1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
On Children's Day, the child got a toy from Delayyy as a present. However, the child is so naughty that he can't wait to destroy the toy.
The toy consists of n parts and m ropes. Each rope
links two parts, but every pair of parts is linked by at most one rope. To split the toy, the child must remove all its parts. The child can remove a single part at a time, and each remove consume an energy. Let's define an energy value of part i as vi.
The child spend vf1 + vf2 + ... + vfk energy
for removing part i where f1, f2, ..., fk are
the parts that are directly connected to the i-th and haven't been removed.
Help the child to find out, what is the minimum total energy he should spend to remove all n parts.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000; 0 ≤ m ≤ 2000).
The second line contains n integers: v1, v2, ..., vn (0 ≤ vi ≤ 105).
Then followed m lines, each line contains two integers xi and yi,
representing a rope from part xi to
part yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n; xi ≠ yi).
Consider all the parts are numbered from 1 to n.
Output the minimum total energy the child should spend to remove all n parts of the toy.
4 3 10 20 30 40 1 4 1 2 2 3
40
4 4 100 100 100 100 1 2 2 3 2 4 3 4
400
7 10 40 10 20 10 20 80 40 1 5 4 7 4 5 5 2 5 7 6 4 1 6 1 3 4 3 1 4
160
One of the optimal sequence of actions in the first sample is:
- First, remove part 3, cost of the action is 20.
- Then, remove part 2, cost of the action is 10.
- Next, remove part 4, cost of the action is 10.
- At last, remove part 1, cost of the action is 0.
So the total energy the child paid is 20 + 10 + 10 + 0 = 40, which is the minimum.
In the second sample, the child will spend 400 no matter in what order he will remove the parts.
题意:有一个玩偶由n部分、m条绳构成,每部分有一个权值,将一个部分分离所需的cost为与其直接相连的部分的权值和,求将n部分分离的最小cost。
思路:贪心。将每部分视作点,绳视作边,那么问题转化为将m条边断开的最小cost。而断开每条边的代价无非是该边所连的点的权值的其中一个,因为要求最小的cost,对于每条边我们取与该边相关联点权值的最小值,最后累加,即贪心策略:依次移分离权值最大的部分(这样与其相连的边取得是最小值)。详见代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN=1000+100;
int n,m;
int a[MAXN];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
ans+=min(a[u],a[v]);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n.
The i-th area contains ai animals
in it. Also there are m roads in the zoo, and each road connects two distinct areas. Naturally the zoo is connected, so you can reach any area of the zoo
from any other area using the roads.
Our child is very smart. Imagine the child want to go from area p to area q.
Firstly he considers all the simple routes from p to q.
For each route the child writes down the number, that is equal to the minimum number of animals among the route areas. Let's denote the largest of the written numbers as f(p, q).
Finally, the child chooses one of the routes for which he writes down the value f(p, q).
After the child has visited the zoo, he thinks about the question: what is the average value of f(p, q) for all pairs p, q (p ≠ q)?
Can you answer his question?
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers: a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Then follow m lines, each line contains two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n; xi ≠ yi),
denoting the road between areas xi and yi.
All roads are bidirectional, each pair of areas is connected by at most one road.
Output a real number — the value of 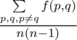 .
.
The answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 4.
4 3 10 20 30 40 1 3 2 3 4 3
16.666667
3 3 10 20 30 1 2 2 3 3 1
13.333333
7 8 40 20 10 30 20 50 40 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 1 4 5 7
18.571429
Consider the first sample. There are 12 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 3, f(p, q) = 30.
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 4, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 1, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 6 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 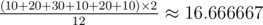 .
.
Consider the second sample. There are 6 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 3 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 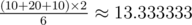 .
.
题意:有n个区域,通过m条路相连通,对于区域 i 有一个权值 a [ i ],对于区域p , q,从区域p到区域q有多条路径,对于每条路径我们记录该路径经过的最小权值,定义f [p , q]为从p到q多个路径记录的最小权值中的最大值。求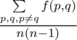 的值。
的值。
思路:最大生成树。我们定义m条边的边权为该边相关联点权值的最小值,将边按权值从大到小排序。利用并查集,用一个cnt数组记录每个点所在联通块的点的个数。依次选边,由于边权从大到小,所以由该边联系的两侧的点到彼端的点的 f 一定为该边权。设相关联的点为x,y,设对应的根为fx , fy,如果fx != fy,则 sum+= cnt[ fx ] * cnt[ fy ] *edge[ i ].w; 最后ave=2 * sum / ( n * ( n - 1 )
)。详见代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN=100000+100;
int n,m;
int a[MAXN],fa[MAXN];
ll cnt[MAXN];
struct Edge
{
int u,v;
ll w;
}edge[MAXN];
bool operator < (Edge u,Edge v)
{
return u.w>v.w;
}
void init()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i,cnt[i]=1;
}
int findset(int x)
{
return fa[x]==x ? x: fa[x]=findset(fa[x]);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("text.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
init();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
edge[i].u=u,edge[i].v=v;
edge[i].w=min(a[u],a[v]);
}
sort(edge,edge+m);
double ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int x=edge[i].u;
int y=edge[i].v;
int fx=findset(x);
int fy=findset(y);
if(fx==fy)
continue;
fa[fy]=fx;
ans+=cnt[fy]*cnt[fx]*edge[i].w;
cnt[fx]+=cnt[fy];
}
ll temp=(ll)n*(n-1);
printf("%.6f\n",2*ans/temp);
return 0;
}
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then
he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
-
Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
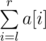 .
. -
Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for
each i (l ≤ i ≤ r). -
Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in
other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) —
initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 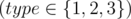 .
.
-
If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n),
which correspond the operation 1. -
If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 2. -
If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
题意:对一个序列有3种操作,第一种输出区间[l , r]的sum ; 第二种将区间[l , r]的元素a[ i ] = a[ i ] mod x; 第三种是将序列第k个元素修改为x。根据命令更新、输出。
思路:线段树。我们维护区间的最大值,如果区间最大值Max<x,那么其下面所有的点都无需更新,之后就是普通的线段树操作了。详见代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN=100000+100;
int n,m;
struct node
{
int l,r,Max;
ll sum;
}segtree[MAXN<<2];
void push_up(int rt)
{
segtree[rt].Max=max(segtree[rt<<1].Max,segtree[rt<<1|1].Max);
segtree[rt].sum=segtree[rt<<1].sum+segtree[rt<<1|1].sum;
}
void build(int rt,int l,int r)
{
segtree[rt].Max=segtree[rt].sum=0;
segtree[rt].l=l,segtree[rt].r=r;
if(l==r)
{
scanf("%d",&segtree[rt].Max);
segtree[rt].sum=segtree[rt].Max;
return ;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(rt<<1,l,mid); build(rt<<1|1,mid+1,r);
push_up(rt);
}
void update(int rt,int p,int x)
{
if(segtree[rt].l==segtree[rt].r)
{
segtree[rt].Max=x; segtree[rt].sum=x;
return ;
}
int mid=(segtree[rt].l+segtree[rt].r)>>1;
if(p<=mid)
update(rt<<1,p,x);
else
update(rt<<1|1,p,x);
push_up(rt);
}
void update2(int rt,int l,int r,int x)
{
if(segtree[rt].Max<x)
return ;
if(segtree[rt].l==segtree[rt].r )
{
segtree[rt].Max%=x;
segtree[rt].sum=segtree[rt].Max;
return ;
}
int mid=(segtree[rt].l+segtree[rt].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid)
update2(rt<<1,l,r,x);
else if(l>mid)
update2(rt<<1|1,l,r,x);
else
{
update2(rt<<1,l,mid,x);
update2(rt<<1|1,mid+1,r,x);
}
push_up(rt);
}
ll query(int rt,int l,int r)
{
if(segtree[rt].l==l && segtree[rt].r==r)
return segtree[rt].sum;
int mid=(segtree[rt].l+segtree[rt].r)>>1;
ll ans=0;
if(r<=mid)
return query(rt<<1,l,r);
if(l>mid)
return query(rt<<1|1,l,r);
return query(rt<<1,l,mid)+query(rt<<1|1,mid+1,r);
}
int main()
{
//freopen("text.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
build(1,1,n);
while(m--)
{
int cmd;
scanf("%d",&cmd);
if(cmd==1)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
printf("%I64d\n",query(1,l,r));
}
if(cmd==2)
{
int l,r,x;
scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&r,&x);
update2(1,l,r,x);
}
if(cmd==3)
{
int p,x;
scanf("%d%d",&p,&x);
update(1,p,x);
}
}
return 0;
}