- IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
- 继续看下getService方法,在getService中对数据进行了序列化封装,并通过BinderProxy的native方法向ServiceManager发送请求,获取Binder的代理对象。看下getService代码:
- /*
- * 从ServiceManager中获取service对应的代理Binder
- * @param na
- * @return
- * @throws RemoteException
- */
- public IBinder getService(String name)
throws RemoteException { - Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
- Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
- data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager.descriptor);
- data.writeString(name);
- mRemote.transact(GET_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply,
0); - IBinder binder = reply.readStrongBinder();
- reply.recycle();
- data.recycle();
- return binder;
- }
- 建立和ServiceManager的连接,获取客户端对象的代理Binder。
- 客户端再通过该代理binder和服务器端进行通信。
Binder机制是android中实现的进程间通信的架构,它采用的是c/s架构,client通过代理完成对server的调用。
ServiceManager
既然这里提到了server,那么我们有必要先了解下在android中是怎么来管理server的。先来看一个重要的Native进程:ServiceManager,从名字可以看出来,这个是用来管理所有server的。在init进程启动之后,会启动另外两个重要的进程,一个是我们上一篇讲的Zygote进程,另外一个就是这个ServiceManager进程了,这两个进程启动之后就建立了android的运行环境和server的管理环境。ServiceManager进程启动之后其他server就可以通过ServiceManager的add_service和check_service来添加和获取特定的server了。关于ServiceManager在接下来会详细介绍,因为Binder会涉及到ServiceManager,所以先简单介绍下,有个大概印象,知道他是干什么的就行了。
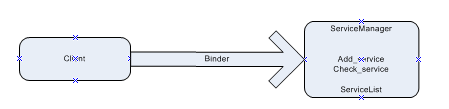
Binder与进程间通信
在本篇介绍中,我们所指的客户端没有特别说明的话就指应用程序。应为service和serviceManager通信也会涉及到IPC。
我们还是从activity的启动开始来研究Binder的机制。来看下startActivity涉及通信的类图:
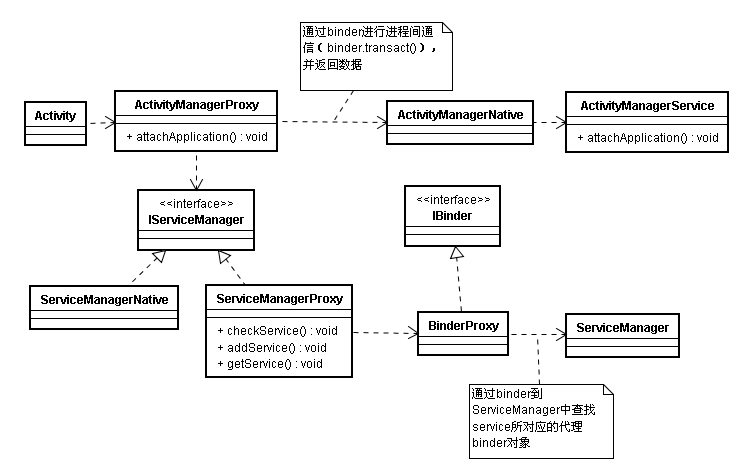
在ActivityManagerProxy中,有这句代码
也就是说,在android中进行IPC的话,需要先通过ServiceManager获得客户端的代理,然后再通过该代理与对应的service进行通信。
真正的Binder
我们在上面所提到的这些Binder实际上只是JVM中的Binder,主要作用是提供了访问C++中的代理Binder,叫做BpBinder(BproxyBinder)。真正的Binder是Linux上的一个驱动设备,专门用来做android的数据交换。

从上面分析可以看出,一次IPC通信大概有以下三个步骤:
- 在JVM中对数据进行序列化,并通过BinderProxy传递到C++中。
- C++中的BpBinder对数据进行处理,并传入到Binder设备中(这里是在ProcessState类中处理并调用BpBinder).
- Service从内核设备中读取数据。
既然在C++中,处理数据主要是在ProcessState中,那么我们就来看看ProcessState的代码,在getContextObject中调用了getStrongProxyForHandle方法,从而获取了代理对象BpBinder:
- sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
- {
- sp<IBinder> result;
- AutoMutex _l(mLock);
- handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
- if (e != NULL) {
- // We need to create a new BpBinder if there isn't currently one, OR we
- // are unable to acquire a weak reference on this current one. See comment
- // in getWeakProxyForHandle() for more info about this.
- IBinder* b = e->binder;
- if (b == NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
- b = new BpBinder(handle);
- e->binder = b;
- if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
- result = b;
- } else {
- // This little bit of nastyness is to allow us to add a primary
- // reference to the remote proxy when this team doesn't have one
- // but another team is sending the handle to us.
- result.force_set(b);
- e->refs->decWeak(this);
- }
- }
- return result;
- }
- status_t BpBinder::transact(
- uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
- {
- // Once a binder has died, it will never come back to life.
- if (mAlive) {
- status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
- mHandle, code, data, reply, flags);
- if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) mAlive =
0; - return status;
- }
- return DEAD_OBJECT;
- }
- 在android中,使用Binder进行进程间的通信,并采用C/S架构
- Android中的Binder分为JVM中的、C++中的、和真正的linux中的Binder块设备
- 进程间通信首先是从JVM中对数据进行转化并传递到C++中,C++中的BpBinder对数据进行处理写入到linux中的Binder设备,并接受Service端得请求,请求完毕后按照原路返回给调用端。
再来看看BpBinder中的transact方法代码:
在BpBinder中的transact函数中,只是调用了IPCThreadState::self()->transact方法,也就是说,数据处理是在IPCThreadState类中的transact。在transact中,它把请求的数据经过Binder设备发送给了Service。Service处理完请求后,又将结果原路返回给客户端。
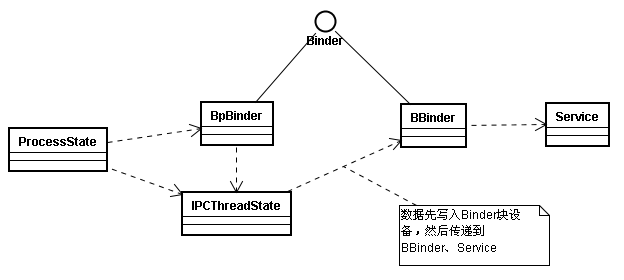
总结: