1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You have decided to watch the best moments of some movie. There are two buttons on your player:
- Watch the current minute of the movie. By pressing this button, you watch the current minute of the movie and the player automatically proceeds to the next minute of the movie.
- Skip exactly x minutes of the movie (x is some fixed positive integer). If the player is now at the
t-th minute of the movie, then as a result of pressing this button, it proceeds to the minute
(t + x).
Initially the movie is turned on in the player on the first minute, and you want to watch exactly
n best moments of the movie, the
i-th best moment starts at the li-th minute and ends at the
ri-th minute (more formally, the
i-th best moment consists of minutes:
li, li + 1, ..., ri).
Determine, what is the minimum number of minutes of the movie you have to watch if you want to watch all the best moments?
The first line contains two space-separated integers n,
x (1 ≤ n ≤ 50,
1 ≤ x ≤ 105) — the number of the best moments of the movie and the value of
x for the second button.
The following n lines contain the descriptions of the best moments of the movie, the
i-th line of the description contains two integers separated by a space
li,
ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 105).
It is guaranteed that for all integers i from
2 to n the following condition holds:
ri - 1 < li.
Output a single number — the answer to the problem.
2 3 5 6 10 12
6
1 1 1 100000
100000
In the first sample, the player was initially standing on the first minute. As the minutes from the
1-st to the 4-th one don't contain interesting moments, we press the second button. Now we can not press the second button and skip
3 more minutes, because some of them contain interesting moments. Therefore, we watch the movie from the
4-th to the 6-th minute, after that the current time is
7. Similarly, we again skip
3 minutes and then watch from the 10-th to the
12-th minute of the movie. In total, we watch
6 minutes of the movie.
In the second sample, the movie is very interesting, so you'll have to watch all
100000 minutes of the movie.
水题,从前往后处理就行,能跳则跳
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf_a.cpp
> Author: ALex
> Mail: 405045132@qq.com
> Created Time: 2014年12月25日 星期四 12时09分34秒
************************************************************************/
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 55;
struct node
{
int l, r;
}tx[N];
int main()
{
int n, x;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &x))
{
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d", &tx[i].l, &tx[i].r);
ans += (tx[i].r - tx[i].l + 1);
}
int cur_at = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int dis = (tx[i].l - cur_at);
dis %= x;
ans += dis;
cur_at = tx[i].r + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You have a new professor of graph theory and he speaks very quickly. You come up with the following plan to keep up with his lecture and make notes.
You know two languages, and the professor is giving the lecture in the first one. The words in both languages consist of lowercase English characters, each language consists of several words. For each language, all words are distinct, i.e. they are spelled
differently. Moreover, the words of these languages have a one-to-one correspondence, that is, for each word in each language, there exists exactly one word in the other language having has the same meaning.
You can write down every word the professor says in either the first language or the second language. Of course, during the lecture you write down each word in the language in which the word is shorter. In case of equal lengths of the corresponding words
you prefer the word of the first language.
You are given the text of the lecture the professor is going to read. Find out how the lecture will be recorded in your notes.
The first line contains two integers, n and
m (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000,
1 ≤ m ≤ 3000) — the number of words in the professor's lecture and the number of words in each of these languages.
The following m lines contain the words. The
i-th line contains two strings
ai,
bi meaning that the word
ai belongs to the first language, the word
bi belongs to the second language, and these two words have the same meaning. It is guaranteed that no word occurs in both languages, and each word occurs in its language exactly
once.
The next line contains n space-separated strings
c1, c2, ..., cn — the text of the lecture. It is guaranteed that each of the strings
ci belongs to the set of strings
{a1, a2, ...
am}.
All the strings in the input are non-empty, each consisting of no more than
10 lowercase English letters.
Output exactly n words: how you will record the lecture in your notebook. Output the words of the lecture in the same order as in the input.
4 3 codeforces codesecrof contest round letter message codeforces contest letter contest
codeforces round letter round
5 3 joll wuqrd euzf un hbnyiyc rsoqqveh hbnyiyc joll joll euzf joll
hbnyiyc joll joll un joll
水题,用一个map就行了
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf_b.cpp
> Author: ALex
> Mail: 405045132@qq.com
> Created Time: 2014年12月25日 星期四 12时30分03秒
************************************************************************/
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3010;
char str[N][15];
char a[15], b[15];
map <string, string> qu;
int main()
{
int n, m;
while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m))
{
qu.clear();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
scanf("%s%s", a, b);
qu[a] = b;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%s", str[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int len1 = strlen(str[i]);
int len2 = strlen(qu[str[i]].c_str());
if (len1 <= len2)
{
printf("%s", str[i]);
}
else
{
printf("%s", qu[str[i]].c_str());
}
if (i < n)
{
printf(" ");
}
else
{
printf("\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Crazy Town is a plane on which there are n infinite line roads. Each road is defined by the equation
aix + biy + ci = 0, where
ai and
bi are not both equal to the zero. The roads divide the plane into connected regions, possibly of infinite space. Let's call each such region a block. We define an intersection as
the point where at least two different roads intersect.
Your home is located in one of the blocks. Today you need to get to the University, also located in some block. In one step you can move from one block to another, if the length of their common border is nonzero (in particular, this means that if the blocks
are adjacent to one intersection, but have no shared nonzero boundary segment, then it are not allowed to move from one to another one in one step).
Determine what is the minimum number of steps you have to perform to get to the block containing the university. It is guaranteed that neither your home nor the university is located on the road.
The first line contains two space-separated integers x1,
y1 ( - 106 ≤ x1, y1 ≤ 106)
— the coordinates of your home.
The second line contains two integers separated by a space
x2, y2 ( - 106 ≤ x2, y2 ≤ 106)
— the coordinates of the university you are studying at.
The third line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 300) — the number of roads in the city. The following
n lines contain 3 space-separated integers ( - 106 ≤ ai, bi, ci ≤ 106;
|ai| + |bi| > 0) — the coefficients of the line
aix + biy + ci = 0, defining the
i-th road. It is guaranteed that no two roads are the same. In addition, neither your home nor the university lie on the road (i.e. they do not belong to any one of the lines).
Output the answer to the problem.
1 1 -1 -1 2 0 1 0 1 0 0
2
1 1 -1 -1 3 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 -3
2
Pictures to the samples are presented below (A is the point representing the house; B is the point representing the university, different blocks are filled with different colors):
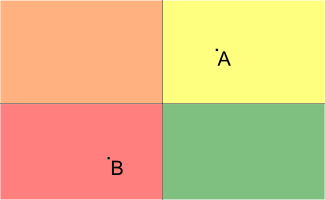
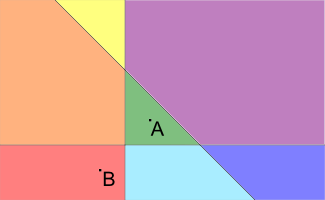
这题挺有意思的,一开始我想复杂了,认为要把每一个块当成点,然后建边,最后单源最短路,其实不是, 我们发现,如果A,B在一条直线的一侧,那么就不需要越过去,反之,一定要越过这条直线,所有step++,因此每次只要判断AB是否在直线的一侧就行了
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: cf_c.cpp
> Author: ALex
> Mail: 405045132@qq.com
> Created Time: 2014年12月25日 星期四 13时38分43秒
************************************************************************/
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2, n;
while (~scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2))
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d", &n);
__int64 ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
__int64 u = (__int64)a * x1 + (__int64)b * y1 + c;
__int64 v = (__int64)a * x2 + (__int64)b * y2 + c;
if (u > 0 && v < 0)
{
ans++;
}
else if(v > 0 && u < 0)
{
ans++;
}
}
printf("%I64d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}