题目大意:给你一个N*M 的矩阵, 矩阵里的每个点代表一个全送阵, 代表当前点可以全送到4个点,你的出发点是(1,1);要到达的点是(n,m),这里要注意的是,一旦任何点到了(n,m)点之后 就会被全送出去,离开整个地图,所以这里算是一个陷阱,您要把(n,m)点能够到达的点,全部置0,(”0“代表他不能到达某个点)
题目分析:
这里是Maxtrix67 大牛总结的 第八个矩阵的经典应用:
给定一个有向图,问从A点恰好走k步(允许重复经过边)到达B点的方案数mod p的值
把 给定的图转为邻接矩阵,即A(i,j)=1当且仅当存在一条边i->j。令C=A*A,那么C(i,j)=ΣA(i,k)*A(k,j),实际上就 等于从点i到点j恰好经过2条边的路径数(枚举k为中转点)。类似地,C*A的第i行第j列就表示从i到j经过3条边的路径数。同理,如果要求经过k步的
路径数,我们只需要二分求出A^k即可;
题目让我们求的是他们是否连通,这里只需用1与0带入即可,
我们这里在乘的过程不是求和,而是用到“与”操作,因为我们要得出的结果不是路径数,而是 是否能经过K步到达该点~
代码+部分注释:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>usingnamespacestruct int30][30];};structintstruct struct for(int1;i<=n;i++) for(int1;j<=n;j++){ c.s[i][j]=0; for(int1;k<=n;k++) //:注意下面这个操作,是“|”而不是“+”这里是求是否能到达 //而不是求 c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]|a.s[i][k]*b.s[k][j]); } return}structint struct struct while(t){ if(t%2==1) ans=multiply(ans,b); b=multiply(b,b); t/=2; } return}int struct memset(unit.s,0,sizeof(unit.s)); char100]; int10]; for(int1;i<=30;i++) unit.s[i][i]=1; int int scanf("%d",&cas); while(cas--){ memset(a.s,0,sizeof(a.s)); scanf("%d,&h,&z); n=h*z; for(i=1;i<=h;i++) for(j=1;j<=z;j++){ scanf("%s",str); sscanf(str,"((%d,%d),(%d,%d),(%d,%d),(%d,%d))",&num[1],&num[2],&num[3],&num[4],&num[5],&num[6],&num[7],&num[8]); s=(i-1)*z+j; for(k=1;k<=8;k+=2){ e=(num[k]-1)*z+num[k+1]; a.s[s][e]=1; } } //:转换成邻接矩阵后,a.s[n][]就是 //代表原来地图里的[n][m]点与其他点的链接状态 //因为题意说,凡是到了[n][m]点之后,就会马上 //全送出去,离开这个地图,所以我们要把[n][m]到其他点的 //状态值都赋为0! for(i=1;i<=n;i++) a.s[n][i]=0; scanf("%d",&p); while(p--){ scanf("%d",&t); struct if(c.s[1][n]==0) printf("False\n"); else{ int for(x=1;x<=n;x++){ if(c.s[1][x]==1) break; } if(n==x) printf("True\n"); else printf("Maybe\n"); } } printf("\n"); }} |
题目:已知 F(n)=3 * F(n-1)+2 * F(n-2)+7 * F(n-3),n>=3,其中F(0)=1,F(1)=3,F(2)=5,对于给定的每个n,输出F(0)+ F(1)+ …… + F(n) mod 2009。
题目分析:这里我们推出S[N]=S[N-1]+F[N];
F[N]=3*F[N-1] +2*F[N-2] +7*F[N-3];
首先我们要知道这点,我们这里在第推计算 F[n]的同时,也要计算出 S[N];
所以您要构造出一个矩阵 把S[N] F[N] 同时收录计算,在这里我构造的矩阵 如下:
由于第一写了很多,完成文章的时候莫名其妙的 成了空白,所以第二次 我没上次那么仔细分析了
您有不懂的 或者指点的地方 请留言 我立即修正 或者给您答疑:
模拟计算过程的矩阵;
1 3 2 7
0 3 2 7
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0
初始状态的矩阵:
9 0 0 0
5 0 0 0
3 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
还有构造一个单位矩阵 unit用来 二分计算 {^_^}
代码+部分注释:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>usingnamespacestruct int5][5];};structstruct struct for(int1;i<=4;i++) for(int1;j<=4;j++){ c.s[i][j]=0; for(int1;k<=4;k++) c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]+(a.s[i][k]*b.s[k][j])%2009)%2009; } return}structint struct struct struct while(t){ if(t%2==1) ans=multiply(ans,a); a=multiply(a,a); t/=2; } b=multiply(ans,b); return}int int5]; f[1]=1;2]=3;3]=5; f[4]=28; memset(unit.s,0,sizeof(unit.s)); memset(res.s,0,sizeof(res.s)); memset(tempt.s,0,sizeof(tempt.s)); for(int1;i<=4;i++) unit.s[i][i]=1; tempt.s[1][1]=1; 1][2]=3; tempt.s[1][3]=2; 1][4]=7; tempt.s[2][2]=3; 2][3]=2; tempt.s[2][4]=7; 3][2]=1; tempt.s[4][3]=1; res.s[1][1]=9; 2][1]=5; res.s[3][1]=3; 4][1]=1; int scanf("%d",&cas); for(k=1;k<=cas;k++){ scanf("%d",&t); t++; if(t<=3){ int0; for(int1;i<=t;i++) sum+=f[i]; printf("Case,k,sum); continue; } struct3); printf("Case,k,c.s[1][1]); } return;} |
题目分析: 首先题目大意是,有n个小孩,初始时每个人有ai个苹果。现在要进行m轮游戏。每进行一轮游戏,第i个小孩的苹果增加
( R*A(i+n-1)%n+L*A(i+1)%n )个,求进行m轮游戏后,每个小孩有多少个苹果。(0<=m<=10^9,结果模M后输出,1<=M<=10^6)!注意原题目的公式是错的,害的我郁闷了好久~真的 faint!
思路分析:
这些都属于 循环同构的矩阵 计算的一个巧妙的算法就是,只算第一行,然后接下来的只要平移一个单位到下面,然后复制!
做这种题目还是要首先构造出一个矩阵 模拟他的递归过程!
我这里构造的矩阵是:
1 L .... R
R 1 L.. 0
0 R 1 L..0
L..... 0 R 1
然后递归多少次,我只要把这个矩阵乘多少次就可以了,这样做的高效远远优于递归的!
代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>usingnamespacestruct int101][101];};intstruct//计算矩阵的幂的时候,因为我要计算的矩阵是//所以只需要计算第一行,其他的N-1行只需要帮他上面一行的//结果平移一个单位,然后再复制下来就OK啦!struct struct int for(i=1;i<=1;i++) for(j=1;j<=n;j++){ c.s[i][j]=0; for(k=1;k<=n;k++){ if(a.s[i][k]&&b.s[k][j]) c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]+(a.s[i][k]*b.s[k][j])%p)%p; } } for(i=2;i<=n;i++){ c.s[i][1]=c.s[i-1][n]; for(j=2;j<=n;j++) c.s[i][j]=c.s[i-1][j-1]; } return}struct struct int for(i=1;i<=n;i++) for(j=1;j<=1;j++){ c.s[i][j]=0; for(k=1;k<=n;k++){ if(a.s[i][k]&&b.s[k][j]) c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]+(a.s[i][k]*b.s[k][j])%p)%p; } } return}void struct int struct while(t){ if(t%2==1) ans=multiply(ans,a); a=multiply(a,a); t/=2; } res=multiply2(ans,res);}int int int102]; memset(unit.s,0,sizeof(unit.s)); for(i=1;i<=100;i++) unit.s[i][i]=1; cin>>cas; while(cas--){ memset(res.s,0,sizeof(res.s)); memset(tempt.s,0,sizeof(tempt.s)); scanf("%d,&n,&t,&r,&l,&p); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",∼[i]); for(j=1,i=n;i>=1;j++,i--){ res.s[j][1]=sim[i]; } tempt.s[1][1]=1; 1][2]=l; tempt.s[1][n]=r; for(i=2;i<=n;i++){ tempt.s[i][1]=tempt.s[i-1][n]; for(j=2;j<=n;j++) tempt.s[i][j]=tempt.s[i-1][j-1]; } paw(); for(i=n;i>1;i--) printf("%d,res.s[i][1]); printf("%d",res.s[i][1]); printf("\n\n"); }} |
题目大意:题目大意给定一系列灯的初始状态,0代表暗,1代表亮,每一秒所有的灯都有可能发生状态切换,
切换规则:当前灯的左边第一个灯是亮的,则当前的灯切换状态,如果当前灯的左边第一盏灯是暗的,则当前灯的状态无需变化!
注意:最左边的参考左右边那栈灯。
题目分析;
首先有两种情况:
左边第一盏灯亮的:
当前灯的动作: 1->0; 0->1;
左边第一盏灯暗的:
当前灯的动作:
1->1; 0->0;
我们可以看到的是, 可以用一个方程来模拟这个过程: F[i] = ( f [ i] +f [i+n-2]%n+1 )%2;
所以我们只要计算这个值就OK啦。
然后由于数据过大,开数组肯定会爆掉~
这里我们要想到的是 矩阵是一个模拟递归的高效算法
这里我们要构造一个 可以计算如上的方程的矩阵:
1 0 0...0 1
1 1 0...0 0
0 1 1..0 0
0 0 1..0 0
. . . 0 ....
. . .0.....
0 0 0..0 1
然后再把f[n]...到f[1]构成一个矩阵和他相乘,正好就是达到了表达式的效果。如果还有不懂的那请您留言,我这里画图不方便悲剧的很
代码+部分注释:
题目分析:
If x < 10 f(x) = x.
If x >= 10 f(x) = a0 * f(x-1) + a1 * f(x-2) + a2 * f(x-3) + …… + a9 * f(x-10);
And ai(0<=i<=9) can only be 0 or 1 .
Now, I will give a0 ~ a9 and two positive integers k and m ,and could you help Lele to caculate f(k)%m.
In each case, there will be two lines.
In the first line , there are two positive integers k and m. ( k<2*10^9 , m < 10^5 )
In the second line , there are ten integers represent a0 ~ a9.
这里就是构造一下矩阵 然后依然是矩阵的多次幂 我前面说的很详细,如果看的不清楚可以看我别的文章
构造一个矩阵

就求a^(t-9)*b
代码:
题目分析:Tr A表示方阵A的迹(主对角线元素之和),求Tr(Ak) % 9973。
由于k最大有10^9,所以只能用矩阵二分快速幂得到Ak,最后求和即可。
代码:
题目大意:
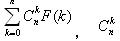 这个是组合数,然后求给定N,P让你求
这个是组合数,然后求给定N,P让你求![$$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$ $$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$](http://xuyemin520.is-programmer.com/user_files/xuyemin520/epics/44f232ccb26e95b71fedea0811c888c3e173dbc3.png) mod
mod
p的值是多少
题目分析:
第一种方法:这里我引用一种常见的母函数:
(a+1)^n=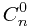 +
+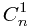 *a^1+
*a^1+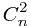 *a^2+....+
*a^2+....+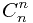 *a^n;
*a^n;
这里我可以知道fibonacci数可以用mitrax=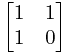 的乘积表示,f[i]=mitrax^i;
的乘积表示,f[i]=mitrax^i;
这里我们的“1”可以用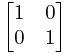 表示
表示
即单位矩阵,这样我们只要求两个矩阵的的 i 次幂就可以了,这就直接转换到矩阵的二分法求快速幂上来了!注意一点,最后输出的[1][2]这个位置的数,别输出错了!
第二种方法:
![$$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$ $$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$](http://xuyemin520.is-programmer.com/user_files/xuyemin520/epics/44f232ccb26e95b71fedea0811c888c3e173dbc3.png) 最后证明结论等于:
最后证明结论等于:![$$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$ $$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$](http://xuyemin520.is-programmer.com/user_files/xuyemin520/epics/44f232ccb26e95b71fedea0811c888c3e173dbc3.png) =
=
F[ 2* N ]
引进fibonacci数的计算方程:
![$$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$ $$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$](http://xuyemin520.is-programmer.com/user_files/xuyemin520/epics/44f232ccb26e95b71fedea0811c888c3e173dbc3.png) ={
={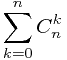 *(
*(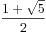 )^k
)^k
-(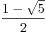 )^k}
)^k}
因为:
(a+1)^n=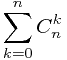 *a^k;
*a^k;
所以将上式化简成:
![$$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$ $$\sum_{k=0}^{n}{C_n^k}{f[k]}$$](http://xuyemin520.is-programmer.com/user_files/xuyemin520/epics/44f232ccb26e95b71fedea0811c888c3e173dbc3.png) =(
=(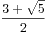 )^n+(
)^n+(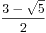 )^n
)^n
分子分母都乘*2 =(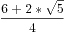 )^n+(
)^n+(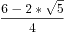 )^n
)^n
=(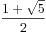 )^2n+(
)^2n+(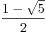 )^2n
)^2n
=F[ 2*N ]
我的代码是第一种的:
文章总结:(a+1)^n=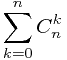 *a^k;这个母函数很好用
*a^k;这个母函数很好用
下次记得灵活运用!
题目大意:求
Fibonacci Numbers如果位数低于8位,则全部输出,否则只输出
前4位与后4位(注意后四位的0别忘记了,不过是什么格式,哪怕
0000都要输出);
题目分析:这里我们上一篇文章以前具体阐述了:
给定矩阵A,请快速计算出A^n(n个A相乘)的结果,输出的每个数都mod p。
由 于矩阵乘法具有结合律,因此A^4 = A * A * A * A = (A*A) * (A*A) = A^2 * A^2。我们可以得到这样的结论:当n为偶数时,A^n = A^(n/2) * A^(n/2);当n为奇数时,A^n = A^(n/2) * A^(n/2) * A (其中n/2取整)。这就告诉我们,计算A^n也可以使用二分快速求幂的方法。例如,为了算出A^25的值,我们只需要递归地计算出A^12、A^6、 A^3的值即可。根据这里的一些结果,我们可以在计算过程中不断取模,避免高精度运算。
然后我们以前有一篇文章已经阐述了,如果利用取对数求第N个fibonacci数的前4位有效数字;如果不清楚的话 请看我以前的一篇文章
“HDU 1568(非常经典微妙的 斐波纳契计算)“
代码:
”
题目分析:
经典题目6 给定n和p,求第n个Fibonacci数mod p的值,n不超过2^31
根 据前面的一些思路,现在我们需要构造一个2 x 2的矩阵,使得它乘以(a,b)得到的结果是(b,a+b)。每多乘一次这个矩阵,这两个数就会多迭代一次。那么,我们把这个2 x 2的矩阵自乘n次,再乘以(0,1)就可以得到第n个Fibonacci数了。不用多想,这个2 x 2的矩阵很容易构造出来:
但是我这里稍微有点区别的是,我是构造: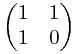
其实这里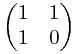 *
*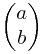 =
=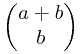
为了计算直观我把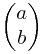 写成
写成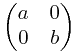 都一样的
都一样的
其实 呵呵
这里我们的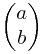 =
=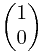
然后我们用二分的方法求矩阵的快速幂!
这里建议大家用结构体传递矩阵 这样很好用的!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
#include<iostream>#include<cstring>#include<cstdio>usingnamespacestruct int5][5];};int10000;struct struct memset(c.s,0,sizeof(c.s)); for(int1;i<=2;i++) for(int1;j<=2;j++) for(int1;k<=2;k++) c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]+ return}structint if(t==1) return else{ struct2); if(t&1){ return } else{ return } }}int int struct a.s[1][1]=a.s[1][2]=a.s[2][1]=1; a.s[2][2]=0; d.s[1][1]=1; d.s[1][2]=0; d.s[2][1]=0; d.s[2][2]=1; while(scanf("%d",&n),n!=-1){ if(n==0){ printf("0\n"); continue; } if(n==1||n==2){ printf("1\n"); continue; } struct1); struct printf("%d\n",b.s[1][1]); }} |
题目分析:
S = A + A2 + A3 + … + Ak.
求 S mod p;
我们要二分考虑
二分求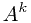 mod
mod
p
首先把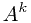 转化成:
转化成:
1) 如果k是偶数 ( 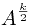 mod
mod
p ) * ( 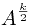 mod
mod
p )这样就把就达到了降幂的作用
2)如果k是奇数 ( 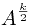 mod
mod
p ) * ( 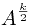 mod
mod
p )* ( A mod p)
然后再对求和的过程进行二分!
如果K是偶数我们把公式转换成 S=A + A2 + A3 + … + 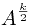 +
+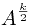 *(A + A2 + A3 +
*(A + A2 + A3 +
… + 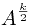 )
)
如果K是奇数 则可以写成: S=A + A2 + A3 + … + 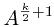 +
+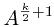 *(A + A2 + A3 +
*(A + A2 + A3 +
… + 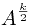 )
)
代码+部分注释:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
#include<iostream>#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>usingnamespacestruct int32][32];};intstruct int struct memset(c.s,0,sizeof(c.s)); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) for(j=1;j<=n;j++) c.s[i][j]=(a.s[i][j]+b.s[i][j])%p; return}struct int struct memset(c.s,0,sizeof(c.s)); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) for(j=1;j<=n;j++) for(k=1;k<=n;k++) c.s[i][j]=(c.s[i][j]+(a.s[i][k]*b.s[k][j])%p)%p; return}structint struct memset(b.s,0,sizeof(b.s)); if(t==0){ for(int1;i<=n;i++) b.s[i][i]=1; return } else{ struct2); if(t&1){ return } else return }}structint if(t==1){ return } else{ struct2); if(t&1){ struct2+1); return } else{ return2))); } }}int int struct cin>>n>>k>>p; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) for(j=1;j<=n;j++){ scanf("%d",&a.s[i][j]); a.s[i][j]%=p; } struct for(i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(j=1;j<n;j++){ cout<<tempt.s[i][j]<<"; } printf("%d\n",tempt.s[i][j]); } return;} |