Aim: Find oˆ such that
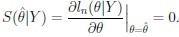
Problem: Analytic solution of likelihood equations not always available.
Example: Censored exponentially distributed observations
Suppose that 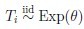 and that the censored times
and that the censored times
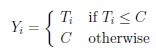
are observed. Let m be the number of uncensored observations. Then
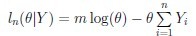
with first and second derivative

Thus we obtain for the observed and expected information
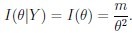
Thus the MLE can be obtained be the Newton-Raphson iteration
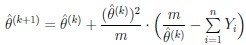
Numerical example: Choose starting value in (0, 1)
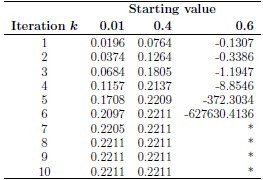
Implementation in R:
#Statistics 24600 - Spring 2004
#Instructor: Michael Eichler
#
#Method : Newton-Raphson method
#Example: Exponential distribution
#----------------------------------
#Log-likelihood with first and second derivative
ln<-function(p,Y,R) {
m<-sum(R==1)
ln<-m*log(p)-p*sum(Y)
attr(ln,"gradient")<-m/p-sum(Y)
attr(ln,"hessian")<--m/p^2
ln
}
#Newton-Raphson method
newmle<-function(p,ln) {
l<-ln(p)
pnew<-p-attr(l,"gradient")/attr(l,"hessian")
pnew
}
#Simulate censored exponentially distributed data
Y<-rexp(10,1/5)
R<-ifelse(Y>10,0,1)
Y[R==0]=10
#Plot first derivative of the log-likelihood
x<-seq(0.05,0.6,0.01)
plot(x,attr(ln(x,Y,R),"gradient"),type="l",
xlab=expression(theta),ylab="Score function")
abline(0,0)
#Apply Newton-Raphson iteration 3 times
p<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)
p
p<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)
p
p<-newmle(p,ln,Y=Y,R=R)
p