MiYu原创, 转帖请注明 : 转载自 ______________白白の屋 ![]()
拷贝构造函数和重载的赋值操作符)
三.必须包含的头文件#include <vector>
capacity返回vector能容纳的元素最大数量。如果插入元素时,元素个数超过capacity,
需要重新配置内部存储器。
->构造、拷贝和析构

->非变动操作
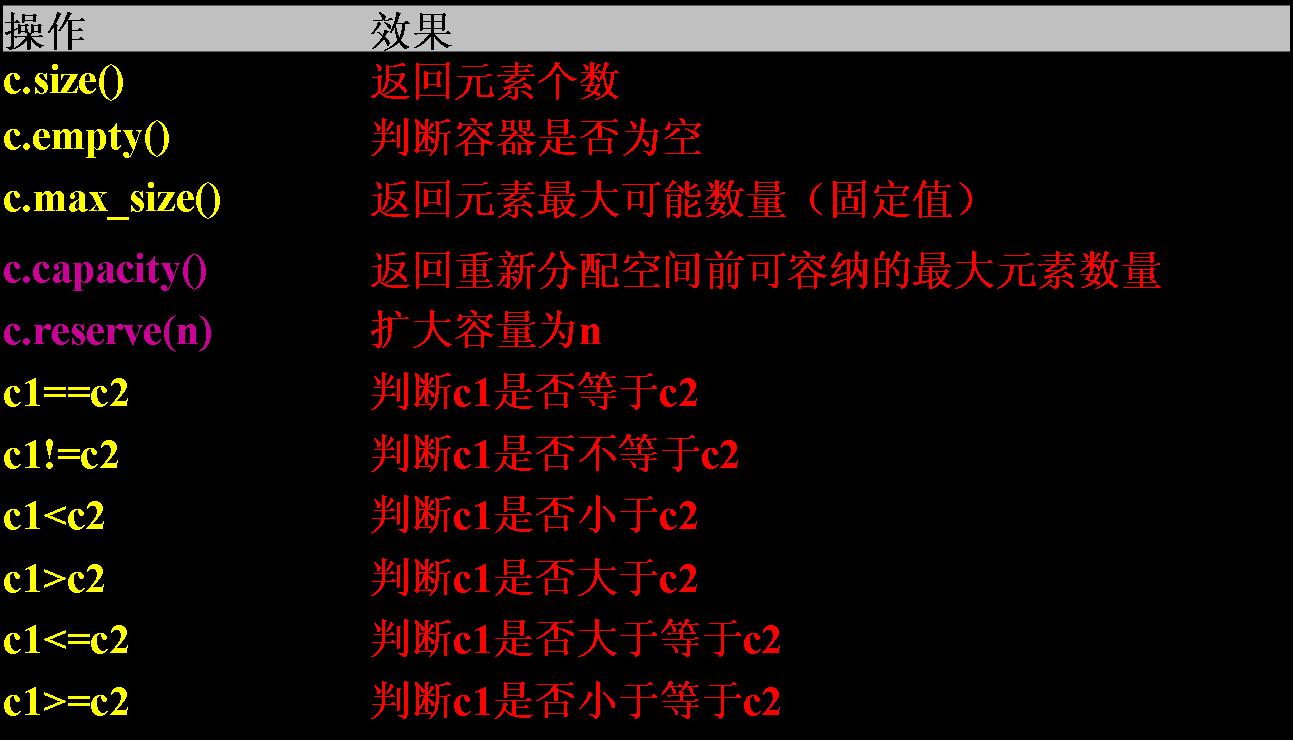
eg.
vector<int> v1(10); cout << "The capacity of v1 is " << v1.capacity() << endl; cout << "The size of v1 is " << v1.size() << endl; vector<int> v2; v2.reserve(20); cout << "The capacity of v2 is " << v2.capacity() << endl; cout << "The size of v2 is " << v2.size() << endl;
output :
The capacity of v1 is 10
The size of v1 is 10
The capacity of v2 is 20
The size of v2 is 0
->赋值操作

所有的赋值操作都有可能调用元素类型的默认构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值操作符和析构函数
如:
eg.
vector<int> v; v.assign( 10, 42 ); for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v.size(); i++ ) { cout << v[i] << " "; } cout << endl;
OutPut :
42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
vector<int> v1;
for( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) {
v1.push_back( i );
}
vector<int> v2;
v2.assign( v1.begin(), v1.end() );
for( vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++ ) {
cout << v2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
output :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
元素存取

下面的操作是错误的:
std::vector<T> v;//empty
eg.
string str;
while( cin >> str ) words.push_back(str);
sort( words.begin(