倒腾了近来两个礼拜,终于在实际开发机上将Qt的Demo跑起来啦!
遇到好多问题但是网上都没有找比较满意的答案!
所以 贴出来和各位分享一下,相互交流! 有问题可以发邮件交流:sunfrank2012#google邮箱
Qt Demo 位置:
http://download.csdn.net/source/3392624
Qt for Android配置(Ubuntu11.04)
一.环境搭建
1. Java
下载安装:
->jdk-6u25-linux-i586.bin
url:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk-6u25-download-346242.html
-> 1、jdk-1_5_0_06-linux-i586.bin下载到/usr/soft,赋予可执行权限:chmod
755 jdk-1_5_0_06-linux-i586.bin
2、执行:./jdk-6u25-linux-i586.bin
空格键翻页,到最后输入yes
3、配置环境变量:在/etc/profile
中加入:
export
PATH=/usr/soft/jdk*.*/bin:$PATH
exportJAVA_HOME=/usr/soft/jdk*.*.*
4、运行:source /etc/profile
使配置文件生效
5、运行:java -version,显示jdk版本,jdk安装成功
->linux操作系统可能默认会安装有openjdk
需要将自己安装的Java设置为默认的:
sudoupdate-alternatives --install /usr/bin/java java /usr/local/jdk1.6.0_26/bin/java1160
2. git GIT
是用于 Linux 开发的版本控制工具
-> unbutu 11.04
安装:
sudo apt-get install git git-core
3. Android SDK
->http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
->解压下载的SDK文件
到 <Android_SDK_Path>
例如:/usr/local/bin/android-sdk-linux_x86-1.5_r2
->修改/etc/profile
文件
->export PATH=${PATH}:<Android_SDK_Path>/tools
例如:export PATH=${PATH}:<SDK_Path>/
android-sdk-linux_x86-1.5_r2/tools
->save
->restart
->输入: sudoandroid
->通过弹出界面配置SDK(此时的SDK并未安装完成,需要通过网络完成全部安装)。
->在Settings
处勾选 force https://......
->在AvailablePackages
处 勾选要安装的包
->Install Selectted
进行安装
->android avd配置信息的生成
->android avd的创建格式为:androidcreate avd -n your-avd-name -t your-targets
->其中:
-n的参数为我们要创建的avd的名字;
-t的参数为Available Android
targets的id,
我们可以使用命令:android list查寻其具体信息。
->$android list
AvailableAndroid targets:
id:1
Name: Android 1.1
Type: Platform
API level: 2
Skins: HVGA-P, HVGA (default), QVGA-P, HVGA-L,QVGA-L
id:2
Name: Android 1.5
Type: Platform
API level: 3
Skins: HVGA-P, HVGA (default), QVGA-P, HVGA-L,QVGA-L
id:3
.....................
->创建avd:$android create avd -n android1.5 -t 2
Android1.5 is a basic Android platform.
Doyou wish to create a custom hardware profile [no]yes
Deviceram size: The amount of physical RAM on the device, in megabytes.
hw.ramSize[96]:128
Touch-screensupport: Whether there is a touch screen or not on the device.
hw.touchScreen[yes]:yes
Track-ballsupport: Whether there is a trackball on the device.
hw.trackBall[yes]:yes
Keyboardsupport: Whether the device has a QWERTY keyboard.
hw.keyboard[yes]:yes
DPadsupport: Whether the device has DPad keys
hw.dPad[yes]:yes
GSMmodem support: Whether there is a GSM modem in the device.
hw.gsmModem[yes]:yes
Camerasupport: Whether the device has a camera.
hw.camera[no]:
Camerasupport: Whether the device has a camera.
hw.camera[no]:yes
Maximumhorizontal camera pixels
hw.camera.maxHorizontalPixels[640]:854
Maximumvertical camera pixels
hw.camera.maxVerticalPixels[480]:480
GPSsupport: Whether there is a GPS in the device.
hw.gps[yes]:yes
Battery support: Whether the device can run on a battery.
hw.battery[yes]:yes
Accelerometer:Whether there is an accelerometer in the device.
hw.accelerometer[yes]:yes
Audiorecording support: Whether the device can record audio
hw.audioInput[yes]:yes
Audioplayback support: Whether the device can play audio
hw.audioOutput[yes]:yes
SDCard support: Whether the device supports insertion/removal of virtual SDCards.
hw.sdCard [yes]:yes
Cachepartition support: Whether we use a /cache partition on the device.
disk.cachePartition[yes]:yes
Cachepartition size
disk.cachePartition.size[66MB]:100MB
CreatedAVD ''android-sdk-15'' based on Android 1.5
->启动模拟器界面: $emulator @android-sdk-15-show-kernel
->配置eclipse,使之支持android sdk(安装ADT插件):
Eclipse,Help->SoftwareUpdates->Available Software(根据提示进行相应操作)
4. Android NDK
->http://developer.android.com/sdk/ndk/index.html
->解压NDK包到指定目录
->配置PATH
->修改/etc/profile
文件
->
NDKROOT=/usr/local/bin/android-ndk-r5c (用户根据自己的实际安装配置)
PATH=$PATH:$NDKROOT
->save
->restart
->测试环境变量:
->cd /usr/local/bin/android-ndk-r5c/samples/hello-jni
->ndk-build
->将看到系统会编译出libhello-jni.so
5.
安装necessitas
http://sourceforge.net/projects/necessitas/files/
(包括Qt的库,Qt Createrfor Android,
同时可以选择安装NDK
和SDK(但是由于网速问题建议不要选择可以自己安装)):
->下载necessitas-0.2-online-sdk-installer-linux
->使用 chmod
添加可执行权限
->安装过程需要网络环境
6. Ministro
需要在android上安装Ministro service
http://sourceforge.net/projects/ministro.necessitas.p/files/
7.
模拟器启动命令
在命令行输入: emulator -help,即可显示emulator支持的所有命令。
Android
Emulator usage:
emulator [options] [-qemu args]
options:
-sysdir<dir> 在目录<dir>中搜索system.img
-system<file> 读取system.img文件<file>
-datadir<dir> 写入用户数据到目录 <dir>
-kernel<file> 使用指定内核kernel-qemu文件
-ramdisk<file> 指定ram 镜像文件ramdisk.img
-image<file> obsolete, use -system <file> instead
-init-data<file> initial data image (default <system>/userdata.img
-initdata<file> same as '-init-data <file>'
-data<file> data image
(default <datadir>/userdata-qemu.i
mg
-partition-size<size> 分区大小MBs
-cache<file> cache.img
-no-cache 禁止缓存
-nocache 禁止缓存
-sdcard<file> sdcard.img
-wipe-data reset the use data image (copy it from initda
ta)
-avd<name> 使用指定AVD设备
-skindir<dir> search skins in <dir> (default <system>/skins
)
-skin<name> select a given skin
-no-skin don't use any emulator skin
-noskin same as -no-skin
-memory<size> 物理内存大小MBs
-netspeed<speed> 最大网速
-netdelay<delay> 网络延迟
-netfast disable network shaping
-trace<name> enable code profiling (F9 to start)
-show-kernel 显示内核消息
-shell 终端启用root shell
-no-jni disable JNI checks in the Dalvik runtime
-nojni same as -no-jni
-logcat<tags> 查看日志
-no-audio disable audio support
-noaudio same as -no-audio
-audio<backend> use specific audio backend
-audio-in<backend> use specific audio input backend
-audio-out<backend> usespecific audio output backend
-raw-keys disable Unicode keyboard reverse-mapping
-radio<device> 无线猫
-port<port> 连接控制台的TCP端口.
-ports <consoleport>,<adbport> TCP ports usedfor the console and adb bridge
-onion<image> use overlay PNG image over screen
-onion-alpha<%age> specify onion-skin translucency
-onion-rotation0|1|2|3 specify onion-skin rotation
-scale <scale> 窗口缩放
-dpi-device<dpi> specify device's resolution in dpi (default 1
65)
-http-proxy<proxy> HTTP/HTTPS 代理
-timezone<timezone> 时区
-dns-server<servers> DNS服务器
-cpu-delay<cpudelay> throttleCPU emulation
-no-boot-anim disable animation for faster boot
-no-window disable graphical window display
-version 版本
-report-console<socket> report console port toremote socket
-gps<device> redirect NMEA GPS to character device
-keyset<name> specify keyset file name
-shell-serial<device> specificcharacter device for root shell
-old-system support old (pre 1.4) system images
-tcpdump<file> 记录网络数据包
-bootchart<timeout> enable bootcharting
-prop<name>=<value> 设置系统属性
-qemuargs... pass arguments to qemu
-qemu-h 显示qemu帮助
-verbose same as '-debug-init'
-debug<tags> enable/disable debug messages
-debug-<tag> enable specific debug messages
-debug-no-<tag> disable specific debug messages
-help 帮助
-help-<option> print option-specific help
-help-disk-images about disk images
-help-keys supported key bindings
-help-debug-tags debug tags for -debug <tags>
-help-char-devices character <device> specification
-help-environment environment variables
-help-keyset-file key bindings configuration file
-help-virtual-device virtual device management
-help-sdk-images about disk images when using the SDK
-help-build-images about disk images when building
Android
-help-all 帮助(所有)
在3的基础上:
emulator –avd Android2.3.3–partition-size 512
(即可启动模拟器)
7.
常用ADB命令:
命令行工具ADB(Andvoid Debug Bridge)是Android提供的一个通用的调试工具,借助这个工具,我们可以管理设备或手机模拟器的状态。还可以进行以下的操作:
1、快速更新设备或手机模拟器中的代码,如应用或Android系统升级;
2、在设备上运行shell命令;
3、管理设备或手机模拟器上的预定端口;
4、在设备或手机模拟器上复制或粘贴文件;
5、安装.apk文件到仿真器上。
以下为一些常用的操作:
1、安装应用到模拟器:
adb install
比较郁闷的是,Android并没有提供一个卸载应用的命令,只能自己手动删除:
adb shell
cd /data/app
rm app.apk
2、进入设备或模拟器的shell:
adb shell
通过上面的命令,就可以进入设备或模拟器的shell环境中,在这个Linux Shell中,你可以执行各种Linux的命令,另外如果只想执行一条shell命令,可以采用以下的方式:
adb shell [command]
如:adb shell dmesg会打印出内核的调试信息。
3、发布端口:
你可以设置任意的端口号,做为主机向模拟器或设备的请求端口。如:
adb forward tcp:5555 tcp:8000
4、复制文件:
你可向一个设备或从一个设备中复制文件,
复制一个文件或目录到设备或模拟器上:
adb push
如:adb push test.txt /tmp/test.txt
从设备或模拟器上复制一个文件或目录:
adb pull
如:adb pull/addroid/lib/libwebcore.so .
5、搜索模拟器/设备的实例:
取得当前运行的模拟器/设备的实例的列表及每个实例的状态:
adb devices
6、查看bug报告:
adb bugreport
7、记录无线通讯日志:
一般来说,无线通讯的日志非常多,在运行时没必要去记录,但我们还是可以通过命令,设置记录:
adb shell
logcat -b radio
8、获取设备的ID和序列号:
adb get-product
adb get-serialno
9、访问数据库SQLite3
adb shell
sqlite3
模拟器上网设置:
1. 在 adb shell
模式下执行以下命令
sqlite3/data/data/com.android.providers.settings/databases/settings.db "INSERTINTO system VALUES(99,'http_proxy','10.10.26.252:1080')"
2. 重新启动Android模拟器,程序可以登录http网站。
3. 如果要删除配置: sqlite3
/data/data/com.android.providers.settings/databases/settings.db"DELETE FROM system WHERE _id=99"
4.在 adb shell
模式下执行查询命令
sqlite3/data/data/com.android.providers.settings/databases/settings.db "SELECT *FROM system"
5.如果还无法连接Internet,则需要设置DNS
$ adbshell
$ getprop
$ getprop会列出系统当前的各项属性
得到模拟器的DNS地址
在结果里可以看到:
[net.dns1]: [10.0.2.3]
[net.dns2]: [10.0.2.4]
[net.dns3]: [10.0.2.5]
[net.dns4]: [10.0.2.6]
把dns改成我们自己的DNS
$ setprop net.dns1 192.168.1.1
注:一般TP-LINK及D-LINK的DNS都是192.168.1.1,如果不是请使用ipcnofig /all命令确认。
注意:
在配置环境变量时,请确保配置路径完全正确,否则不要操作 /etc/profile文件,因为这个文件不正确可能导致系统无法启动,
所以可以在当前用户目录下找到.bashrc,
配置环境变量,这样配置的值适合当前用户使用不是全局的。)
二.
创建工程
1.打开necessitas
(当前虚拟机上安装在:/home/frank/necessitas/
QtCreator/bin/),你可以在桌面创建快捷方式,或者将其配置到环境变量中。
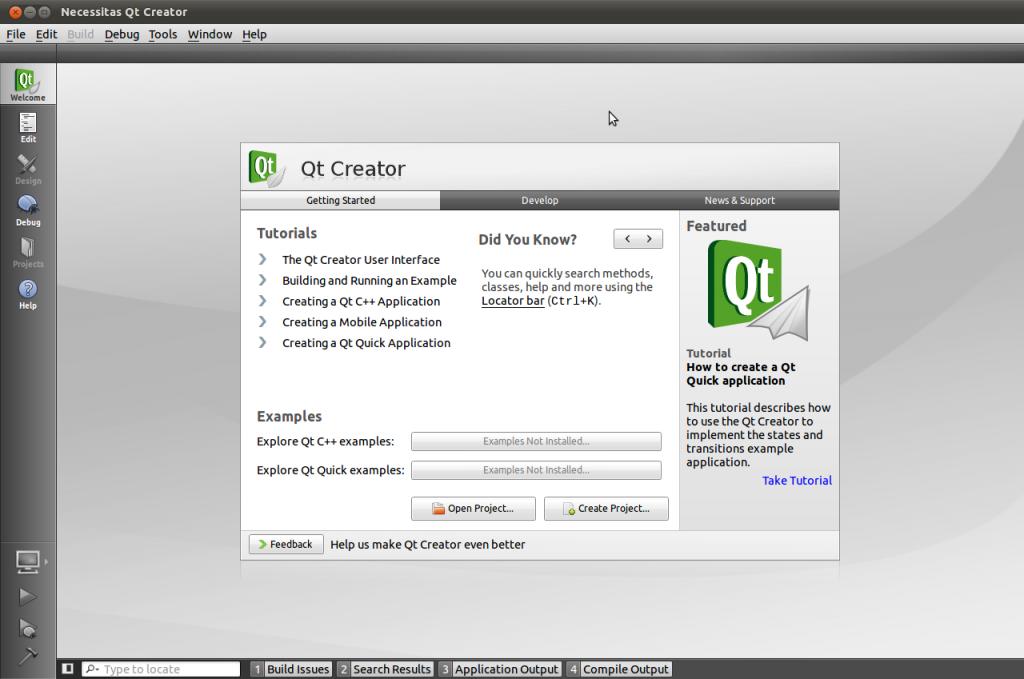
主界面如下:
可以通过File打开一个*.pro工程文件或者自己创建一个
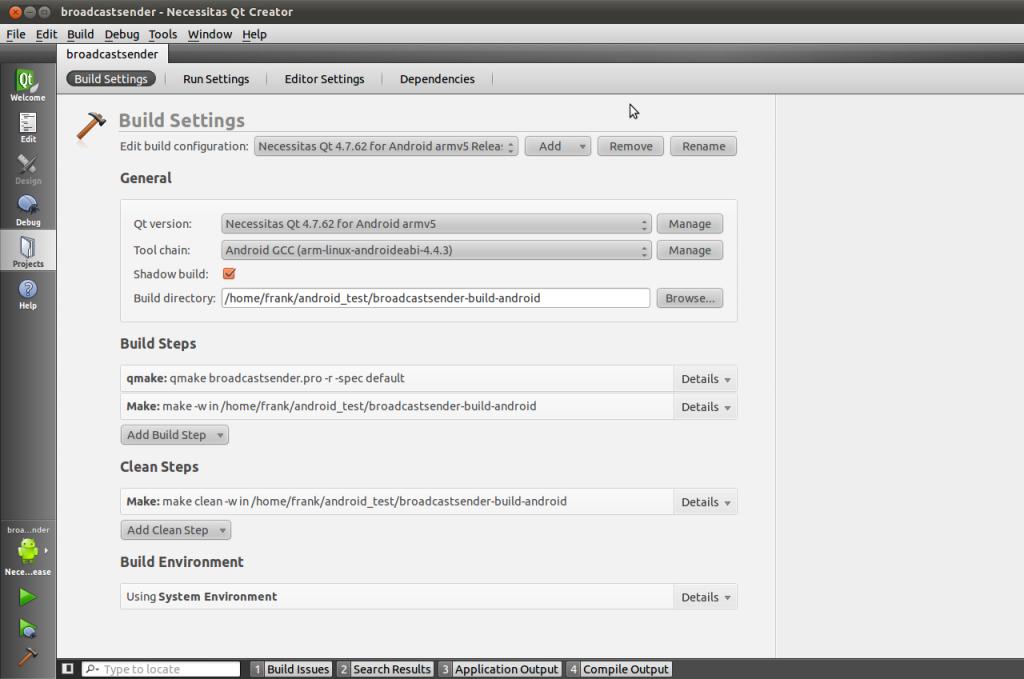
在Project选项中可以进行相应的设置
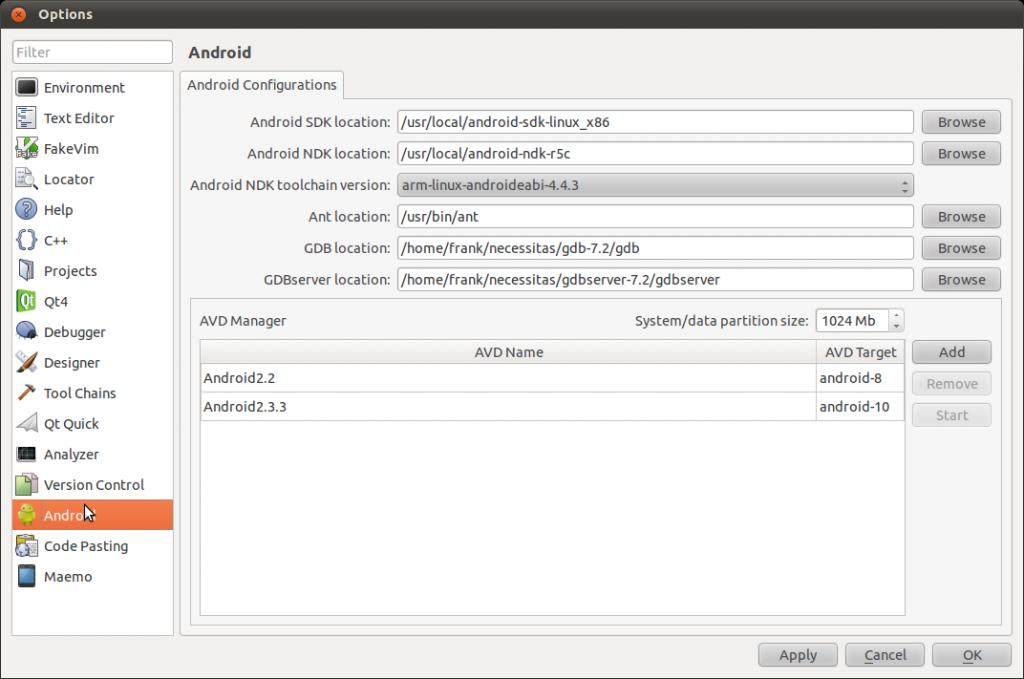
在Qt Version选项处点击Manage弹出一下对话框,根据现有的SDK、NDK和Ant的安装进行设置:
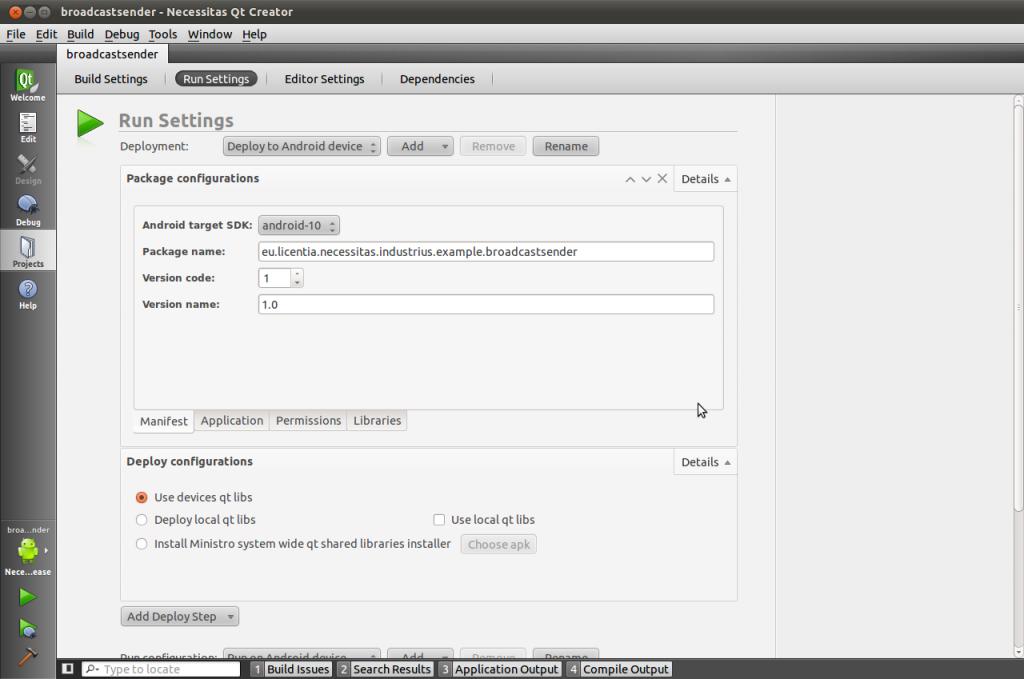
注意Run Settings
中设置Package为10或者更高否则无法使用Qt编译通过:
此时点击Build
可以编译程序,如果模拟器没有打开necessitas会自动打开模拟器。
其它的设置可以根据自己的实际需求进行相应的设置。
Qt Demo(animatedtiles)运行效果图:

附:
1. tar用法实例 tar命令
tar文件是几个文件和(或)目录在一个文件中的集合。这是创建备份和归档的佳径。
tar使用的选项有:
-c—
创建一个新归档。
-f—
当与 -c 选项一起使用时,创建的tar
文件使用该选项指定的文件名;当与 -x
选项
一起使用时,则解除该选项指定的归档。
-t—
显示包括在 tar 文件中的文件列表。
-v—
显示文件的归档进度。
-x—
从归档中抽取文件。
-z—
使用 gzip 来压缩 tar
文件。
-j—
使用 bzip2 来压缩 tar
文件。
要创建一个 tar
文件,键入:
tar-cvf filename.tar directory/file
可以使用 tar
命令同时处理多个文件和目录,方法是将它们逐一列出,并用空格间隔:
tar-cvf filename.tar /home/mine/work /home/mine/school
上面的命令把 /home/mine
目录下的 work 和 school
子目录内的所有文件都放入当前
目录中一个叫做 filename.tar
的新文件里。
要列出 tar
文件的内容,键入:
tar-tvf filename.tar
要抽取 tar
文件的内容,键入
tar-xvf filename.tar
这个命令不会删除 tar
文件,但是它会把被解除归档的内容
复制到当前的工作目录下,并保留归档文件所使用的任何
目录结构。譬如,如果这个 tar
文件中包含一个叫做
bar.txt的文件,而这个文件包含在foo/
目录中,那么,
抽取归档文件将会导致在你当前的工作目录中创建
foo/目录,该目录中包含bar.txt
文件
tar默认不压缩文件。
要创建一个使用 tar
和 bzip 来归档压缩的文件,使用 -j
选项:
tar-cjvf filename.tbz file
以上命令创建了一个归档文件,然后将其压缩为 filename.tbz