
然后Rank和为(p1[i]+p2[i])*(n-1)! + ... + (p1[n]+p2[n])*0! = p3[1]*(n-1)! + ... + p3[n]*0! ,但是得出的表达式可能不是规整的形式,这是我们需要检测一边,从后往前扫,如果p3[i] >= (n-i+1), 说明第 i 项已经超过 (n-i+1)*(n-i), 那么就应进位到(n-i+1)!,
即p3[i-1]+=1,依此类推。
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let's define the sum of two permutations p andq of numbers
0, 1, ..., (n - 1) as permutation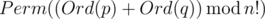 , wherePerm(x)
, wherePerm(x)
is the x-th lexicographically permutation of numbers
0, 1, ..., (n - 1) (counting from zero), and
Ord(p) is the number of permutation
p in the lexicographical order.
For example, Perm(0) = (0, 1, ..., n - 2, n - 1),Perm(n! - 1) = (n - 1, n - 2, ..., 1, 0)
Misha has two permutations, p and
q. Your task is to find their sum.
Permutation a = (a0, a1, ..., an - 1) is called to be lexicographically smaller than permutationb = (b0, b1, ..., bn - 1),
if for somek following conditions hold:
a0 = b0, a1 = b1, ..., ak - 1 = bk - 1, ak < bk.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000).
The second line contains n distinct integers from0 to
n - 1, separated by a space, forming permutationp.
The third line contains n distinct integers from0 to
n - 1, separated by spaces, forming permutationq.
Print n distinct integers from
0 to n - 1, forming the sum of the given permutations. Separate the numbers by spaces.
2 0 1 0 1
0 1
2 0 1 1 0
1 0
3 1 2 0 2 1 0
1 0 2
Permutations of numbers from 0 to 1 in the lexicographical order:
(0, 1), (1, 0).
In the first sample Ord(p) = 0 andOrd(q) = 0, so the answer is
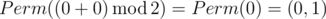 .
.
In the second sample Ord(p) = 0 andOrd(q) = 1, so the answer is
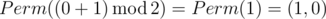 .
.
Permutations of numbers from 0 to 2 in the lexicographical order:
(0, 1, 2), (0, 2, 1), (1, 0, 2), (1, 2, 0), (2, 0, 1), (2, 1, 0).
In the third sample Ord(p) = 3 andOrd(q) = 5, so the answer is
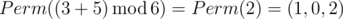 .
.
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int bit[200010],n;
void update(int x,int val)
{
for(int i=x;i<=n;i+=i&-i)
bit[i]+=val;
}
int psum(int x)
{
int sum=0;
for(int i=x;i>0;i-=i&-i)
sum+=bit[i];
return sum;
}
int p[200010],a[200010];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
update(i,1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>p[i];
a[i]=psum(p[i]);
update(p[i]+1,-1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
update(i,1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>p[i];
a[i]+=psum(p[i]);
update(p[i]+1,-1);
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(i)
a[i-1]+=a[i]/(n-i);
a[i]%=n-i;
}
memset(bit,0,sizeof(bit));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
update(i,1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int l=1,r=n;
while(l<=r)
{
int m=(l+r)>>1;
if(psum(m)-1<a[i])
l=m+1;
else
r=m-1;
}
if(i)
cout<<" ";
cout<<l-1;
update(l,-1);
}
}