1 Linux I2C驱动架构
Linux下I2C驱动的架构图如下:

图1.1 Linux下I2C驱动架构
如上图所示,每条I2C总线会对应一个adapter,而每条I2C总线上则可以有多个 client,在linux kernel中,通过I2C core层将I2C client与I2C adapter关联起来,Linux 中I2C驱动代码位于drivers/i2c目录。
Linux中I2C可以分为三个层次,分别为I2C core层、I2C adapter driver层、I2C device driver层。
1.1 I2C core层
I2C core是用于维护Linux的I2C核心部分,提供了核心的数据结构,I2C适配器驱动和设备驱动的注册、注销管理等API,同时还提供了I2C总线读写访问的一般接口(具体的实现在与I2C控制器相关的I2C adapter中实现)。
该层为硬件平台无关层,向下屏蔽了物理总线适配器的差异,定义了统一的访问策略和接口;向上则提供了统一的接口,以便I2C设备驱动可以通过总线适配器进行数据收发。
Linux中,I2C core层的代码位于driver/i2c/ i2c-core.c。由于该层是平台无关层,本文将不再叙述,有兴趣可以查阅相关资料。
1.2 I2C adapter driver层
I2C adapter driver层即I2C适配器驱动层,每种处理器平台都有自己的适配器驱动,属于平台移植相关层。它的职责是为系统中每条I2C总线实现相应的读写方法。但是适配器驱动本身并不会进行任何的通讯,而是等待设备驱动调用其函数。
在系统开机时,I2C适配器驱动被首先装载。一个适配器驱动用于支持一条特定的I2C总线的读写。一个适配器驱动通常需要两个模块,一个struct i2c_adapter和一个struct i2c_algorithm来描述。
i2c adapter 构造一个对I2C core层接口的数据结构,并通过相应的接口函数向I2C core注册一个适配器。i2c_algorithm主要实现对I2C总线访问的算法,master_xfer和smbus_xfer即I2C adapter底层对I2C总线读写方法的实现,相关的数据结构如下:
/*
* The following structs are for those who like to implement new bus drivers:
* i2c_algorithm is the interface to a class of hardware solutions which can
* be addressed using the same bus algorithms - i.e. bit-banging or the PCF8584
* to name two of the most common.
*/
struct i2c_algorithm {
/* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
using common I2C messages */
/* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
processed, or a negative value on error */
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);
};
主要就是master_xfer方法,其和具体的总线控制器相关,不同的CPU在实现上会有差异。
/*
* i2c_adapter is the structure used to identify a physical i2c bus along
* with the access algorithms necessary to access it.
*/
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;
unsigned int id;
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
void *algo_data;
/* data fields that are valid for all devices */
struct rt_mutex bus_lock;
int timeout; /* in jiffies */
int retries;
struct device dev; /* the adapter device */
int nr;
char name[48];
struct completion dev_released;
struct list_head userspace_clients;
};
Algo是和底层硬件的接口,标识了具体的物理总线传输的实现。
Userspace_clients为使用该总线的client链表。
Nr为该适配器也就是某条I2C总线占据的全局编号。
bus_lock总线的互斥锁,防止总线冲突。
Linux中,I2C adapter driver层的代码位于drivers/i2c/busses目录,第3章会详细介绍该层的内容。
1.3 I2C device driver层
I2C device driver层为用户接口层,其为用户提供了通过I2C总线访问具体设备的接口。
I2C的device driver层可以用两个模块来描述,struct i2c_driver和struct i2c_client。
i2c_client和i2c_driver分别构造对I2C core层接口的数据结构,并且通过相关的接口函数向 I2C Core注册I2C设备驱动。相关的数据结构如下:
/**
* struct i2c_driver - represent an I2C device driver
* @class: What kind of i2c device we instantiate (for detect)
* @attach_adapter: Callback for bus addition (for legacy drivers)
* @detach_adapter: Callback for bus removal (for legacy drivers)
* @probe: Callback for device binding
* @remove: Callback for device unbinding
* @shutdown: Callback for device shutdown
* @suspend: Callback for device suspend
* @resume: Callback for device resume
* @command: Callback for bus-wide signaling (optional)
* @driver: Device driver model driver
* @id_table: List of I2C devices supported by this driver
* @detect: Callback for device detection
* @address_list: The I2C addresses to probe (for detect)
* @clients: List of detected clients we created (for i2c-core use only)
*
* The driver.owner field should be set to the module owner of this driver.
* The driver.name field should be set to the name of this driver.
*
* For automatic device detection, both @detect and @address_data must
* be defined. @class should also be set, otherwise only devices forced
* with module parameters will be created. The detect function must
* fill at least the name field of the i2c_board_info structure it is
* handed upon successful detection, and possibly also the flags field.
*
* If @detect is missing, the driver will still work fine for enumerated
* devices. Detected devices simply won't be supported. This is expected
* for the many I2C/SMBus devices which can't be detected reliably, and
* the ones which can always be enumerated in practice.
*
* The i2c_client structure which is handed to the @detect callback is
* not a real i2c_client. It is initialized just enough so that you can
* call i2c_smbus_read_byte_data and friends on it. Don't do anything
* else with it. In particular, calling dev_dbg and friends on it is
* not allowed.
*/
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
/* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared or is about to be
* removed. You should avoid using this if you can, it will probably
* be removed in a near future.
*/
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
/* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.
* The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.
* For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed
* as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").
*/
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
/* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions
* with the device.
*/
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
Driver是为device服务的,i2c_driver注册时会扫描i2c bus上的设备,进行驱动和设备的绑定。主要有两种接口attach_adapter和probe,二者分别针对旧的和新式的驱动。
/**
* struct i2c_client - represent an I2C slave device
* @flags: I2C_CLIENT_TEN indicates the device uses a ten bit chip address;
* I2C_CLIENT_PEC indicates it uses SMBus Packet Error Checking
* @addr: Address used on the I2C bus connected to the parent adapter.
* @name: Indicates the type of the device, usually a chip name that's
* generic enough to hide second-sourcing and compatible revisions.
* @adapter: manages the bus segment hosting this I2C device
* @driver: device's driver, hence pointer to access routines
* @dev: Driver model device node for the slave.
* @irq: indicates the IRQ generated by this device (if any)
* @detected: member of an i2c_driver.clients list or i2c-core's
* userspace_devices list
*
* An i2c_client identifies a single device (i.e. chip) connected to an
* i2c bus. The behaviour exposed to Linux is defined by the driver
* managing the device.
*/
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */
unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */
/* addresses are stored in the */
/* _LOWER_ 7 bits */
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on */
struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines */
struct device dev; /* the device structure */
int irq; /* irq issued by device */
struct list_head detected;
};
通常来说i2c_client对应着I2C总线上某个特定的slave或者是user space的某个用户对应,而此时的slave可以动态变化。
Linux中,I2C device driver层的代码位于drivers/i2c/chips目录,第4章将详细介绍该层的内容。
2 OMAP3630 I2C控制器
OMAP3630具有4个高速I2C控制器,每个控制器都通过I2C串行总线为本地主机即OAMP3630 MPU和I2C总线兼容设备提供了一个通讯接口,支持多达8-bit的数据传送和接收。
每个I2C控制器都能配置成一个主机或者从机设备,而且他们都能配置成在一个2线的串行的摄像头控制总线(SCCB总线)上作为主设备,I2C2和I2C3还能配置成在一个3线的SCCB总线上作为主设备。
I2C4控制器位于PRCM模块,可以进行动态电压控制和电源序列测定。
OMAP3630的I2C控制器模块图如下:

图2.1 OMAP3630 I2C控制器模块图
控制器1,2,3具有以下特征:
? 兼容飞利浦I2C 2.1版本
? 支持标准I2C标准模式(100Kbps)和快速模式(400Kpbs)
? 支持高达3.4Mbps的高速发送模式
? 支持I2C2和I2C3 模块的3线/2线的SCCB主从模式,I2C1 模块的2线的SCCB主从模式,高达100kbit/s
? 7-bit和10bit的设备地址模式
? 多主控发送/从接收模式
? 多主控接收/从发送模式
? 联合的主机发送/接收和接收/发送模式
? 内置FIFO(8,16,32,64字节大小)用于缓存读取和接收
? 模块使能/关闭
? 可编程的时钟
? 8-bit的数据存取
? 低功耗的设计
? 两个DMA通道
? 支持中断机制
? 自动空闲机制
? 空闲请求和应答握手机制
主从的发送机I2C4控制器有以下特征:
? 支持高速和快速模式
? 只能支持7-bit地址模式
? 只支持主发送模式
关于I2C控制器的详细介绍请参考OMAP36XX_ES1.1_NDA_TRM_V_G.pdf的第17章。
3 OMAP3630 I2C adapter驱动
在Linux内核中,I2C adapter驱动位于drivers/i2c/busses目录下,OMAP3630 的I2C adapter驱动程序为i2c-omap.c。
I2C adapter驱动,本质上就是实现了具体的总线传输算法并向核心层注册适配器。该驱动的注册采用Platform驱动和设备机制。
3.1 I2C adapter的Platform device
Andrord 2.1中Platform device的注册的代码位于内核的arch/arm/plat-omap/i2c.c,arch/arm/mach-omap2/board-xxxx.c中。
3.1.1 Platform device的定义
在文件arch/arm/plat-omap/i2c.c中,Platform device定义如下:
#define OMAP_I2C_SIZE 0x3f
#define OMAP1_I2C_BASE 0xfffb3800
#define OMAP2_I2C_BASE1 0x48070000
#define OMAP2_I2C_BASE2 0x48072000
#define OMAP2_I2C_BASE3 0x48060000
static const char name[] = "i2c_omap";
#define I2C_RESOURCE_BUILDER(base, irq) /
{ /
.start = (base), /
.end = (base) + OMAP_I2C_SIZE, /
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, /
}, /
{ /
.start = (irq), /
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, /
},
static struct resource i2c_resources[][2] = {
{ I2C_RESOURCE_BUILDER(0, 0) },
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP24XX) || defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP34XX)
{ I2C_RESOURCE_BUILDER(OMAP2_I2C_BASE2, INT_24XX_I2C2_IRQ) },
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP34XX)
{ I2C_RESOURCE_BUILDER(OMAP2_I2C_BASE3, INT_34XX_I2C3_IRQ) },
#endif
};
#define I2C_DEV_BUILDER(bus_id, res, data) /
{ /
.id = (bus_id), /
.name = name, /
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(res), /
.resource = (res), /
.dev = { /
.platform_data = (data), /
}, /
}
static u32 i2c_rate[ARRAY_SIZE(i2c_resources)];
static struct platform_device omap_i2c_devices[] = {
I2C_DEV_BUILDER(1, i2c_resources[0], &i2c_rate[0]),
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP24XX) || defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP34XX)
I2C_DEV_BUILDER(2, i2c_resources[1], &i2c_rate[1]),
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_OMAP34XX)
I2C_DEV_BUILDER(3, i2c_resources[2], &i2c_rate[2]),
#endif
};
可以看到,这边定义了三个I2C适配器的Platform device,id分别为“1,2,3”,name都为“i2c_omap”,变量resource中定义了适配器的寄存器基地址,irq中断号等。
3.1.2 Platform device的注册
Platform device的注册是由内核启动后,具体产品的板级初始化完成的。xxxx项目的I2C adapter的Platform device注册过程如下图:

图3.1 Platform device注册过程
函数omap_i2c_add_bus()中,通过函数platform_device_register()注册Platform device到platform bus上,代码如下:
static int __init omap_i2c_add_bus(int bus_id)
{
struct platform_device *pdev;
struct resource *res;
resource_size_t base, irq;
……
……
return platform_device_register(pdev);
}
注册完成后,中断号及寄存器的基地址等信息会在设备树中描述了,此后只需利用platform_get_resource等标准接口自动获取即可,实现了驱动和资源的分离。
3.2 I2C adapter的Platform driver
Andrord 2.1中Platform driver的注册的代码位于内核的drivers/i2c/busses/ i2c-omap.c中,该驱动的注册目的是初始化OMAP3630的I2C adapter,提供I2C总线传输的具体实现,并且向I2C core注册I2C adapter。
3.2.1 Platform driver的定义
在文件drivers/i2c/busses/ i2c-omap.c中,platform driver定义如下:
static struct platform_driver omap_i2c_driver = {
.probe = omap_i2c_probe,
.remove = omap_i2c_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "i2c_omap",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
3.2.2 Platform driver的注册
在文件drivers/i2c/busses/ i2c-omap.c中,platform driver注册如下:
/* I2C may be needed to bring up other drivers */
static int __init
omap_i2c_init_driver(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&omap_i2c_driver);
}
subsys_initcall(omap_i2c_init_driver);
通过platform_driver_register()函数注册Platform driver omap_i2c_driver时,会扫描platform bus上的所有设备,由于匹配因子是name即"i2c_omap",而之前已经将name为"i2c_omap"的Platform device注册到platform bus上,因此匹配成功,调用函数omap_i2c_probe将设备和驱动绑定起来。
在drivers/i2c/busses/ i2c-omap.c中会涉及到一个数据结构omap_i2c_dev,这个结构定义了omap3630的I2C控制器,结构如下:
struct omap_i2c_dev {
struct device *dev;
void __iomem *base; /* virtual */
int irq;
struct clk *iclk; /* Interface clock */
struct clk *fclk; /* Functional clock */
struct completion cmd_complete;
struct resource *ioarea;
u32 speed; /* Speed of bus in Khz */
u16 cmd_err;
u8 *buf;
size_t buf_len;
struct i2c_adapter adapter;
u8 fifo_size; /* use as flag and value
* fifo_size==0 implies no fifo
* if set, should be trsh+1
*/
u8 rev;
unsigned b_hw:1; /* bad h/w fixes */
unsigned idle:1;
u16 iestate; /* Saved interrupt register */
u16 pscstate;
u16 scllstate;
u16 sclhstate;
u16 bufstate;
u16 syscstate;
u16 westate;
};
Base对应I2C控制器寄存器的虚拟地址。
Irq对应I2C控制器的中断号。
Buf对应上层传下来的需要发送数据或者I2C控制接收到数据的缓存空间,buf_len是其大小。
Adapter对应I2C控制器的适配器结构。
U16类型的各个state变量是用于对应I2C控制器的寄存器的值。
函数omap_i2c_probe的执行流程如下图:

图3.2 omap_i2c_probe的执行流程
函数omap_i2c_probe的简要代码如下:
static int __init
omap_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct omap_i2c_dev *dev;
struct i2c_adapter *adap;
struct resource *mem, *irq, *ioarea;
irq_handler_t isr;
……
/* NOTE: driver uses the static register mapping */
mem = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
……
irq = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, 0);
……
dev = kzalloc(sizeof(struct omap_i2c_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
……
dev->dev = &pdev->dev;
dev->irq = irq->start;
dev->base = ioremap(mem->start, mem->end - mem->start + 1);
……
/* reset ASAP, clearing any IRQs */
omap_i2c_init(dev);
isr = (dev->rev < OMAP_I2C_REV_2) ? omap_i2c_rev1_isr : omap_i2c_isr;
r = request_irq(dev->irq, isr, 0, pdev->name, dev);
……
adap = &dev->adapter;
i2c_set_adapdata(adap, dev);
adap->owner = THIS_MODULE;
adap->class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON;
strncpy(adap->name, "OMAP I2C adapter", sizeof(adap->name));
adap->algo = &omap_i2c_algo;
adap->dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
/* i2c device drivers may be active on return from add_adapter() */
adap->nr = pdev->id;
r = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(adap);
……
return 0;
……
}
这里定义了I2C adapter的中断处理函数omap_i2c_isr(),该函数对I2C控制器的中断事件进行响应,主要实现了对I2C数据收发中断事件的处理。
这边还涉及到了一个i2c_algorithm结构的变量omap_i2c_algo,该变量的定义如下:
static const struct i2c_algorithm omap_i2c_algo = {
.master_xfer = omap_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = omap_i2c_func,
};
omap_i2c_xfer接口函数实现了底层I2C数据传输的方法。
omap_i2c_probe函数最后使用了 i2c_add_numbered_adapter()将adapter注册到i2c-core层,adapter的总线号保存在平台设备数组 omap_i2c_devices中,见3.1.1节,由于该数组中有三个成员,即三条I2C总线,所以这里会建立三个I2C adapter,总线号分别为1,2,3。
4 OMAP3630 I2C device驱动
在Linux内核中,I2C device驱动位于drivers/i2c/chips目录下,可以看到该目录下有很多相关的device驱动,这里以xxxx项目的mma7455为例介绍device驱动的注册过程,对应的device驱动程序为mma7455.c。
既然有device驱动,那么必定有相应的device,I2C的device是什么呢?其实就是我们在1.3节中提到的i2c_client,所以在device驱动注册之前先来了解下i2c_client的注册过程。
4.1 Mma7455 device注册
Mma7455 device即i2c_client的创建以及注册分为两步。
4.1.1 将mma7455设备信息加入到设备链表
在板级初始化时将I2C device的名称,地址和相关的信息加入到链表__i2c_board_list中,该链表记录了具体开发板上的I2C设备信息。
在board-xxxx.c中,定义了mma7455的设备信息定义如下:
static struct i2c_board_info __initdata xxxx_i2c_bus3_info[] = {
……
#ifdef CONFIG_SENSORS_MMA7455
{
I2C_BOARD_INFO("mma7455", 0x1D),
.platform_data = &xxxx_mma7455_platform_data,
},
#endif
};
Mma7455加入到设备链表__i2c_board_list的流程图如下图:

图4.1 mma7455加入到I2C设备链表的过程
i2c_register_board_info()函数的定义如下:
int __init i2c_register_board_info(int busnum,
struct i2c_board_info const *info, unsigned len)
{
……
for (status = 0; len; len--, info++) {
struct i2c_devinfo *devinfo;
devinfo = kzalloc(sizeof(*devinfo), GFP_KERNEL);
……
devinfo->busnum = busnum;
devinfo->board_info = *info;
list_add_tail(&devinfo->list, &__i2c_board_list);
}
……
}
4.1.2 创建并注册i2c_client
i2c_client的创建和注册在I2C adapter驱动注册过程中完成,I2C adapter驱动的注册可以参考3.2.2节,i2c_add_numbered_adapter()函数在注册I2C adapter驱动的同时会扫描4.1.1中提到的I2C设备链表__i2c_board_list,如果该总线上有对应的I2C设备,则创建相应的i2c_client,并将其注册到I2C core中。流程图如下所示:
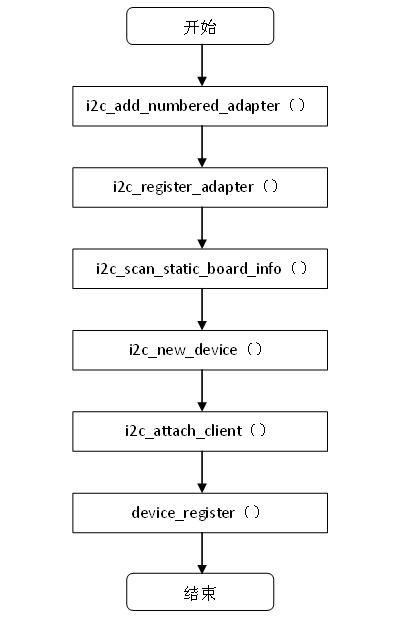
图4.2创建并注册i2c_client
相应的代码位于i2c-core.c如下:
static void i2c_scan_static_board_info(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)
{
……
list_for_each_entry(devinfo, &__i2c_board_list, list) {
if (devinfo->busnum == adapter->nr
&& !i2c_new_device(adapter,
&devinfo->board_info))
……
}
……
}
在i2c_scan_static_board_info()函数中遍历I2C设备链表__i2c_board_list,设备的总线号和adapter的总线号相等,则使用函数i2c_new_device()创建该设备。
struct i2c_client *
i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
……
client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;
client->adapter = adap;
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
if (info->archdata)
client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;
client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->irq = info->irq;
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));
……
status = i2c_attach_client(client);
……
}
在函数i2c_new_device()中创建一个i2c_client,初始化该结构体的adapter,addr,name等变量,这里的client->name被初始化为info->type,在4.1.1中,info->type初始化为“mma7455”, client->name后面会用于I2C device和I2C driver匹配时使用,最后调用i2c_attach_client()将该client注册到I2C core。
int i2c_attach_client(struct i2c_client *client)
{
struct i2c_adapter *adapter = client->adapter;
……
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
……
res = device_register(&client->dev);
……
}
函数i2c_attach_client()进一步初始化i2c_client结构体,将该设备的总线初始化为i2c_bus_type,说明该设备被放在I2C总线上,用于后面跟I2C driver匹配时使用,最后使用device_register(&client->dev)注册该i2c_client设备。
4.2 Mma7455 device驱动注册
在mma7455.c中,定义了mma7455的device驱动,代码如下:
static struct i2c_driver mma7455_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "mma7455",
},
.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON,
.probe = mma7455_probe,
.remove = mma7455_remove,
.id_table = mma7455_id,
……
};
注册的简要示意图如下:
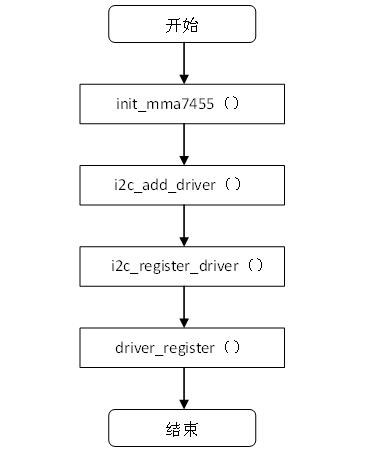
图4.3 device驱动的注册
相应的代码位于mma7455.c和i2c-core.c。
static int __init init_mma7455(void)
{
……
res = i2c_add_driver(&mma7455_driver);
……
return (res);
}
在模块加载的时候首先调用init_mma7455(),然后init_mma7455()调用函数i2c_add_driver()注册mma7455_driver结构体。
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver)
{
…….
/* add the driver to the list of i2c drivers in the driver core */
driver->driver.owner = owner;
driver->driver.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
……
res = driver_register(&driver->driver);
if (res)
return res;
……
}
函数i2c_register_driver()初始化该驱动的总线为i2c_bus_type,然后使用函数driver_register(&driver->driver)注册该驱动,因此内核会在I2C总线上遍历所有I2C设备,由于该mma7455 device驱动的匹配因子name变量为“mma7455”,因此正好和在4.1.2里创建的name也为“mma7455”的i2c client匹配。因此总线的probe函数将会被调用,I2C总线的probe函数为i2c_device_probe(),具体代码如下:
static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev)
{
struct i2c_client *client = to_i2c_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver);
int status;
if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table)
return -ENODEV;
client->driver = driver;
…….
status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client));
……
return status;
}
在i2c_device_probe()函数中,语句client->driver = driver将I2C device和I2C driver绑定,然后直接调用具体设备的probe函数,这里即mma7455的probe函数mma7455_probe()。
在mma7455_probe()函数会完成一些具体I2C设备相关的初始化等操作,这边就不再详述。
5 用户空间的支持
图1.1Linux I2C的架构图中的i2c-dev部份是一个通用的I2C设备的驱动程序,通过一个带有操作集file_operations的标准字符设备驱动为用户空间提供了访问接口,使用户空间可以通过I2C core,进而访问I2C adapter。
5.1 I2c-dev的注册
该部分的源代码位于drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c,首先定义了I2C device驱动i2cdev_driver:
static struct i2c_driver i2cdev_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "dev_driver",
},
.attach_adapter = i2cdev_attach_adapter,
.detach_adapter = i2cdev_detach_adapter,
};
i2cdev_driver注册代码如下:
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
……
res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops);
……
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
……
res = i2c_add_driver(&i2cdev_driver);
……
}
首先注册了一个主设备号为I2C_MAJOR,操作集为i2cdev_fops,名字为“i2c”的字符设备。在文件drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.h中,I2C_MAJOR被定义为89。在i2c-dev.c中i2cdev_fops的定义如下:
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = i2cdev_read,
.write = i2cdev_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl,
.open = i2cdev_open,
.release = i2cdev_release,
};
该操作集是用户空间访问该字符设备的接口。
然后调用函数i2c_add_driver(&i2cdev_driver)将i2cdev_driver驱动注册到i2c core中,i2cdev_driver驱动注册的流程图如下:
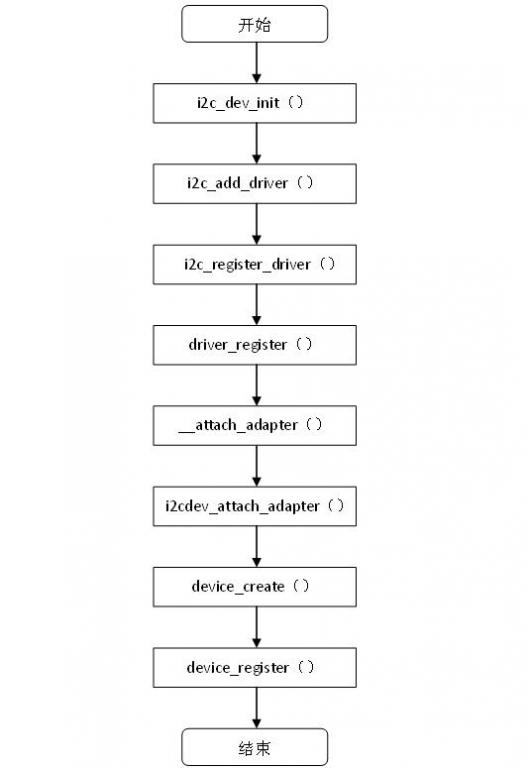
图5.1 i2cdev_driver注册过程
注册i2c_driver时,会将驱动和adapter绑定起来,然后将调用i2c_driver 的attach_adapter 方法,即i2cdev_attach_adapter()函数,建立dev设备节点,每个adapter都会对应一个dev设备节点,并维护了一个i2c_dev链表保存设备节点和adapter的关系。
i2cdev_attach_adapter()函数的代码如下:
static int i2cdev_attach_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
……
/* register this i2c device with the driver core */
i2c_dev->dev = device_create(i2c_dev_class, &adap->dev,
MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, adap->nr), NULL,
"i2c-%d", adap->nr);
……
res = device_create_file(i2c_dev->dev, &dev_attr_name);
……
}
以I2C_MAJOR和adap->nr为主从设备号创建并注册设备节点,如果系统有udev或者是hotplug,那么就会在/dev下自动创建相关的设备节点了。
5.2 I2c-dev的打开
I2c-dev的open函数如下:
static int i2cdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
……
i2c_dev = i2c_dev_get_by_minor(minor);
if (!i2c_dev) {
ret = -ENODEV;
goto out;
}
adap = i2c_get_adapter(i2c_dev->adap->nr);
……
client = kzalloc(sizeof(*client), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client) {
i2c_put_adapter(adap);
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
snprintf(client->name, I2C_NAME_SIZE, "i2c-dev %d", adap->nr);
client->driver = &i2cdev_driver;
client->adapter = adap;
file->private_data = client;
……
}
Open操作是用户空间程序和内核驱动交换的第一步,最终返回给用户空间的就是struct file结构体。对于I2C 驱动来说,用户空间所获得的就是client这个关键信息,在其中可以找到所有有关的信息如client所在的adapter及i2c_driver。
用open函数将i2c-dev设备打开以后,就可以通过ioctl函数的各种命令来设定要访问从设备的地址,I2C设备读写等操作,也可以通过 read和write函数完成对I2C设备的读写。
对I2C设备的具体操作在这里不再具体阐述,可以参看i2c-dev.c源代码。
6 I2C数据收发的框架
I2C架构的读写支持两种协议类型,I2C协议与SMBUS协议。
I2C协议和SMBUS协议不完成等同,SMBUS是I2C的子集,SMBUS由I2C衍生而来。SMBUS总线上传输的数据一定是I2C的格式的,但是SMBUS上传输的数据不一定能满足具体某个I2C从设备的通信要求。
6.1 SMBUS协议的数据收发
如果控制器不支持SMBUS协议,框架层可以用i2c_transfer模拟SMBUS协议的实现,系统默认的I2C传输函数一般都是基于I2C模拟的SMBUS方法传输的,如i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(),i2c_smbus_read_byte_data()等。
在设备mma7455的驱动程序中,使用了SMBUS协议,而OMAP3630控制器使用的是I2C协议,因此在mma7455的驱动程序中就用到了基于I2C模拟的SMBUS方法。
下面以函数i2c_smbus_write_byte_data()为例来说明SMBUS协议下的数据发送的过程。
在i2c-core.c中,函数i2c_smbus_write_byte_data()的定义如下:
/**
* i2c_smbus_write_byte_data - SMBus "write byte" protocol
* @client: Handle to slave device
* @command: Byte interpreted by slave
* @value: Byte being written
*
* This executes the SMBus "write byte" protocol, returning negative errno
* else zero on success.
*/
s32 i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(struct i2c_client *client, u8 command, u8 value)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
data.byte = value;
return i2c_smbus_xfer(client->adapter,client->addr,client->flags,
I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA,&data);
}
函数i2c_smbus_write_byte_data()的调用流程图如下:
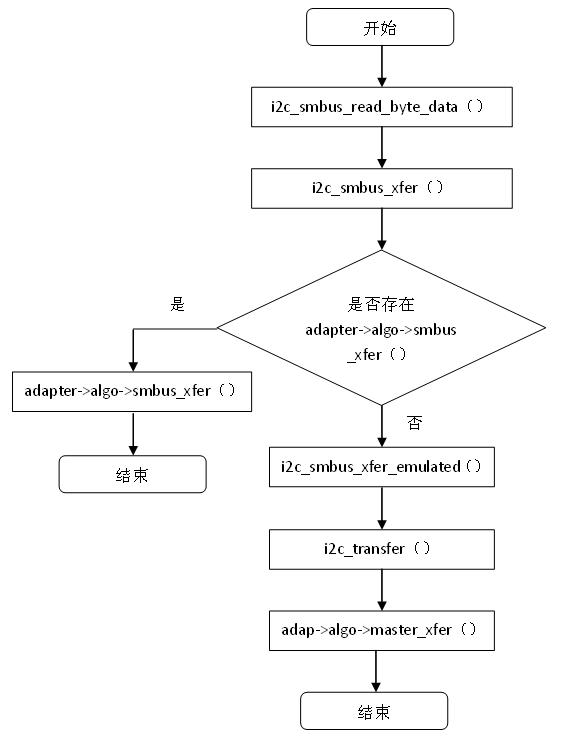
图6.1 SMBUS协议下的数据发送过程
从图6.1可以看到,走哪条分支取决于I2C控制器的i2c_algorithm算法,当定义了方法smbus_xfer,则直接调用该方法,如果没有则通过先调用i2c_smbus_xfer_emulated(),进而通过i2c_transfer()最终调用I2C协议下的master_xfer方法,所以我们说SMBUS总线上传输的数据一定是I2C的格式的。
6.2 I2C协议的数据收发
I2C协议下的数据收发函数就是常用的I2C传输函数:i2c_master_send()和i2c_master_recv()。
下面以函数i2c_master_send ()为例来说明I2C协议下的数据发送的过程。
在i2c-core.c中,函数i2c_master_send()定义如下:
/**
* i2c_master_send - issue a single I2C message in master transmit mode
* @client: Handle to slave device
* @buf: Data that will be written to the slave
* @count: How many bytes to write
*
* Returns negative errno, or else the number of bytes written.
*/
int i2c_master_send(struct i2c_client *client,const char *buf ,int count)
{
int ret;
struct i2c_adapter *adap=client->adapter;
struct i2c_msg msg;
msg.addr = client->addr;
msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN;
msg.len = count;
msg.buf = (char *)buf;
ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1);
/* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes
transmitted, else error code. */
return (ret == 1) ? count : ret;
}
从源代码中可以看出,函数i2c_master_send()先构造i2c_msg结构体,然后直接调用函数i2c_transfer。简单的示意图如下:

图6-2 I2C协议下的数据发送过程
本篇文章来源于 Linux公社网站(www.linuxidc.com) 原文链接:http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-05/35577.htm