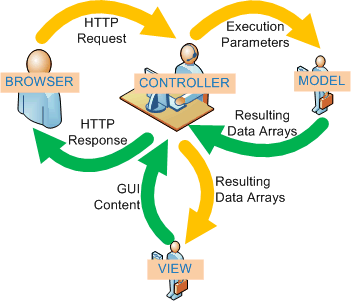
MVC模式如今大量应用与web开发中,其优势明显,收到了众多开发者的欢迎和支持,struts框架的核心架构也用到了MVC,既然MVC如此犀利,我们就应该深入理解其中的流程,而作为一个IT精英,我们肯定会想到看相关的源码,看完理解之后,我个人认为最高的境界就是自己写一个类似的框架出来,下面我就把自己理解编写的MVC框架分享给大家!
struts1.X中有两个 核心的配置:
action和form-bean
对应每个客户端页面,发送请求时都会把该页面的参数封装到一个form-bean中,这也就是form-bean的基本作用。
action元素是用来配置业务Action类,在struts中充当控制器,原则上每个请求的路径都会被拦截到对应的action,并调用action中的某个方法。
于是我仿制的struts.config 配置文件的格式就出来了,如下:
<mvc-config> <!-- form-beans标签只有一个 --> <form-beans> <!-- form-bean标签有多个 --> <form-bean name="newsForm" type="net.localer.news.form.NewsForm"/> <form-bean name="userForm" type="net.localer.news.form.UserForm"/> </form-beans> <!-- action-mappings标签只有一个 --> <action-mappings> <!-- action元素:配置业务Action类 path : 请求的路径 type : 业务Action类的类路径 --> <!-- action标签有多个 --> <action path="/index" type="net.localer.news.action.NewsAction" name="newsForm"/> <action path="/user" type="net.localer.news.action.UserAction" name="userForm"/> </action-mappings> </mvc-config>
看到这里很多人应该会知道其中的type属性将来会通过反射形成一个具体的object对象。当然配置文件出来了肯定就要与之相对应的bean类,否则是无法识别的,当然既然与配置文件对应,那bean类也相当的简单!如下:
public class ActionConfig {
private String path;
private String type;
private String name;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class FormBeanConfig {
private String name;
private String type;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
配置文件里还可以看出 action 和 form 要通过name 关联起来。为什么要关联呢?之前说页面的请求封装到form里面 并且 请求会传到action 所以form也会要传给action 所以当请求发出的时候:首先根据请求路径找到对应的action 然后根据action里面name 找到对应的form,将form反射出来后 再传进 对应的action里面!
同时我们还需要一个类,这个类比较特殊
/**
*缓存所有已经读取到的ActionConfig对象
*和FormBeanConfig对象
*
*/
public class ActionMappingConfig {
//actionInfo的key键是path
private Map<String,ActionConfig> actionInfo = null;
//formbeanInfo中的key是name
private Map<String,FormBeanConfig> formbeanInfo = null;
public ActionMappingConfig(){
actionInfo = new Hashtable<String, ActionConfig>();
formbeanInfo = new Hashtable<String, FormBeanConfig>();
}
public void setActionConfig(ActionConfig config) {
actionInfo.put(config.getPath(), config);
}
public ActionConfig getActionConfig(String path) {
return actionInfo.get(path);
}
public void setFormBeanConfig(FormBeanConfig config) {
formbeanInfo.put(config.getName(), config);
}
public FormBeanConfig getFormBeanConfig(String name) {
return formbeanInfo.get(name);
}
}
运行的时候我们需要找一个类把所有的actionbean 和 formbean 缓存起来 ActionMappingConfig 类就是干这个的。
那么缓存是要缓存 可是怎么缓存起来呢 这就要用到另外一个类:XMLParser
代码如下:
public class XMLParser {
/**
*
* @param path XML文档的路径
* @return 是一已经封装好XML信息的ActionMappingConfig对象
*/
public static ActionMappingConfig getActionMappingConfig(String path) {
//1、构造SAX解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2、创建一个空的ActionMappingConfig对象
ActionMappingConfig config = new ActionMappingConfig();
try {
//3、获得整个对象
Document doc = reader.read(path);
//4、获得根元素
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
//5、解析并封装FormBeanConfig的方法
formBeanParser(root,config);
//6、解析并封装ActionConfig的方法
actionParser(root,config);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return config;
}
/**
*
* @param root文档的根元素
* @param config 空的ActionMappingConfig对象
*/
private static void formBeanParser(Element root, ActionMappingConfig config) {
Element beans = root.element("form-beans");
List<Element> list = beans.elements();
for (Element e : list) {
String name = e.attribute("name").getValue();
String type = e.attribute("type").getValue();
//构建FormBeanConfig对象
FormBeanConfig formBean = new FormBeanConfig();
formBean.setName(name);
formBean.setType(type);
config.setFormBeanConfig(formBean);
}
}
private static void actionParser(Element root, ActionMappingConfig config) {
Element beans = root.element("action-mappings");
List<Element> list = beans.elements();
for (Element e : list) {
String name = null;
if (null != e.attribute("name")) {
name = e.attribute("name").getValue();
}
String type = e.attribute("type").getValue();
String path = e.attribute("path").getValue();
ActionConfig action = new ActionConfig();
action.setName(name);
action.setPath(path);
action.setType(type);
config.setActionConfig(action);
}
}
}
一看好像一个非常复杂的类 但是 一学就会 就是一个普通的解析xml的java代码,网上一搜一堆,不懂可以百度,在这不多浪费时间!
到这里我们已经完成了第一大步,把所有的基础config数据备好,
下面要进行的就是核心精髓的部分:action类,actionForm类,actionForward类等地编写!