Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1506
Problem Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights
2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
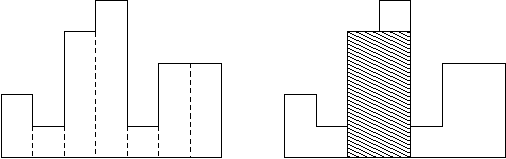
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned
at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned
at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000.
These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
题解:枚举每个点i,找连续h[j]>=h[i]的j的最大,最小值。查找j的过程可以用DP提高效率。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
LL num[100005];
LL l[100005],r[100005];
int main()
{
int n;
LL ans;
for(;scanf("%d",&n),n;)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) scanf("%I64d",&num[i]);
num[0]=num[n+1]=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) l[i]=r[i]=i;
//dp,根据之前拓展的l,r再拓展,可以提高效率
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
//第i个高度拓展,h[j]>=h[i]的最小j
for(;num[l[i]-1]>=num[i];)
l[i]=l[l[i]-1];
for(int i=n;i>=1;--i)
//第i个高度拓展,h[j]>=h[i]的最大j
for(;num[r[i]+1]>=num[i];)
r[i]=r[r[i]+1];
ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
if(ans<num[i]*(r[i]-l[i]+1))
ans=num[i]*(r[i]-l[i]+1);
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}