当从某个点开始绕一周,要么全顺时针拐弯,要么全逆时针
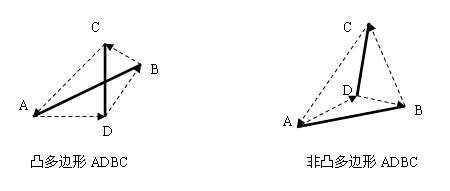
/* * 判断两线段(线段AB和CD)是否相交,是返回1,否0 * 判断四边形ACBD是否是一个凸四边形 */
int SegmentIntersection(Point A, Point B, Point C, Point D)
{
Vector AC = VectorConstruct(A, C);
Vector CB = VectorConstruct(C, B);
Vector BD = VectorConstruct(B, D);
Vector DA = VectorConstruct(D, A);
double c[4];
c[0] = CrossProduct(AC, CB);
c[1] = CrossProduct(CB, BD);
c[2] = CrossProduct(BD, DA);
c[3] = CrossProduct(DA, AC);
int f1=0, f2=0;
// 计算正数,负数的个数
int i;
for (i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if (c[i] > 0)
f1++;
if (c[i] < 0)
f2++;
}
if (f1 > 0 && f2 > 0)
// 有正,有负,返回无交集
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
5 C语言平面几何5-两点确定一条直线
/* 两个不同点A,B确定一条直线,AB相同返回的值全0 * 直线方程:Ax+By+c=0 * A = y2 - y1; * B = x1 - x2; * C = -A*x1 - B*y1 = x2*y1 - x1*y2; */
Line LineMake(Point A, Point B)
{
Line l;
l.A = B.y - A.y;
l.B = A.x - B.x;
l.C = B.x * A.y - A.x * B.y;
return l;
}
6 C语言平面几何6-判断线段是否与矩形范围有交及
判断线段AB是否与矩形范围有交集
这里的矩形指的是边与坐标轴平行的矩形,可用x和y上最大最小值表示。
判断是否相交,先快速排斥,再做跨立,通过向量的叉积判断矩形的四个顶点是否在线段的两侧,是说明有交集。
(如果判断与矩形的边是否有交集的话,可判断线段是否与矩形的每条边是否有交集,线段与线段的交集判断。)
这里在介绍另外一种方法,降维的方法:
例如,有线段AB和矩形MN,如图所示:
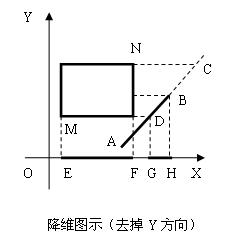
通过M和N点的y坐标计算直线AB上的D和C点,B和C点中取y值小的点B,A和D点中取y值大的点D,
最后确定了线段BD在x轴上的投影GH,矩形在x轴上的投影EF,判断EF和GH是否有交集。
C语言代码如下:
/* * 判断区间[x1, x2]和区间[x3, x4](x4可能小于x3)是否有交集,有返回1,无0 */
int IntervalOverlap(double x1, double x2, double x3, double x4)
{
double t;
if (x3 > x4)
{
t = x3;
x3 = x4;
x4 = t;
}
if (x3 > x2 || x4 < x1)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
/* * 判断矩形r和线段AB是否有交集,有返回1,无0 */
int RSIntersection(Rectangle r, Point A, Point B)
{
if (A.y == B.y)
// 线段平行于x轴
{
if (A.y <= r.ymax && A.y >= r.ymin)
{
return IntervalOverlap(r.xmin, r.xmax, A.x, B.x);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
// AB两点交换,让B点的y坐标最大
Point t;
if (A.y > B.y)
{
t = A;
A = B;
B = t;
}
// 在线段AB上确定点C和D
// 两点确定一条直线: (x-x1)/(x2-x1)=(y-y1)/(y2-y1)
double k = (B.x - A.x)/(B.y - A.y);
Point C, D;
if (A.y < r.ymin)
{
C.y = r.ymin;
C.x = k * (C.y - A.y) + A.x;
}
else
C = A;
if (B.y > r.ymax)
{
D.y = r.ymax;
D.x = k * (D.y - A.y) + A.x;
}
else
D = B;
if (D.y >= C.y) // y维上有交集
{
return IntervalOverlap(r.xmin, r.xmax, D.x, C.x);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
7 C语言平面几何7-直线与圆的位置关系
直线与圆的位置关系有3种:
1,相离,有0个交点
2,相切,只有1个交点
3,相交,有2个交点
C语言代码如下:
// 直线与圆的位置关系:0-相离,1-相切,2-相交
int LineAndCircle(Line l, Circle c)
{
double d = DistanceOfPointToLine(c.centre, l);
double r = c.radius;
if (dequals(d, r)) // 相切,交点为1
return 1;
else if (d > r) // 相离,交点为0
return 0;
else // 相交,交点为2
return 2;
}
类似的,点与圆的位置关系有:圆外,圆上,圆内
// 点与圆的位置关系:(-1)-圆外,0-圆上,1-圆内
int PointAndCircle(Point A, Circle c)
{
double d = DistanceOfPoints(A, c.centre);
double r = c.radius;
if (dequals(d, r))
return 0;
else if (d > r)
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
8 C语言平面几何8-两直线的位置关系
平面中,两直线不相交就平行,相交中又分垂直相交和非垂直相交,两直线重合可认为是特殊的平行。
C语言代码如下:
/* 两直线的关系 * 平面中,两直线不相交就平行 */
TwoLines(Line m, Line n)
{ // 平行:A1/B1 = A2/B2
if (m.A * n.B == m.B * n.A)
{
// 两直线斜率相同
if (m.C * n.B == m.B * n.C)
return 1;
// 重合
else
return 2;
// 平行
}
// 相交
else
{
if (m.A * n.A + m.B * n.B == 0) // 垂直充要条件:A1*A2 + B1*B2 = 0
return 3;
// 垂直相交
else
return 4;
// 相交
}
}