http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Round-robin_tournament
You need to organize a football tournament. There are n teams given.
You need to prepare a schedule for the matches so that each team plays with every
other team and on the same day no team plays twice. You want to finish the tournament as early as possible.
If  is the number of competitors, a pure round robin tournament requires
is the number of competitors, a pure round robin tournament requires  games.
games.
If  is even, then in each of
is even, then in each of  rounds,
rounds,  games
games
can be run in parallel, provided there exist sufficient resources (e.g. courts for a tennis tournament). If  is
is
odd, there will be  rounds, each with
rounds, each with  games,
games,
and one competitor having no game in that round.
The standard algorithm for round-robins is to assign each competitor a number, and pair them off in the first round …
Round 1. (1 plays 14, 2 plays 13, ... ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
then fix one competitor (number one in this example) and rotate the others clockwise one position(固定1,顺时针选择其他所有的数)
Round 2. (1 plays 13, 14 plays 12, ... ) 1 14 2 3 4 5 6 13 12 11 10 9 8 7
Round 3. (1 plays 12, 13 plays 11, ... ) 1 13 14 2 3 4 5 12 11 10 9 8 7 6
until you end up almost back at the initial position
Round 13. (1 plays 2, 3 plays 14, ... ) 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 14 13 12 11 10 9
If there are an odd number of competitors, a dummy competitor can be added, whose scheduled opponent in a given round does not play and has a bye.
The schedule can therefore be computed as though the dummy were an ordinary player, either fixed or rotating. Instead of rotating one position, any number relatively
prime to  will generate a complete schedule. The upper and lower rows can indicate home/away
will generate a complete schedule. The upper and lower rows can indicate home/away
in sports, white/black in chess, etc.; to ensure fairness, this must alternate between rounds since competitor 1 is always on the first row. If,
say, competitors 3 and 8 were unable to fulfil their fixture in the third round, it would need to be rescheduled outside the other rounds, since both competitors would already be facing other opponents in those rounds. More complex scheduling constraints may
require more complex algorithms. This schedule is applied in chess and draughts tournaments of rapid games, where players physically move round a table.
Alternatively Berger tables,[6] named after
their inventor Johann Berger, are widely used in the planning of tournaments.
Round 1. 1-14 2-13 3-12 4-11 5-10 6-9 7-8 Round 2. 14-8 9-7 10-6 11-5 12-4 13-3 1-2 Round 3. 2-14 3-1 4-13 5-12 6-11 7-10 8-9 … Round 13. 7-14 8-6 9-5 10-4 11-3 12-2 13-1
This constitutes a schedule where player 14 has a fixed position, and all other players are rotated clockwise 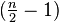 positions.
positions.
This schedule alternates colours and is easily generated manually. To construct the next round, the last player, number 8 in the first round, moves to the head of the table, followed by player 9 against player 7, player 10 against 6, until player 1 against
player 2.