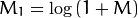#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char ** argv)
{
const char* filename = argc >=2 ? argv[1] : "lena.jpg";
Mat I = imread(filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if( I.empty())
return -1;
Mat padded; //expand input image to optimal size
int m = getOptimalDFTSize( I.rows );
int n = getOptimalDFTSize( I.cols ); // on the border add zero values
copyMakeBorder(I, padded, 0, m - I.rows, 0, n - I.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0));
Mat planes[] = {Mat_<float>(padded), Mat::zeros(padded.size(), CV_32F)};
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI); // Add to the expanded another plane with zeros
dft(complexI, complexI); // this way the result may fit in the source matrix
// compute the magnitude and switch to logarithmic scale
// => log(1 + sqrt(Re(DFT(I))^2 + Im(DFT(I))^2))
split(complexI, planes); // planes[0] = Re(DFT(I), planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]);// planes[0] = magnitude
Mat magI = planes[0];
magI += Scalar::all(1); // switch to logarithmic scale
log(magI, magI);
// crop the spectrum, if it has an odd number of rows or columns
magI = magI(Rect(0, 0, magI.cols & -2, magI.rows & -2));
// rearrange the quadrants of Fourier image so that the origin is at the image center
int cx = magI.cols/2;
int cy = magI.rows/2;
Mat q0(magI, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Left - Create a ROI per quadrant
Mat q1(magI, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Right
Mat q2(magI, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Left
Mat q3(magI, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Right
Mat tmp; // swap quadrants (Top-Left with Bottom-Right)
q0.copyTo(tmp);
q3.copyTo(q0);
tmp.copyTo(q3);
q1.copyTo(tmp); // swap quadrant (Top-Right with Bottom-Left)
q2.copyTo(q1);
tmp.copyTo(q2);
normalize(magI, magI, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX); // Transform the matrix with float values into a
// viewable image form (float between values 0 and 1).
imshow("Input Image" , I ); // Show the result
imshow("spectrum magnitude", magI);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
任一函数都可以表示成无数个正弦和余弦函数的和的形式。傅立叶变换就是一个用来将函数分解的工具。 2维图像的傅立叶变换可以用以下数学公式表达:
式中 f 是空间域(spatial domain)值, F 则是频域(frequency domain)值。 转换之后的频域值是复数, 因此,显示傅立叶变换之后的结果需要使用实数图像(real image) 加虚数图像(complex image), 或者幅度图像(magitude
image)加相位图像(phase image)。在实际的图像处理过程中,仅仅使用了幅度图像,因为幅度图像包含了原图像的几乎所有我们需要的几何信息。
操作过程:
-
将图像延扩到最佳尺寸. 离散傅立叶变换的运行速度与图片的尺寸息息相关。当图像的尺寸是2, 3,5的整数倍时,计算速度最快。 因此,为了达到快速计算的目的,经常通过添凑新的边缘像素的方法获取最佳图像尺寸。函数 getOptimalDFTSize() 返回最佳尺寸,而函数 copyMakeBorder() 填充边缘像素:
Mat padded; //将输入图像延扩到最佳的尺寸
int m = getOptimalDFTSize( I.rows );
int n = getOptimalDFTSize( I.cols ); // 在边缘添加0
copyMakeBorder(I, padded, 0, m - I.rows, 0, n - I.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0));
添加的像素初始化为0.
C++: void copyMakeBorder(InputArray src,
OutputArray dst, int top, int bottom,
int left, int right, int borderType,
const Scalar& value=Scalar() )
|
Parameters: |
- src – Source image.
- dst – Destination image of the same type as src and
the size Size(src.cols+left+right,src.rows+top+bottom) .
- top –
- bottom –
- left –
- right – Parameter specifying how many pixels in each direction from the source image rectangle to extrapolate. For example, top=1, bottom=1, left=1, right=1 mean
that 1 pixel-wide border needs to be built.
- borderType – Border type. See borderInterpolate() for
details.
- value – Border value if borderType==BORDER_CONSTANT .
|
-
为傅立叶变换的结果(实部和虚部)分配存储空间. 傅立叶变换的结果是复数,这就是说对于每个原图像值,结果是两个图像值。 此外,频域值范围远远超过空间值范围, 因此至少要将频域储存在 float 格式中。 结果我们将输入图像转换成浮点类型,并多加一个额外通道来储存复数部分:
Mat planes[] = {Mat_<float>(padded), Mat::zeros(padded.size(), CV_32F)};
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI); // 为延扩后的图像增添一个初始化为0的通道
- C++: void merge(const Mat* mv, size_t count, OutputArray dst)
- C++: void merge(InputArrayOfArrays mv, OutputArray dst
Parameters:
|
- mv –
input array or vector of matrices to be merged; all the matrices in mv must
have the same size and the same depth.
- count – number of input matrices when mv is a plain
C array; it must be greater than zero.
- dst – output array of the same size and the same depth as mv[0];
The number of channels will be the total number of channels in the matrix array.
|
-
进行离散傅立叶变换. 支持图像原地计算 (输入输出为同一图像):
dft(complexI, complexI); // 变换结果很好的保存在原始矩阵中
-
将复数转换为幅度.复数包含实数部分(Re)和复数部分 (imaginary - Im)。 离散傅立叶变换的结果是复数,对应的幅度可以表示为:
转化为OpenCV代码:
split(complexI, planes); // planes[0] = Re(DFT(I), planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]);// planes[0] = magnitude
Mat magI = planes[0];
C++: void magnitude(InputArray x, InputArray y, OutputArray magnitude)
| Parameters: |
- x –
floating-point array of x-coordinates of the vectors.
- y – floating-point array of y-coordinates of the vectors; it must have the same size as x.
- magnitude – output array of the same size and type as x.

|
-
对数尺度(logarithmic scale)缩放. 傅立叶变换的幅度值范围大到不适合在屏幕上显示。高值在屏幕上显示为白点,而低值为黑点,高低值的变化无法有效分辨。为了在屏幕上凸显出高低变化的连续性,我们可以用对数尺度来替换线性尺度:
转化为OpenCV代码:
magI += Scalar::all(1); // 转换到对数尺度
log(magI, magI);
-
剪切和重分布幅度图象限. 还记得我们在第一步时延扩了图像吗? 那现在是时候将新添加的像素剔除了。为了方便显示,我们也可以重新分布幅度图象限位置(注:将第五步得到的幅度图从中间划开得到四张1/4子图像,将每张子图像看成幅度图的一个象限,重新分布即将四个角点重叠到图片中心)。 这样的话原点(0,0)就位移到图像中心。
magI = magI(Rect(0, 0, magI.cols & -2, magI.rows & -2));
int cx = magI.cols/2;
int cy = magI.rows/2;
Mat q0(magI, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Left - 为每一个象限创建ROI
Mat q1(magI, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Right
Mat q2(magI, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Left
Mat q3(magI, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Right
Mat tmp; // 交换象限 (Top-Left with Bottom-Right)
q0.copyTo(tmp);
q3.copyTo(q0);
tmp.copyTo(q3);
q1.copyTo(tmp); // 交换象限 (Top-Right with Bottom-Left)
q2.copyTo(q1);
tmp.copyTo(q2);
-
归一化. 这一步的目的仍然是为了显示。 现在我们有了重分布后的幅度图,但是幅度值仍然超过可显示范围[0,1] 。我们使用 normalize() 函数将幅度归一化到可显示范围。
normalize(magI, magI, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX); // 将float类型的矩阵转换到可显示图像范围
// (float [0, 1]).
C++: void normalize(InputArray src,
OutputArray dst, double alpha=1, double beta=0,
int norm_type=NORM_L2, int dtype=-1, InputArray mask=noArray() )
|
Parameters: |
- src – input array.
- dst – output array of the same size as src .
- alpha – norm value to normalize to or the lower range boundary in case of the range normalization.
- beta – upper range boundary in case of the range normalization; it is not used for the norm normalization.
- normType – normalization type (see the details below).
- dtype – when negative, the output array has the same type as src;
otherwise, it has the same number of channels as src and the depth =CV_MAT_DEPTH(dtype).
- mask – optional operation mask.
|
The functions normalize scale and shift the input array elements so that
(where p=Inf, 1 or 2) when normType=NORM_INF, NORM_L1,
or NORM_L2, respectively; or so that
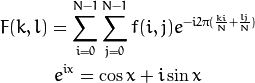
![M = \sqrt[2]{ {Re(DFT(I))}^2 + {Im(DFT(I))}^2}](http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/_images/math/6c1cb9937a9552acbd5675c7fefc0f17da665709.png)