struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
创建链表——头插
struct node* CreateHeadList()
{
int i;
struct node* head = NULL; //声明头节点
struct node* new; //声明新节点
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));//new指向一个struct node的地址
new->data = i; //数据域赋值
new->next = head; //指针域指向头节点
head = new; //head指针指向这个new的首地址
}
return head; //返回头指针
}
创建链表——尾插
struct node* CreateTailList() //尾插法
{
struct node* head = NULL; //声明头指针,用来返回一个链表的头
struct node* tail = NULL; //声明尾指针
struct node* new;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); //new指向了一个struct node结构的首地址
if(0 == i){
head = new; //当链表只有一个元素的时候,head和tail都是指向new的
tail = new;
}
new->data = i; //数据域赋值
new->next = NULL; //指针域指向空
tail->next = new; //在此之前,tail还在上一个节点上,这里是将tail的指针域指向new
tail = new; //tail的首地址赋值给new
}
return head; //返回头指针
}
在头部插入元素:
struct node* InsertIntoListOnHead(struct node* head, int data)
{
struct node* new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new->data = data;
new->next = head;
head = new; //更新头节点,指向new节点
return head;
}
在尾部插入元素:
struct node* InsertIntoListOnTail(struct node* head, int data)
{
struct node* tail = head;//记录头节点,后续需要偏移这个指针
struct node* new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
while(tail->next != NULL){
tail = tail->next;//找到最后一个节点
}
tail->next = new;//将最后一个节点指向新增加的节点
tail = new; //偏移tail指针
new->data = data;//数据域赋值
new->next = NULL;//指针域指向null,因为这是链表的最后一个元素,它的next域要指向空
return head;
}
插入元素(不是头或者尾)
struct node* InsertIntoList(struct node* head, int data, int index) //比如要在数据域为2的后面插入,那么index就是2
{
struct node* tail = head; //记录头指针位置
struct node* new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//申请新节点
while(tail->data != index){//找位置
tail = tail->next;
}
new->data = data; //数据域赋值
new->next = tail->next; //新节点的指针域指向要插入节点的下个节点
tail->next = new; //tail的指针域指向新节点
return head;
}
删除某一元素:
struct node* DeleteFromList(struct node* head, int data) //data是要删除的数据
{
struct node* tail = head; //记录头节点
while(tail->data != data){ //遍历链表,找要删除的数据
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = tail->next->next; //tail的指针域直接指向要删除节点的下一个节点
//tail->next = NULL; //如果tail->next = null的话,那么data节点的后面所有节点就都删除了
return head;
}
倒序链表:
struct node* ReserveList(struct node* head)
{
struct node* next;
struct node* prev = NULL; //记录当前节点的上一个节点,也就是倒序后的下一个节点,初始化的时候是null的
while(head != NULL){
next = head->next;
head->next = prev;
prev = head;
head = next;
}
return prev;
}
中间的四个操作引用http://blog.csdn.net/autumn20080101/article/details/7607148的两幅图片:
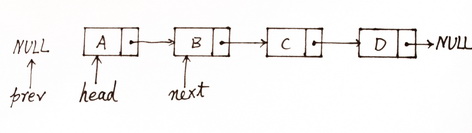
图1

图2
由图1到图2,经历了四个步骤:
head->next = prev; prev = head; head = next; next = head->next;
遍历链表:
int main()
{
struct node *head = NULL;
head = CreateTailList();
head = CreateList();
while (head != NULL)
{
printf("%d\n", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}