HttpModule是向实现类提供模块初始化和处置事件。当一个HTTP请求到达HttpModule时,整个ASP.NET Framework系统还并没有对这个HTTP请求做任何处理,也就是说此时对于HTTP请求来讲,HttpModule是一个HTTP请求的“必经之 路”,所以可以在这个HTTP请求传递到真正的请求处理中心(HttpHandler)之前附加一些需要的信息在这个HTTP请求信息之上,或者针对截获 的这个HTTP请求信息作一些额外的工作,或者在某些情况下干脆终止满足一些条件的HTTP请求,从而可以起到一个Filter过滤器的作用。
1、asp.net的HTTP请求处理过程
说明:
(1)、客户端浏览器向服务器发出一个http请求,此请求会被inetinfo.exe进程 截获,然后转交给aspnet_isapi.dll进程,接着它又通过Http Pipeline的管道,传送给aspnet_wp.exe这个进程,接下来就到了.net framework的HttpRunTime处理中心,处理完毕后就发送给用户浏览器。
(2)、当一个 http请求被送入到HttpRuntime之后,这个Http请求会继续被送入到一个被称之为HttpApplication Factory的一个容器当中,而这个容器会给出一个HttpApplication实例来处理传递进来的http请求,而后这个Http请求会依次进入 到如下几个容器中:HttpModule --> HttpHandler Factory --> HttpHandler。当系统内部的HttpHandler的ProcessRequest方法处理完毕之后,整个Http Request就被处理完成了,客户端也就得到相应的东东了。
(3)完整的http请求在asp.net framework中的处理流程:
HttpRequest-->inetinfo.exe->ASPNET_ISAPI.DLL-->Http Pipeline-->ASPNET_WP.EXE-->HttpRuntime-->HttpApplication Factory-->HttpApplication-->HttpModule-->HttpHandler Factory-->HttpHandler-->HttpHandler.ProcessRequest()
也就是说一个HTTP请求在HttpModule容器的传递过程中,会在某一时刻(ResolveRequestCache事件)将这个HTTP请 求传递给HttpHandler容器。在这个事件之后,HttpModule容器会建立一个HttpHandler的入口实例,但是此时并没有将HTTP 请求控制权交出,而是继续触发AcquireRequestState事件以及PreRequestHandlerExcute事件。在 PreRequestHandlerExcute事件之后,HttpModule窗口就会将控制权暂时交给HttpHandler容器,以便进行真正的 HTTP请求处理工作。
而在HttpHandler容器内部会执行ProcessRequest方法来处理HTTP请求。在容器HttpHandler处理完毕整个 HTTP请求之后,会将控制权交还给HttpModule,HttpModule则会继续对处理完毕的HTTP请求信息流进行层层的转交动作,直到返回到 客户端为止。
PS:红色的HttpApplication实例在HttpModule的Init方法中会用到。
(4)如果想在中途截获一个httpRequest并做些自己的处理,就应该在HttpRuntime运行时内部来做到这一点,确切的说是在HttpModule这个容器中来实现。
2、HttpModule工作原理
负责监听HttpRequest,同时对HttpRequest增添或者过滤掉一部分内容。也 就是说,当一个HTTP请求到达HttpModule时,整个ASP.NET Framework系统还并没有对这个HTTP请求做任何处理,也就是说此时对于HTTP请求来讲,HttpModule是一个HTTP请求的“必经之 路”,所以可以在这个HTTP请求传递到真正的请求处理中心(HttpHandler)之前附加一些需要的信息在这个HTTP请求信息之上,或者针对截获 的这个HTTP请求信息作一些额外的工作,或者在某些情况下干脆终止满足一些条件的HTTP请求,从而可以起到一个Filter过滤器的作用。
HttpModule实现了接口IHttpModule,我们可以自定义实现该接口的类,从而取代HttpModule。
asp.net默认的HttpModule如下:
System.Web.Security.WindowsAuthenticationModule;
System.Web.Security.FormsAuthenticationModule;
System.Web.Security.PassportAuthenticationModule;
System.Web.Security.UrlAuthorizationModule;
System.Web.Security.FileAuthorizationModule;
3、编写自己的HttpModule
要实现HttpModule,必须实现接口IHttpModule。下面是IHttpModule接口分析:
namespace System.Web;
{
public interface IHttpModule
{
// 销毁不再被HttpModule使用的资源
void Dispose();
// 初始化一个Module,为捕获HttpRequest做准备
void Init(HttpApplication context);
}
}
 View Code
View Code
{
public class MyHttpModule : IHttpModule
{
public void Dispose() { }
public void Init(HttpApplication context)
{
context.BeginRequest
+= new EventHandler(Application_BeginRequest);context.EndRequest
+= new EventHandler(Application_EndRequest);}
public void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= sender as HttpApplication;HttpContext context
= application.Context;HttpResponse response
= context.Response;response.Write(
"这是来自自定义HttpModule中有BeginRequest");}
public void Application_EndRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= sender as HttpApplication;HttpContext context
= application.Context;HttpResponse response
= context.Response;response.Write(
"这是来自自定义HttpModule中有EndRequest");}
}
}
<add name="myHttpModule" type="ClassLibrary1.MyHttpModule,ClassLibrary1"/>
</httpModules>
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Response.Write("<br/><br/>来自Default.aspx页面<br/>");
}
}
4、HttpModule内部事件机制和生命周期
HttpModule对HttpApplication实例进行处理,而HttpApplication有很多事件(对应不同的生命期),这样就衍生出HttpModule内部事件机制和生命周期。
(1)、HttpModule的事件
| BeginRequest | 指示请求处理开始 |
| AuthenticateRequest | 封装请求身份验证过程 |
| AuthorizeRequest | 封装检查是否能利用以前缓存的输出页面处理请求的过程 |
| ResolveRequestCache | 从缓存中得到相应时候触发 |
| AcquireRequestState | 加载初始化Session时候触发 |
| PreRequestHandlerExecute | 在Http请求进入HttpHandler之前触发 |
| PostRequestHandlerExecute | 在Http请求进入HttpHandler之后触发 |
| ReleaseRequestState | 存储Session状态时候触发 |
| UpdateRequestCache | 更新缓存信息时触发 |
| EndRequest | 在Http请求处理完成的时候触发 |
| PreSendRequestHenaders | 在向客户端发送Header之前触发 |
| PreSendRequestConternt | 在向客户端发送内容之前触发 |
说明:
a、BenginRequest和EndRequest分别是HttpModule容器最开始的和最后的事件;
b、EndRequest之后还会触发PreSendRequestHeaders事件和PreSendRequestContent事件,这不是在HttpModule外的两个事件,表示HttpModule结束,即将开始向Client发送数据。
(2)、验证HttpModule生命周期
与HttpHandler的交互: 
说明:
a、HttpModule容器会将HttpRequest传递到HttpHandler容器,这个时间点是ResolveRequestCache事件
b、HttpModule容器会建立HttpHandler实例作为入口——Session从此生效
c、触发AcquireRequestState事件以及PreRequestHandlerExecute事件
d、HttpModule容器便将对HttpRequest的控制权转让给HttpHandler容器
e、HttpHandler容器处理HttpRequest——使用自身的ProcessRequest方法,将对其控制权又还给HttpModule容器——之后Session失效。
 View Code
View Code
{
public class ValidaterHttpModuleEvents : IHttpModule
{
public void Dispose()
{ }
/// <summary>
/// 验证HttpModule事件机制
/// </summary>
/// <param name="application"></param>
public void Init(HttpApplication application)
{
application.BeginRequest
+= new EventHandler(application_BeginRequest);application.EndRequest
+= new EventHandler(application_EndRequest);application.AcquireRequestState
+= new EventHandler(application_AcquireRequestState);application.AuthenticateRequest
+= new EventHandler(application_AuthenticateRequest);application.AuthorizeRequest
+= new EventHandler(application_AuthorizeRequest);application.PreRequestHandlerExecute
+= new EventHandler(application_PreRequestHandlerExecute);application.PostRequestHandlerExecute
+= new EventHandler(application_PostRequestHandlerExecute);application.ReleaseRequestState
+= new EventHandler(application_ReleaseRequestState);application.ResolveRequestCache
+= new EventHandler(application_ResolveRequestCache);application.PreSendRequestHeaders
+= new EventHandler(application_PreSendRequestHeaders);application.PreSendRequestContent
+= new EventHandler(application_PreSendRequestContent);}
private void application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_BeginRequest<br/>");}
private void application_EndRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_EndRequest<br/>");}
private void application_PreRequestHandlerExecute(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_PreRequestHandlerExecute<br/>");}
private void application_PostRequestHandlerExecute(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_PostRequestHandlerExecute<br/>");}
private void application_ReleaseRequestState(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_ReleaseRequestState<br/>");}
private void application_AcquireRequestState(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_AcquireRequestState<br/>");}
private void application_PreSendRequestContent(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_PreSendRequestContent<br/>");}
private void application_PreSendRequestHeaders(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_PreSendRequestHeaders<br/>");}
private void application_ResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_ResolveRequestCache<br/>");}
private void application_AuthorizeRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_AuthorizeRequest<br/>");}
private void application_AuthenticateRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application
= (HttpApplication)sender;application.Context.Response.Write(
"application_AuthenticateRequest<br/>");}
}
}
<add name="HttpModule2" type="MyHttpModule.HttpModule2,MyHttpModule"/>
HttpModule1和HttpModule2模仿ValidaterHttpModuleEvents编写(除了类名改变外,事件和方法不变),不贴代码了。运行结果如下:
从运行结果可以看到,在web.config文件中引入自定义HttpModule的顺序就决定了多个自定义HttpModule在处理一个HTTP请求的接管顺序。
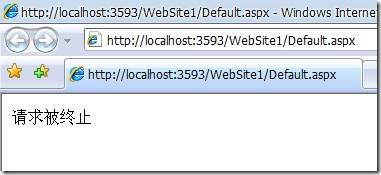
(3)、利用HttpModule实现终止此次HttpRequest请求
在BeginRequest事件中,使用HttpApplication.CompleteRequest()方法可以实现当满足一定条件时终止此次HttpRequest请求
using System.Web; namespace ClassLibrary1
{
public class MyHttpModule : IHttpModule
{
public void Dispose() { }
public void Init(HttpApplication context)
{
context.BeginRequest += new EventHandler(Application_BeginRequest);
}
public void Application_BeginRequest(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
HttpApplication application = sender as HttpApplication;
application.CompleteRequest();
application.Context.Response.Write(
}
}
}
说明:
a、对于一个HttpModule,在BeginRquest中终止,但是仍然会调用EndRequest事件,以及 PreSendRequestHeaders事件和PreSendRequestContent事件。也可以说是直接跳转到EndRequest事件,而 不会调用这期间的事件
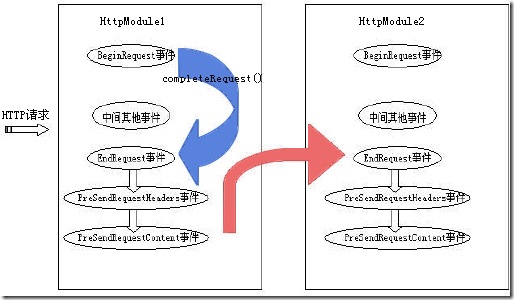
b、如果有两个HttpModule,在第一个HttpModule的BeginRequest中终止,仅仅不会调用第二 个HttpModule的BeginRequest,但仍然会调用两个EndRequest事件,以及PreSendRequestHeaders事件和 PreSendRequestContent事件。看下面的图示:
HttpHandler实现了类似于ISAPI Extention的功能,他处理请求(Request)的信息和发送响应(Response)。HttpHandler功能的实现通过实现 IHttpHandler接口来达到。而HttpModule实现了类似于ISAPI Filter的功能。
HttpModules实现了类似于ISAPI Filter的功能,在开发上,通常需要经过以下步骤:
1.编写一个类,实现IhttpModule接口
2.实现Init 方法,并且注册需要的方法
3.实现注册的方法
4.实现Dispose方法,如果需要手工为类做一些清除工作,可以添加Dispose方法的实现,但这不是必需的,通常可以不为Dispose方法添加任何代码。
5.在Web.config文件中,注册您编写的类
下面是一个HttpModules的示例,在这个示例中,只是简单的注册了HttpApplication 的BeginRequest 和 EndRequest事件,并且通过这些事件的实现方法,将相关的信息打印出来。
例1: |
程序的开始引用了如下名称空间:
using System; |
因为HttpApplication、HttpContext、HttpResponse等类在System.Web中定义,因此,System.Web名称空间是必须引用的。
MyModule类实现了IhttpModule接口。在Init方法中,指明了实现BeginRequest 和EndRequest 事件的方法。在这两个方法中,只是简单的分别打印了一些信息。
下面,在Web.config文件中注册这个类,就可以使用这个HttpModule了,注册的方法如下:
<configuration> |
现在来看一下效果。编写一个Aspx页面test.aspx,内容如下:
<% |
运行以后的界面如图所示:

HttpModule通过对HttpApplication对象的一系列事件的处理来对HTTP处理管道施加影响,这些事件在HttpModule的Init方法中进行注册,包括:
BeginRequest |
其中部分事件同Global.asax中的事件相对应,对应关系如下:
| HttpModule | Global.asax |
| BeginRequest | Application_BeginRequest |
| AuthenticateRequest | Application_AuthenticateRequest |
| EndRequest | Application_EndRequest |
在例1中,处理了BeginRequest和EndRequest事件,其他事件的处理方式基本上类似。
同 HttpHandler对应来看,这些事件,有些在HttpHandler之前发生,有些在HttpHandler处理完后发生。了解事件发生的顺序非常 重要,因为,服务器端的对象在不同的时间段有着不同的表现。例子之一是Session的使用。不是所有的事件中都能对Session进行处理,而只能在有 限的几个事件中进行处理。详细的过程可以参考下面的HTTP Request处理生命周期图。